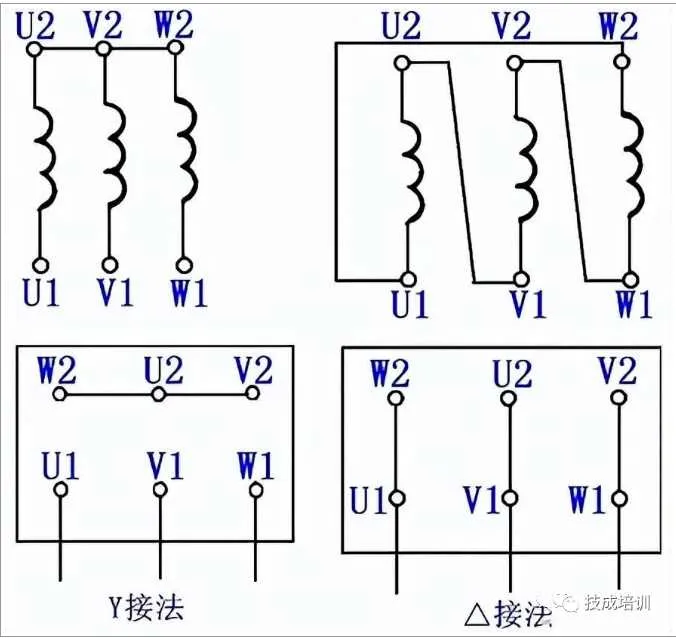
Ensure each terminal is connected precisely to match the system requirements for proper functionality. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions to avoid damage to components. For optimal efficiency, the wiring should follow specific standards based on voltage ratings and load distribution.
When dealing with a setup involving multiple power sources, each component’s input should be balanced correctly. Proper isolation of connections is essential to prevent short circuits and ensure safety. Use color-coded wires to simplify identification and avoid any confusion during installation.
Pay attention to polarity when linking the components. Reversed connections can result in erratic operation or even failure of the equipment. Also, be cautious with grounding; improper grounding can lead to dangerous electrical shocks or malfunctions.
For any adjustments to the electrical connections, always double-check voltage levels with a meter before making any permanent changes. Maintaining appropriate voltage levels is critical for both the longevity of your setup and the efficiency of the system.
Connecting Induction Machines for Optimal Performance
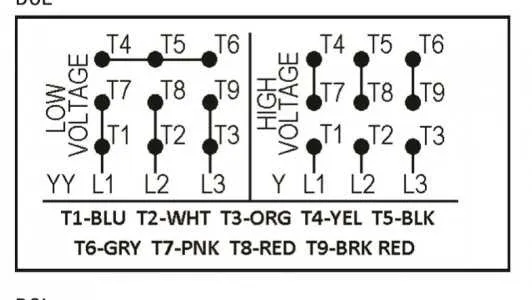
To ensure a reliable connection, begin by properly identifying the leads from the electrical supply. These will typically include three conductors representing each segment of the current. Make sure that each of these wires is securely connected to the terminals of the device, as incorrect connections can result in inefficiency or even failure.
Important Consideration: When setting up the electrical terminals on the device, always double-check that the conductor attached to the neutral is distinct from those connected to the active supply. A faulty connection here may lead to a potential imbalance in the operation.
For machines with a star connection, ensure that all the winding ends are joined together at a single point. This forms a neutral connection, which should then be connected to the neutral of the power source. For delta arrangements, the ends of each winding should be connected in a triangular form, ensuring that each winding segment is connected to the corresponding active line.
After establishing these connections, verify the direction of rotation. If the direction is incorrect, swap any two active conductors to reverse the movement. This is a quick way to ensure that the machine operates in the correct direction.
Tip: Always perform a continuity test before powering up the system. This step will confirm that no short circuits or incorrect connections exist.
Correct Motor Connections for Delta and Star Configurations
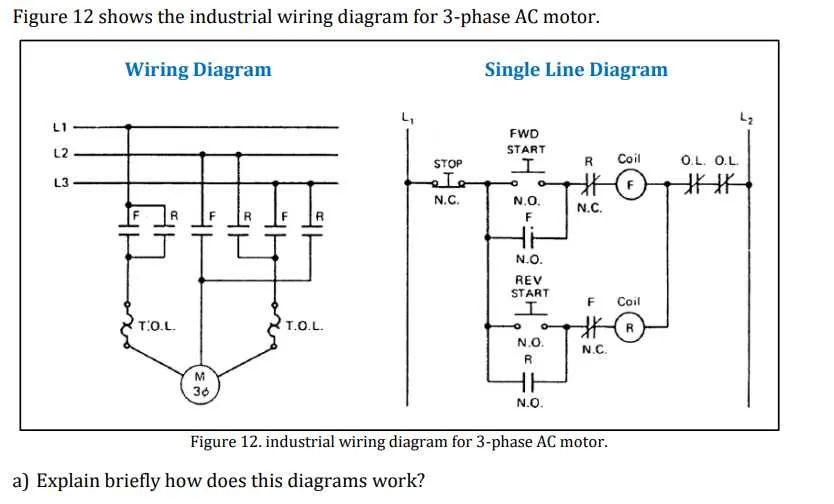
For proper operation, ensure correct terminal connections based on the chosen configuration.
- Delta (Δ) Configuration: Each winding is connected end-to-end, forming a closed loop. This is typically used for high torque applications.
- Star (Y) Configuration: One end of each winding connects to a common point, while the other ends are connected to the supply. This setup is suitable for starting the motor at reduced voltage.
For Delta connection:
- Ensure that each winding’s terminals are connected without overlapping with others.
- Typically, the L1, L2, and L3 lines from the supply should connect to the terminals of the windings in a way that forms a loop.
- Verify that the windings are not short-circuited and that the insulation is intact to avoid malfunction.
For Star connection:
- Check that all three windings are joined at a single central point, known as the neutral point.
- Each winding should have one free end connected to the corresponding line (L1, L2, L3).
- Ensure that the neutral point is properly grounded if required by the system.
Important Notes:
- Use voltage ratings that correspond with the selected configuration, as misconfigurations can cause overheating or damage.
- For motors operating on a star connection, a reduction in voltage will occur, lowering the torque output. Delta connections should be used when higher torque is required.
Understanding Voltage and Phase Sequence for Proper Wiring
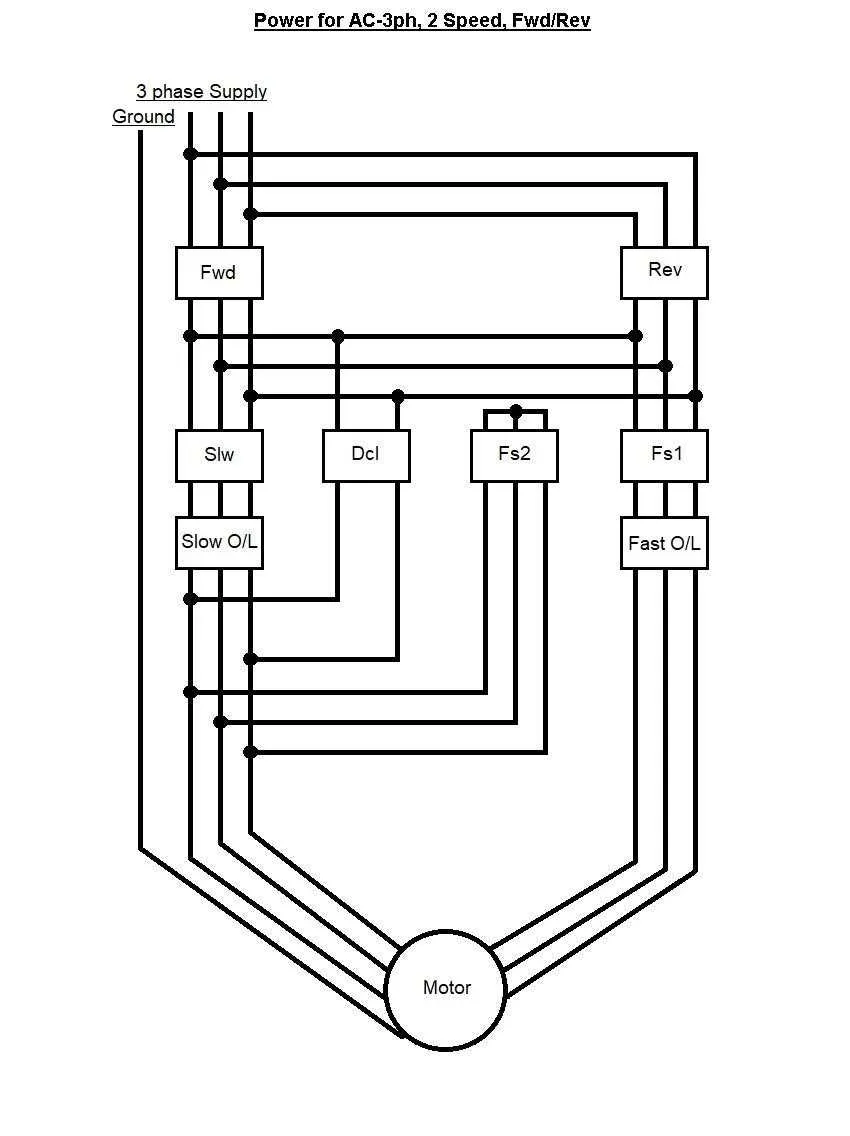
Ensure correct voltage levels before connecting the equipment to avoid damage. For balanced power distribution, voltage must match the specifications of the device. Check the supply voltage with a multimeter to confirm it aligns with the device’s rated voltage.
Phase sequence is critical for correct operation. Reversing the sequence can cause the equipment to rotate in the opposite direction, which might damage the system or cause malfunction. Use a phase sequence indicator to check the order before connection.
| Voltage Specifications | Common Voltage Ratings |
|---|---|
| Low Voltage | 208V, 220V |
| Medium Voltage | 380V, 415V |
| High Voltage | 690V |
For proper device operation, always adhere to the correct voltage tolerance and verify the phase sequence using an appropriate tool to prevent potential risks and inefficiencies.
Common Wiring Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Ensure proper rotation direction by double-checking the connections to the terminals. Reversing two leads can cause the unit to rotate incorrectly, potentially damaging the equipment or creating unsafe conditions.
Before powering up, verify that all grounding is correctly installed. A missing ground connection can result in electrical shocks or equipment failure.
Pay attention to voltage ratings. Incorrect voltage applied to the connections can result in overheating and possible damage to components. Always match the system’s specifications with the voltage input.
Use the correct wire gauge for the amperage. Under-sized wires can lead to overheating, creating a fire hazard. Over-sizing can also result in unnecessary cost and difficulty in installation.
Ensure that the start capacitor is installed properly. A faulty or improperly connected capacitor can lead to motor failure or inefficient operation, especially during startup.
Avoid over-tightening connectors. Over-tightened terminals can damage the wire or the terminal itself, potentially leading to poor conductivity and overheating.
Use only compatible components. Mixing different brands or incompatible parts can lead to system instability, higher wear, and greater risk of failure.