
For improved handling and durability, a well-structured system is crucial for a heavy-duty truck. A thorough understanding of the components and their functions allows for better maintenance and performance. Start by focusing on key parts such as the control arms, steering knuckles, coil springs, and shock absorbers, all of which work together to ensure a smooth ride and stability. Ensuring proper alignment and wear checks is vital for safety and efficiency.
Inspecting the ball joints and tie rods is essential for maintaining precise steering control and preventing any potential failures that could lead to costly repairs or safety risks. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of worn-out parts like the bushings and mounts can extend the vehicle’s lifespan and improve ride quality, especially under heavy loads or off-road conditions.
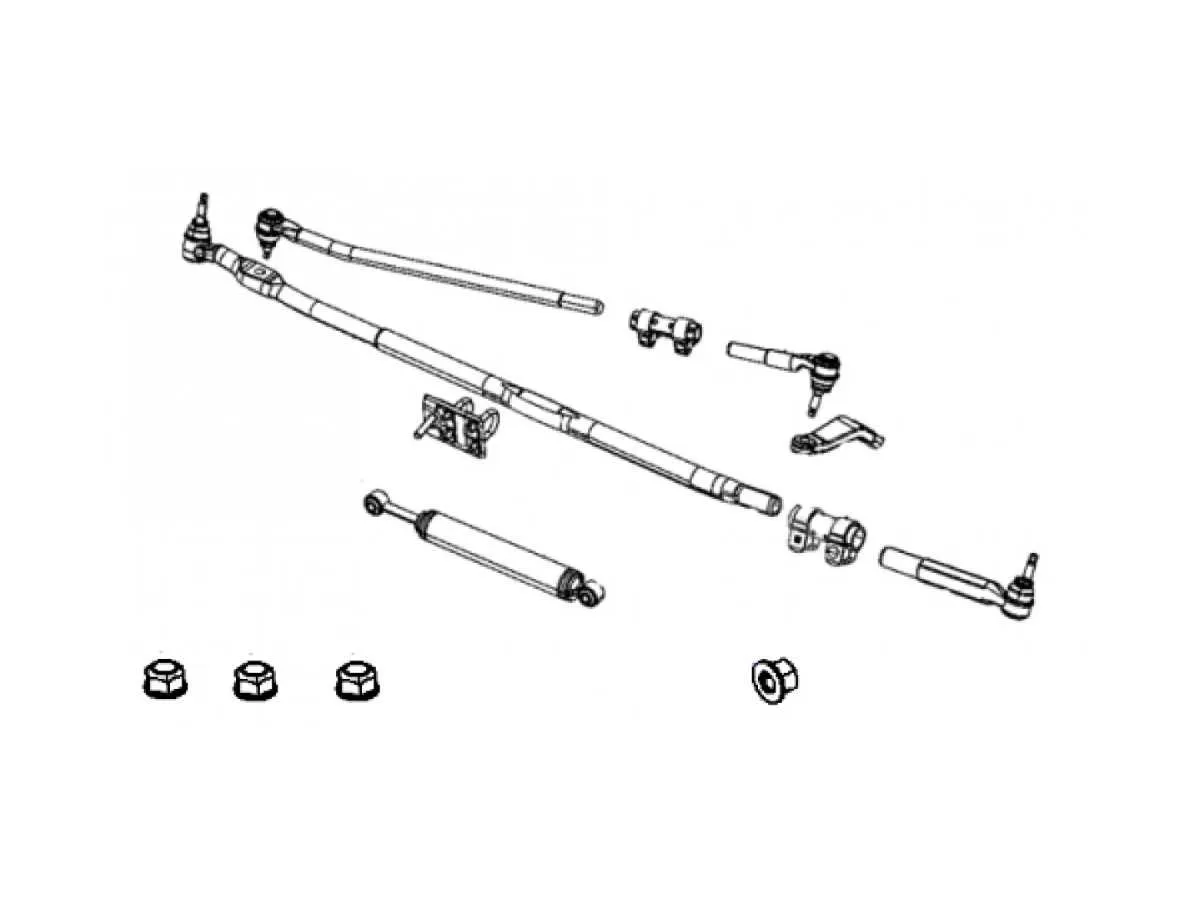
When analyzing the drivetrain linkages, it’s also important to understand how the system interacts with other mechanical components, such as the axle and differential. Ensure all parts are properly lubricated and free from debris to avoid unnecessary friction and wear. Pay attention to any changes in handling, as this could indicate issues with alignment or part degradation.
Front Axle System Overview
The axle assembly in the vehicle plays a crucial role in handling and stability. For optimal performance, it is essential to ensure proper alignment and functioning of key components, including the control arms, tie rods, and shock absorbers.
To maintain maximum durability, regularly inspect ball joints and bushings. Worn-out components can lead to reduced ride quality and increased wear on tires. Keep an eye on the steering knuckle for any signs of corrosion, as this could affect steering precision.
For best results, replace any faulty part with OEM or high-quality aftermarket components. Periodic inspections of the assembly and its alignment should be conducted every 20,000 to 30,000 miles to ensure continued performance and safety.
When performing repairs or replacements, verify the torque specifications for each part to prevent over-tightening, which can cause damage. Always follow manufacturer guidelines for torque settings to maintain the structural integrity of the system.
Additionally, when performing a lift or lowering, make sure to adjust the components accordingly to preserve handling characteristics and prevent unnecessary stress on the entire system.
Understanding Key Components of the Dodge Ram 2500 Front Suspension System
To maintain optimal handling and comfort, it’s crucial to understand the core parts of the steering and shock absorption system of your truck. Key elements include the coil springs, shock absorbers, control arms, and the steering knuckles.
Coil springs serve as the primary load-bearing components, offering flexibility and durability under weight. They help absorb the impact from road irregularities, contributing significantly to the vehicle’s stability. Regular inspection for signs of wear, such as cracking or flattening, is necessary for optimal performance.
Shock absorbers work with the springs to dampen vibrations and smooth out the ride. They regulate the upward and downward motion of the vehicle, ensuring a controlled rebound after hitting bumps. Over time, shock absorbers can lose their effectiveness, so check for oil leakage or reduced damping ability as indicators of when replacement is required.
The control arms allow movement of the wheel while connecting it to the main vehicle frame. They are often designed with ball joints to permit smooth movement. Proper lubrication and regular checks for any signs of bending or excessive wear can help avoid costly repairs.
Steering knuckles play an integral role in connecting the wheels to the suspension components. They facilitate turning and allow the wheels to rotate around a pivot point. If there are any noticeable sounds or handling issues, it’s vital to inspect the knuckles for cracks or signs of wear.
Ensure regular maintenance and timely replacements of these components to prevent damage to other parts of the vehicle and to maintain smooth performance over time.
How to Diagnose Issues in the Chassis of a Dodge Ram 2500
Start by checking for unusual noises such as clunking or squeaking when driving over bumps or making turns. These sounds often point to worn-out components in the steering system or damage to other parts of the assembly. Pay attention to any loose or rattling parts during a visual inspection.
Examine the shocks and struts for leakage or physical damage. If the shock absorbers are leaking fluid, it’s a clear sign of wear. Additionally, check for any noticeable dents or cracks in the struts that could affect vehicle stability.
Inspect the control arms, bushings, and ball joints for wear or degradation. Broken or worn bushings often lead to increased play in the steering system, which can make driving feel unstable or imprecise. A loose or damaged ball joint could cause excessive tire wear and steering difficulty.
Next, check the alignment by noticing whether the vehicle pulls to one side when driving straight. Misalignment can lead to uneven tire wear and poor handling, which often requires a professional adjustment.
Finally, assess the tire condition. Uneven tire wear, especially on the inner or outer edges, may indicate problems with the steering linkage or other components, requiring attention to maintain proper handling and safety.
Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing Suspension Components
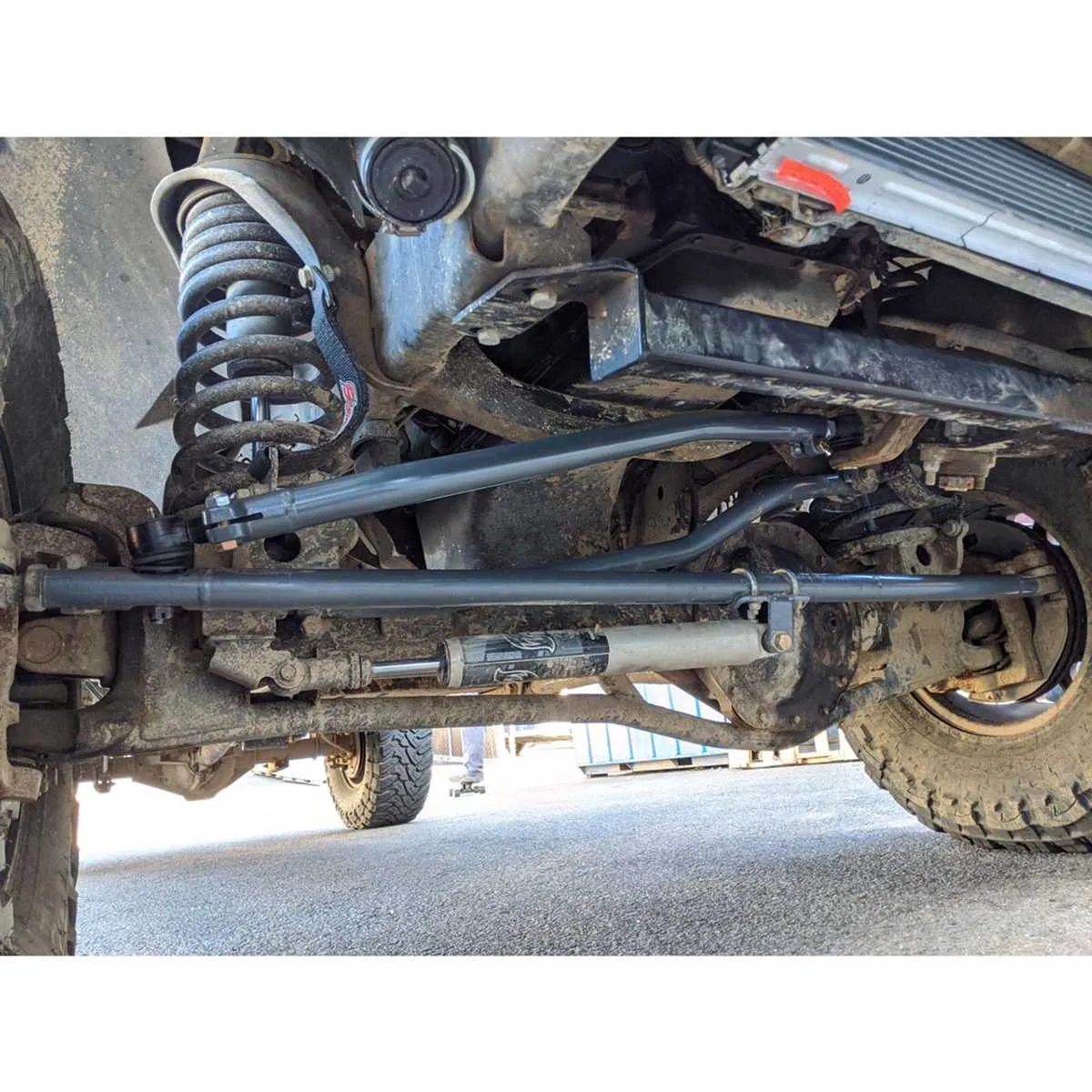

To replace the key suspension components, ensure the vehicle is securely elevated and supported. Follow these specific steps for a successful replacement.
- Lift the vehicle using a hydraulic jack, ensuring it is stable. Position jack stands for added security.
- Remove the wheel by loosening the lug nuts with a wrench.
- Inspect the components that need replacement–commonly, these include control arms, bushings, or tie rods.
- Disconnect the steering linkage from the knuckle or spindle. This may involve removing bolts or nuts holding the parts together.
- Remove the bolts securing the upper and lower control arms to the frame and axle. Keep track of each fastener for reinstallation.
- Take out the old bushings and clean the area for new ones. Apply grease to the new bushings before installation to prevent squeaking.
- Install the new control arms or other relevant components. Ensure all bolts are torqued to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Reattach the steering linkage, aligning it with the knuckle or spindle. Tighten the fasteners securely.
- Double-check all connections and torque settings before reinstalling the wheel.
- Lower the vehicle and tighten the lug nuts to the specified torque value.
- Test drive the vehicle to verify proper operation and eliminate any unusual noises.
Ensure all tools are in good condition and follow the vehicle’s service manual for any specific torque values or part specifications.