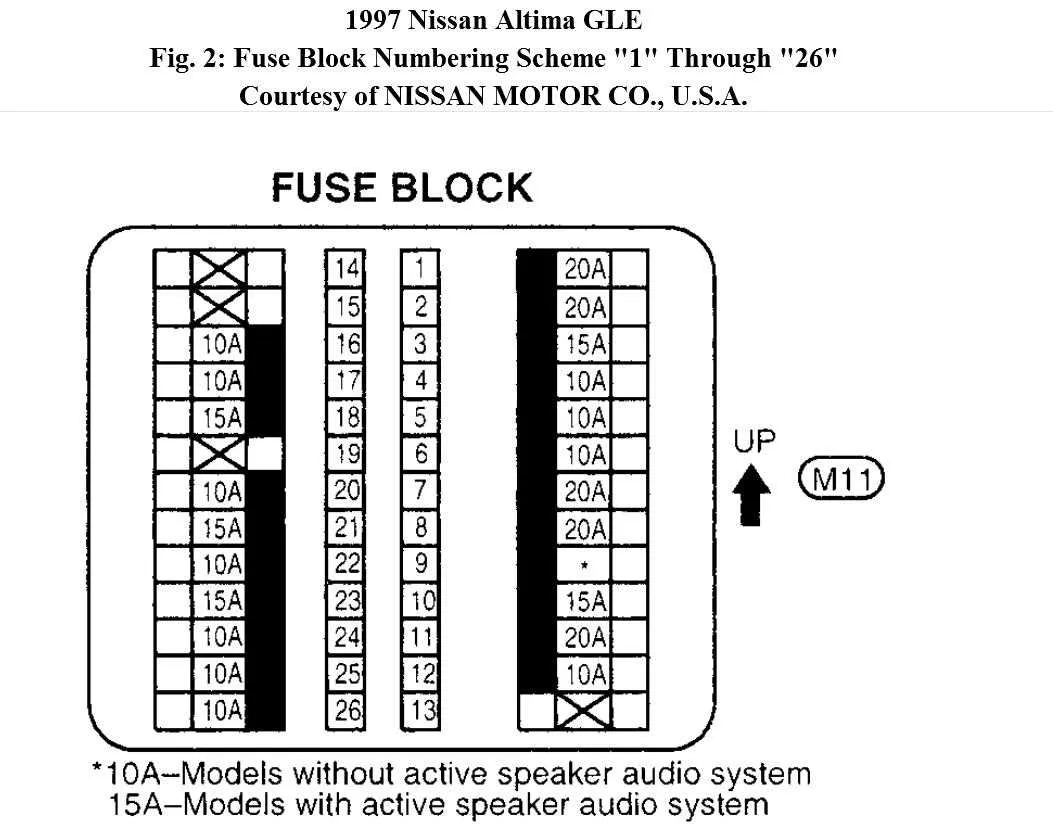
If you’re experiencing issues with your car’s electrical components, checking the power distribution unit is the first step. This component plays a key role in managing the flow of electricity throughout your vehicle. The layout of the relays and circuits within this section is crucial for troubleshooting and repairs. If a malfunction occurs, a quick visual inspection of the connections and their corresponding labels can save you a lot of time.
The first thing to do is locate the central unit, which is typically found in the engine compartment or beneath the dashboard. Understanding the arrangement of the fuses and relays in this unit can help you identify the specific circuit that may be malfunctioning. Pay attention to the layout provided by the manufacturer to avoid any confusion when replacing or testing individual units.
Make sure to use the correct amperage replacement components when addressing any faults. The specific fuse ratings are labeled clearly on the cover, ensuring that each unit is compatible with the car’s electrical demands. Be cautious when working with the power distribution system, as improper handling can lead to further damage.
For better clarity, refer to the printed guide that details the placement and specifications of each component within this unit. This guide will enable you to quickly identify which component controls what feature, such as air conditioning, lighting, or engine management. Having this diagram at hand speeds up diagnosis and ensures precise replacements without unnecessary confusion.
05 Vehicle Electrical System Layout
For efficient troubleshooting, refer to the specific layout of the electrical control units. The main panel located inside the cabin contains essential fuses, while the secondary compartment in the engine area houses relays and additional protection components.
To access the cabin unit, remove the cover under the dashboard on the driver’s side. The unit contains fuses for critical components such as the ignition, lighting, air conditioning, and infotainment system. Each fuse is clearly labeled to identify its corresponding function.
The engine compartment houses another protection panel. This unit controls electrical systems for high-power components such as the engine management system, power steering, and radiator fans. Locate the cover near the engine bay and remove it to access the relays and fuses. These are essential for the proper operation of the vehicle’s major systems.
Ensure you always use the correct fuse amperage for replacement to avoid potential electrical damage. Keep a spare set of fuses on hand for emergency repairs, especially for critical systems like the ignition and engine control units.
Refer to the vehicle’s manual for a detailed list of each fuse’s function and location within the two panels. This will help you quickly address any electrical issues without unnecessary delay.
Locating the Electrical Distribution Panels in the 2005 Model
For quick access to the electrical system, the main control panels are situated in two distinct areas:
- Under the hood: Situated near the engine compartment, this panel is easily accessible by lifting the hood. It is located on the driver’s side, towards the rear, near the windshield. This panel is crucial for the high-voltage circuits and various engine-related components.
- Inside the cabin: This panel is positioned on the lower left side of the dashboard, beneath the steering wheel. To access it, open the driver’s side door and remove the protective cover. It houses the majority of circuits responsible for cabin features such as lighting, climate control, and audio systems.
In both locations, the compartments are secured with latches or clips, which can be easily removed for maintenance or repairs. Make sure to always replace the cover properly after inspecting or modifying any connections.
How to Read the Electrical Component Layout for the 2005 Model
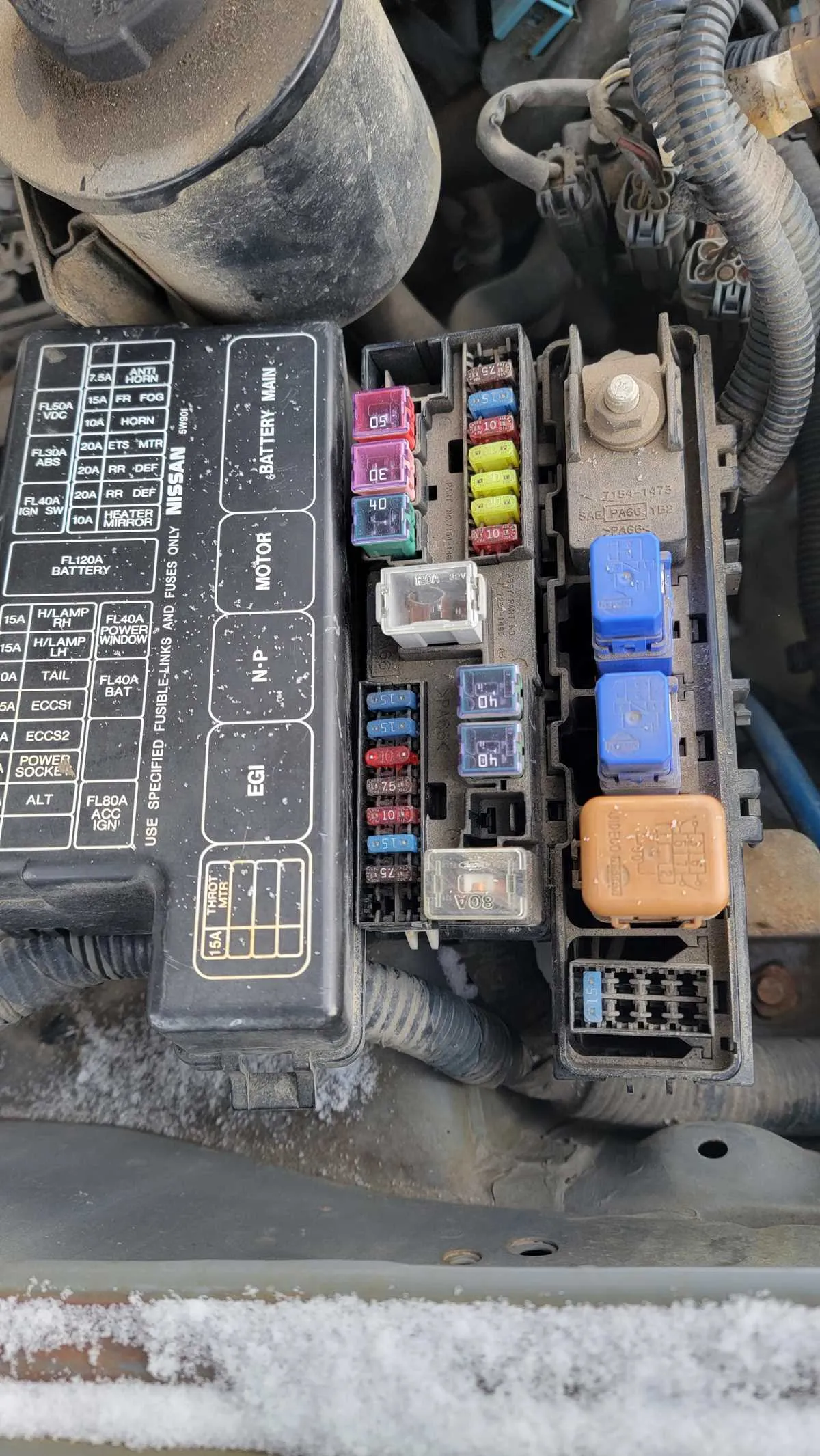
Start by locating the cover, which often includes a clear, labeled chart. Each row typically corresponds to a different circuit. Check the numbering system: odd numbers generally refer to components on the left, while even numbers are on the right. Pay attention to the amperage ratings indicated next to each item, ensuring that you replace components with the correct capacity.
Identify the type of each unit, whether it’s a relay or a small electrical unit. Some models feature a secondary setup under the dashboard or in the engine compartment, so verify both locations for comprehensive coverage. Use the reference key to cross-check the locations based on functionality, such as lights, air conditioning, or wipers.
If a specific section shows a malfunction, focus on its immediate components rather than checking all units. This will save you time and ensure accurate diagnosis. Finally, make sure to handle all electrical units carefully, avoiding any shorts or accidental damage during checks or replacements.
Common Electrical Panel Issues and Troubleshooting Tips for the 2005 Vehicle

When experiencing electrical malfunctions, check the panel connections first. Loose or corroded connections can cause intermittent issues with electrical components. Use a multimeter to test voltage at each terminal and ensure there is no significant voltage drop between points.
Burned-Out Relays or Components: If specific features stop working, the problem may lie in faulty relays or circuit elements. Inspect each component for signs of damage or overheating. If you notice discoloration or melted parts, replacing the damaged parts is necessary. A blown relay can prevent circuits from activating, so test the relays with a multimeter to ensure they are functioning correctly.
Corrosion: Corrosion on terminals is a common issue, especially in areas with high humidity. Clean the terminals with a wire brush or specialized cleaning solution to ensure a good connection. Be cautious when handling the panel to avoid damaging sensitive parts.
Loose Wiring: Over time, the wiring may loosen due to vibrations or aging. Check for any loose wires, paying close attention to the connections near the terminals. If any wires seem frayed or disconnected, repair or replace them as necessary.
Unexpected Circuit Breaker Trips: If the breaker frequently trips, there might be an overload or short circuit. Inspect all circuits to ensure there are no exposed wires that could be causing the short. A malfunctioning circuit can also be caused by faulty components, so double-check each part for wear and tear.
Incorrect Fuse Ratings: Ensure that replacement fuses match the specified amperage. Using an incorrect rating can lead to electrical system damage or fire hazards. Always refer to the owner’s manual for the correct fuse ratings for each circuit.
Continuity Testing: If none of the above methods resolve the issue, perform a continuity test on individual wires. This will help identify breaks in the circuit that are not immediately visible. Use a simple tester or multimeter to confirm the integrity of the wiring.
By regularly inspecting the electrical system and promptly addressing these issues, you can maintain reliable operation and prevent more serious electrical failures.