When working on the 2.3-liter engine in the 1993 XL model, it’s crucial to first familiarize yourself with the essential elements that keep it running smoothly. Knowing the exact layout and function of each part will save time during repairs and ensure optimal performance.
Start by focusing on the engine block, as it serves as the foundation for all internal components. Pay attention to the cylinder head, pistons, and crankshaft positioning. These are fundamental in controlling the engine’s compression and rotation. Make sure to reference a detailed schematic for accurate alignment when reassembling the unit.
Examine the fuel delivery system carefully, including the fuel injectors and fuel lines. Inadequate fuel flow or misdirected injection can lead to poor engine efficiency and increased wear. Check for leaks, clogs, or signs of wear that could cause performance issues.
Next, prioritize inspecting the electrical system, especially the ignition components like spark plugs, coil packs, and wiring. These elements are vital for starting and maintaining the engine’s power. Regularly replacing old or damaged parts can prevent future ignition failures.
Finally, consult the manufacturer’s technical charts to understand the connections between different mechanical systems. This will give you a clear visual guide to reassembling the engine, and will also help troubleshoot any potential problems based on the diagram’s breakdown of parts.
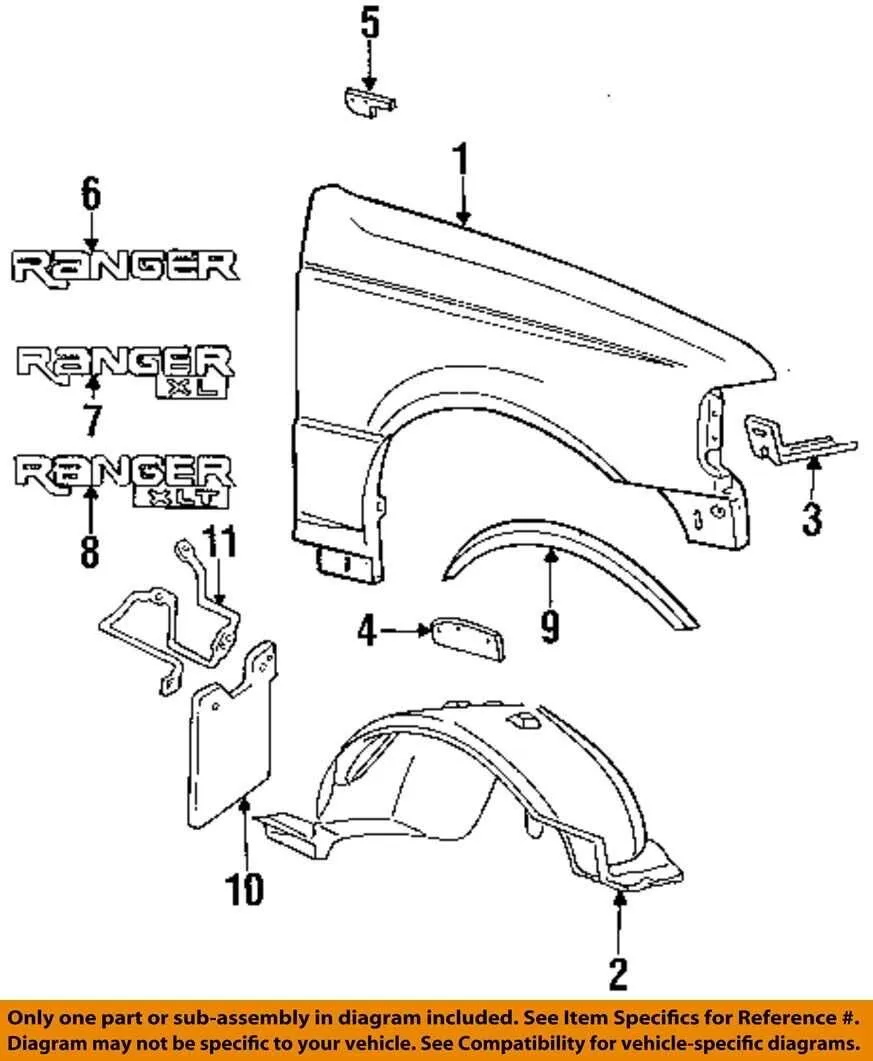
Essential Components Breakdown for the XL Model
For accurate replacement or repair, it’s vital to identify each individual element of the vehicle. Start by reviewing the engine assembly, ensuring all components, like pistons, valves, and camshaft, are intact. Pay close attention to the ignition system, particularly the spark plugs and distributor, which are crucial for optimal performance.
Next, inspect the fuel system, ensuring the fuel filter, fuel pump, and injectors are functioning without clogs. The cooling system should not be overlooked; check the radiator, hoses, and thermostat for any signs of wear or leaks. Also, ensure the serpentine belt is in good condition to maintain proper engine function.
For the suspension and drivetrain, focus on the shock absorbers, leaf springs, and axle components. Regularly checking the exhaust system, including the muffler and catalytic converter, will prevent unnecessary engine strain. Brake components, such as pads, rotors, and calipers, should be evaluated for wear to ensure safe stopping power.
Finally, always verify the condition of the electrical components: battery terminals, alternator, and wiring. Replace any corroded parts and ensure there is a secure connection to prevent electrical failures.
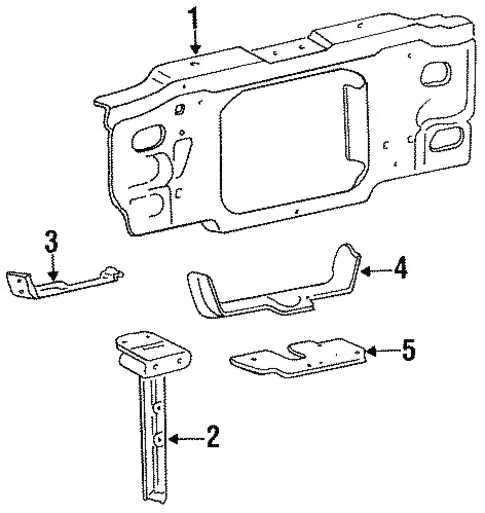
Identifying Key Engine Components in the 1993 Ford Ranger XL 2.3L Parts Diagram
To effectively troubleshoot or upgrade the engine, it is essential to know the key components within the powertrain. The following list highlights major engine elements commonly found in this vehicle’s setup:
- Intake Manifold: This component is critical for directing air into the engine’s cylinders. It connects the throttle body to the cylinder head, ensuring optimal airflow.
- Timing Belt: A crucial part of the engine, responsible for synchronizing the rotation of the crankshaft and camshaft, ensuring proper valve timing.
- Fuel Injectors: Responsible for delivering fuel into the combustion chamber in a precise manner, influencing both performance and fuel efficiency.
- Crankshaft Pulley: The crankshaft pulley is connected to the engine’s crankshaft, used to drive various components like the alternator and water pump.
- Exhaust Manifold: This part directs exhaust gases from the engine’s cylinders to the exhaust system, influencing vehicle emissions and performance.
- Water Pump: It circulates coolant through the engine and radiator, maintaining the engine’s operating temperature.
- Oil Filter: Essential for keeping engine oil clean by filtering out contaminants before it circulates back through the engine.
- Alternator: Converts mechanical energy into electrical power, supplying current to the vehicle’s electrical systems and charging the battery.
Each component plays a vital role in ensuring smooth engine performance, and knowing their positions can help in both maintenance and repair tasks. Always reference a detailed schematic for accurate part identification.
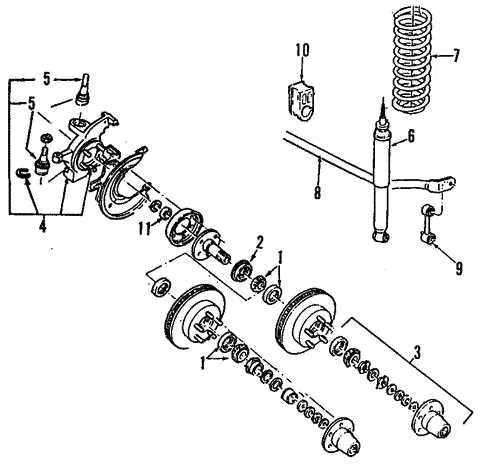
Understanding the Suspension and Steering System Components
For optimal vehicle performance, ensure that all components in the suspension and steering system are properly maintained and functioning. Key elements include the shock absorbers, struts, control arms, ball joints, and tie rods, all of which play a critical role in smooth handling and road stability. Shock absorbers and struts are responsible for damping vibrations, while control arms and ball joints allow for controlled wheel movement. The tie rods connect the steering rack to the wheels, ensuring precise response to driver input.
Inspect the bushings regularly, as they can wear out over time, leading to unwanted noise or misalignment in the steering. Replace any worn parts immediately to avoid further damage and ensure safe handling. Ensure that the steering rack is free from leaks and properly lubricated to prevent erratic steering responses.
When upgrading or replacing any suspension component, always choose high-quality OEM or equivalent replacements. This ensures that the vehicle’s alignment, ride quality, and overall handling remain consistent with the original design specifications. Proper alignment adjustments and torque settings are critical when reassembling the suspension system.
How to Locate and Replace Transmission Components Using the Vehicle’s Manual
To identify and replace faulty transmission components, start by consulting the vehicle’s official manual. This reference offers detailed illustrations of each assembly, showing the exact placement of parts like the clutch, gears, and shifter components.
Step 1: Locate the Transmission Assembly
The first task is locating the transmission housing within the manual’s visual guide. Once found, pay close attention to surrounding components, such as the linkage system and mounts, which may need to be disconnected before removal.
Step 2: Identify Specific Faulty Components
Use the diagrams to pinpoint damaged or worn parts. Common issues in the transmission can include cracked gears, worn bearings, or damaged seals. Compare the visual details with the actual system to confirm the problem area.
Step 3: Remove the Old Components
Once the issue is identified, follow the manual’s instructions to remove the defective parts. This usually involves unbolting components like the bellhousing or disconnecting linkage rods. Be sure to have the proper tools for this job, such as a torque wrench for reinstallation.
Step 4: Install New Components
Align the new components with the original setup using the manual’s guide. Ensure all parts are correctly seated and that any seals are properly fitted to prevent leaks. Tighten bolts and reassemble in reverse order of removal.
Step 5: Test the System
After installation, test the vehicle’s transmission functionality. Shift through all gears to ensure smooth operation. If problems persist, double-check the installation using the manual’s diagrams and confirm that all components are properly aligned and secured.