
For immediate troubleshooting of electrical components, refer to the layout map that outlines the exact positioning of relays and circuits. This will help you quickly identify the fuses associated with critical systems, including the engine, air conditioning, and lighting. Knowing which fuse corresponds to each function is essential for maintaining optimal performance and minimizing downtime.
Make sure to check the connections before replacing any components to avoid short-circuiting or damage to the system. In case of fuse failure, always ensure the replacement matches the required amperage to prevent further electrical issues. Use a reliable test light or multimeter to verify that the fuses are intact before assuming replacement is necessary.
While working on your vehicle’s electrical system, it’s crucial to also understand the arrangement of power distribution. The system uses a combination of high and low-current circuits that should be handled with caution. An inaccurate fuse replacement can affect the overall system’s operation, especially if high-powered components are connected to the wrong circuit.
Always keep a detailed map on hand and refer to it regularly for maintenance. Having a proper understanding of your vehicle’s electrical layout can save time and reduce the likelihood of costly mistakes.
Electrical Relay Layout and Component Locations
The first step in troubleshooting electrical issues in your vehicle is locating the relay panel. It’s essential to identify the exact layout of the components to ensure proper diagnosis and repair. The relay assembly is located near the engine compartment, typically to the left side. The position of each component is clearly marked on the panel for quick access.
For better serviceability, each section of the panel houses relays that correspond to different vehicle systems. These include the ignition, lights, cooling system, and other crucial functions. Understanding the individual position and function of each relay can save time when replacing damaged or malfunctioning parts.
Make sure to use the correct amperage for each relay to avoid overloading circuits. Always replace a faulty relay with one that matches the specifications outlined in the owner’s manual. Properly securing the relay assembly ensures that all electrical components function as intended without interruption.
In case of a malfunction, it’s recommended to check for blown relays by inspecting the fuse connections. If issues persist, the wiring harness might be damaged, requiring deeper inspection. Keep the area around the assembly clean to avoid debris buildup, which could cause short circuits.
Identifying Relay and Circuit Locations and Functions
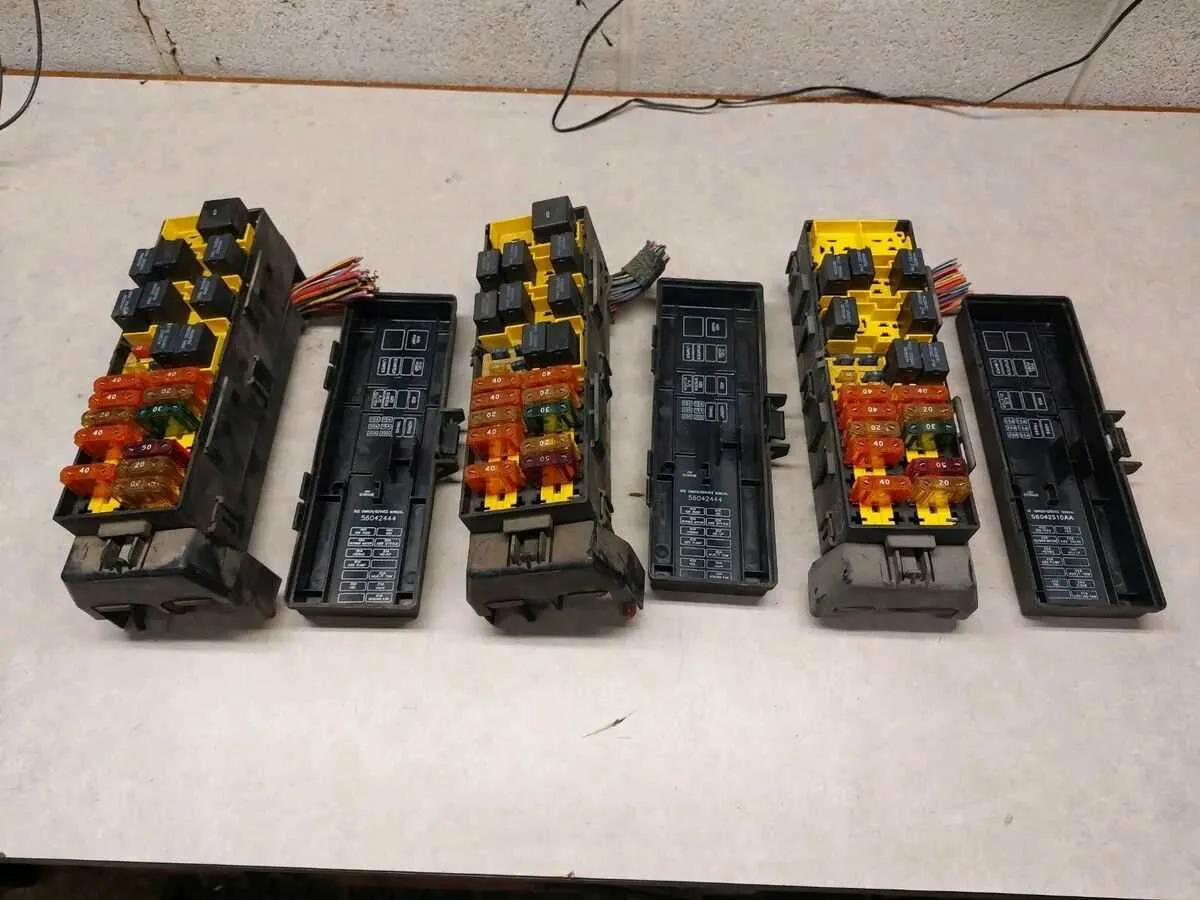

Check the main electrical relay panel for essential components that control the engine, lights, and other vital systems.
- Relay for Engine Control: Powers critical components in the ignition and fuel systems. Locate this relay near the central section of the panel.
- Headlamp Relay: Manages both high and low beam circuits. It is typically located near the outer edge of the panel for easy access.
- Climate Control Relay: Regulates the heating and air conditioning systems. This relay is usually placed near the bottom section of the assembly.
- ABS Relay: Manages the Anti-lock Braking System. Check for placement near the corner of the panel for quick troubleshooting.
- Horn Relay: Found centrally, responsible for activating the horn circuit. This relay often fails due to frequent usage.
Verify each component’s functionality by ensuring they are securely connected and free from corrosion.
- Ground Connections: Essential for proper circuit flow. Inspect ground points for wear or oxidation.
- Connections to the Battery: Check the primary power distribution block to ensure the main connection is tight and free from signs of wear.
- Circuit Tracing: For faulty components, use a multimeter to test continuity along the circuit paths leading from each relay.
If any of the relays fail to activate or show signs of electrical issues, replace them promptly to maintain reliable performance.
How to Replace a Blown Fuse in the Engine Compartment Electrical Panel
Start by identifying the specific component that is no longer functioning. Check the owner’s manual for the location of the electrical panel in the engine area. Once located, examine the individual elements for any visible signs of damage or a broken wire inside.
Use a pair of pliers to remove the faulty element from its socket. Ensure you have the proper replacement ready, matching both amperage and size specifications as indicated in the vehicle’s manual. Insert the new part into the same slot and press firmly to secure it in place.
After installation, test the system to ensure proper operation. If the new part blows immediately, inspect the electrical wiring and connections for any underlying issues that could be causing an overload.
For additional safety, wear gloves while handling electrical components to avoid any accidental shock or damage.
Common Electrical Issues and Troubleshooting Tips
If the vehicle’s electrical components aren’t functioning properly, first check the relays and wiring connections for signs of corrosion or wear. Often, faulty connections cause intermittent problems like flickering lights or malfunctioning accessories. Use a multimeter to check for continuity across the terminals. A lack of continuity indicates a broken wire or faulty relay.
If certain systems, like the air conditioning or headlights, aren’t working, inspect the relay that powers them. Sometimes, a simple relay replacement is all that’s needed to restore functionality. When replacing a relay, always ensure that the new part matches the amperage specifications indicated in the owner’s manual.
For persistent electrical issues, inspect the ground connections. Poor grounding can lead to voltage drops, resulting in unreliable system performance. Clean the ground points and make sure the contacts are tight. Use a wire brush to remove any rust or dirt, then reattach the cables securely.
Electrical shorts are another common problem. If any system is constantly losing power or blowing fuses, locate the short by inspecting each circuit for exposed wires or damaged insulation. Once the issue is located, repair the wiring or replace the damaged components.
In case of frequent fuse failures, check for excessive load on specific circuits. Overloaded circuits can lead to blown fuses. If a fuse keeps blowing, investigate the connected components to ensure they’re within the proper power range. If needed, reroute power or upgrade components to handle the increased load.