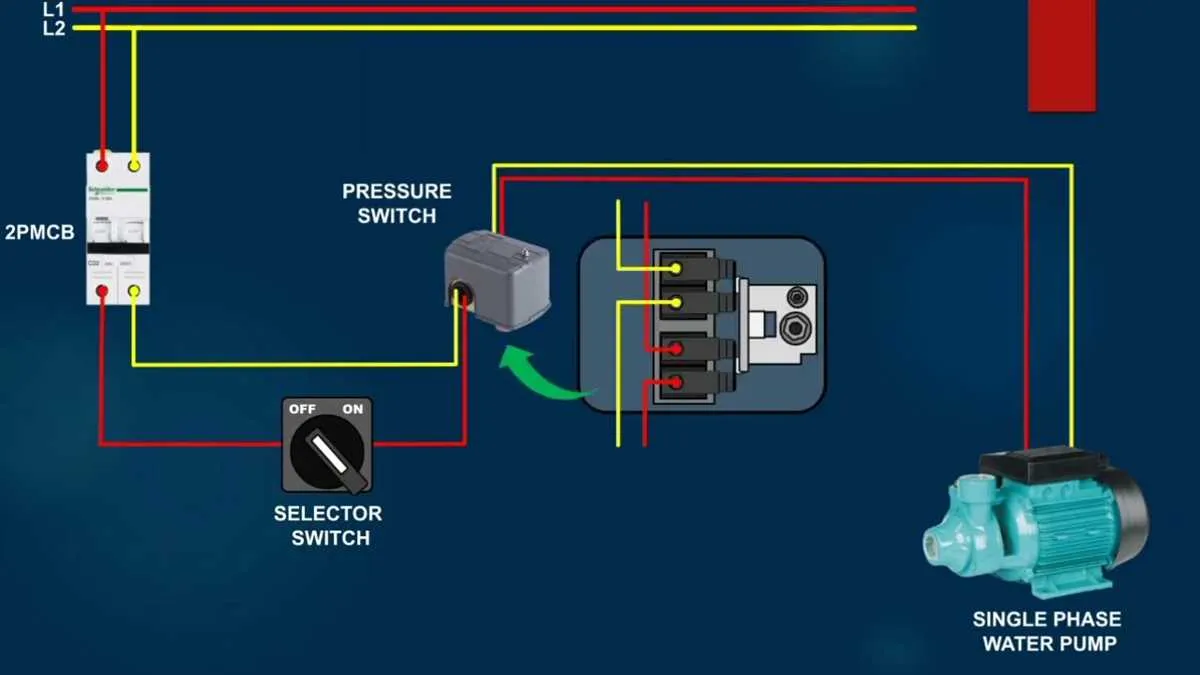
When installing a pressure control device, ensure you connect it according to the correct configuration for optimal performance. First, identify the terminals for the supply voltage and the signal output. These should be clearly marked on the component itself. The input terminal typically receives the power supply, while the output terminal provides the signal used to control the device it’s linked to.
Next, pay close attention to the ground connection. This is essential for avoiding voltage fluctuations that could affect the accuracy of the readings. A stable ground connection ensures reliable functionality and helps avoid false triggering or misreadings in the control system.
For accuracy, always check the wiring sequence and confirm that each terminal is securely attached to the respective wire. Using proper tools for tightening can prevent any loose connections that may cause malfunction. Also, consider using shielded cables to prevent electromagnetic interference, which could distort sensor readings.
Lastly, always consult the specific model’s manual for precise instructions. Some devices might have additional connections, such as a reset or calibration input, which could influence the setup process.
Electrical Connections for the Pressure Control Device
To establish proper functionality, connect the terminals of the control component as follows: the first terminal should be linked to the input power source, while the second terminal connects to the actuator or load. Ensure the third terminal is grounded to prevent electrical hazards. The fourth terminal is typically used for the signal output, which transmits the data to the monitoring device.
Important: Always verify the polarity before establishing any connections. Incorrect wiring can cause device malfunction or damage. Use a multimeter to check the continuity and ensure there are no shorts between the terminals.
Tip: When connecting the output to a monitoring or control system, ensure the signal type (voltage or current) is compatible with the receiving device to avoid damage.
Use insulated connectors to prevent accidental shorts, and confirm all connections are tight and secure to avoid issues during operation. Periodically inspect the wiring for wear and tear, especially in environments with high vibrations or moisture.
Understanding the Basic Connections of a Pressure Sensor
To establish reliable electrical connections, ensure the following key points are followed when setting up the device:
- Contact Terminals: Most devices have two terminals for current input and output. These should be clearly identified based on the device’s specifications.
- Power Supply: Connect the positive and negative terminals of the power supply correctly, ensuring the appropriate voltage and current values match the requirements of the sensor.
- Signal Output: For transmitting information to external devices, connect the output terminal to a corresponding receiver or controller. This ensures accurate monitoring of the sensor’s state.
Proper grounding is critical to avoid interference or damage. A stable ground connection will ensure proper operation and reduce the risk of electrical noise affecting the readings. Make sure the grounding wire is securely connected to the system’s main ground point.
- Double-check Connections: Always verify that all connections are tight and secure before testing. Loose terminals can lead to inaccurate readings or device failure.
- Insulation: If the system is exposed to harsh environments, consider using insulated cables to protect the connections from potential corrosion or short-circuiting.
Before powering the system, review the manufacturer’s documentation for any additional requirements related to device calibration or special connection considerations.
Choosing the Right Components for Pressure Switch Wiring
Select high-quality conductors with adequate insulation to handle the voltage and current levels in your application. Ensure that the gauge of the wire matches the power requirements of the system. For low-power connections, opt for thinner wires, while higher power setups require thicker ones to minimize resistance and heat buildup.
Use durable connectors that provide a solid, corrosion-resistant contact, especially in environments subject to moisture or extreme temperatures. Opt for materials like stainless steel or gold-plated contacts for better performance and longevity.
Choose a reliable control unit that matches the specific voltage rating and operational limits of your components. Verify that the relay or interface unit is rated for the exact switching current to avoid overheating and system failures. Be sure to check for proper load capacity and response time for optimal performance.
For robust protection, incorporate a fuse or circuit breaker in your setup. The fuse should match the current rating of the system, acting as a safeguard against potential short circuits or overcurrent situations. Select a fuse with a fast response time if your system requires rapid fault detection.
Consider environmental factors when selecting components. In harsh conditions, opt for components rated for moisture, dust, or extreme temperatures. Sealed or weatherproof options can ensure the longevity of the system when exposed to outdoor elements or challenging industrial settings.
Troubleshooting Common Connection Issues in Pressure Monitoring Devices
Start by checking for proper alignment of terminals. Ensure all connections are secure and that no wires are frayed or loose. A poor connection can cause intermittent operation or prevent activation altogether.
Verify that the device is receiving the correct voltage. An incorrect power supply can lead to malfunction. Use a multimeter to confirm the expected voltage at the device’s terminals and check against the manufacturer’s specifications.
If the unit is not responding, inspect for short circuits. Damaged insulation or incorrectly positioned cables can cause shorts, triggering failure. Also, check for any signs of corrosion or moisture that might have impacted the integrity of the electrical connections.
Confirm that the terminal blocks are free from debris. Accumulated dust, dirt, or moisture can disrupt conductivity, leading to false readings or complete failure. Clean the terminals carefully with a dry cloth and inspect for any signs of wear.
If the system is not activating at the correct threshold, recalibrate the sensor as needed. Improper settings could result in the device either activating too soon or too late, which affects overall system performance.
Test continuity in each conductor to ensure there are no breaks within the circuit. A continuity tester or multimeter will help you pinpoint issues like broken wires or disconnected elements within the setup.
Finally, inspect the grounding. Improper grounding can cause erratic behavior or false readings. Make sure the grounding is solid and follows all manufacturer guidelines for safety and performance.