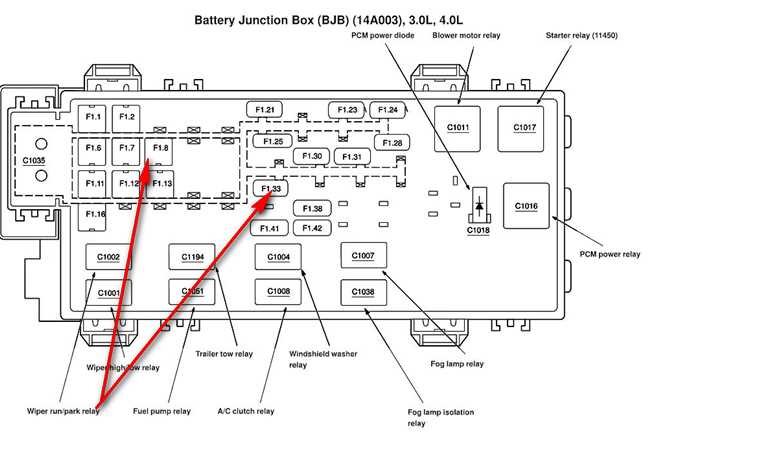
The 2000 Ford F650 is a heavy-duty truck known for its power and reliability. Whether you use it for hauling heavy loads or as a commercial vehicle, understanding its electrical system is crucial for ensuring its proper functioning. One essential component of the electrical system is the fuse box, which protects various electrical circuits from overloads and short circuits.
The fuse box in the 2000 Ford F650 is located in the engine compartment and contains a series of fuses and relays. Each fuse is designed to protect a specific electrical circuit, such as the headlights, brake lights, or radio. By referring to the fuse box diagram, you can easily identify which fuse corresponds to a particular circuit.
The fuse box diagram is a visual representation of the fuse box layout and provides information about the fuse’s amperage rating and the circuits it protects. This information is essential for troubleshooting electrical issues and replacing blown fuses. By understanding the fuse box diagram, you can quickly identify the fuse responsible for a malfunctioning circuit and resolve the issue efficiently.
Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a truck owner looking to understand your vehicle’s electrical system better, having access to the 2000 Ford F650 fuse box diagram is crucial. It enables you to take control of your truck’s maintenance and ensure its smooth operation. So, let’s dive into the details of the fuse box diagram and unlock the mysteries of the 2000 Ford F650’s electrical system!
Ford F650 Fuse Box Diagram: A Complete Guide for 2000 Models
If you own a 2000 Ford F650, it’s essential to have a clear understanding of the fuse box diagram. The fuse box diagram provides a visual representation of the fuse layout and the corresponding electrical components. This guide will help you identify the fuses and their functions, making it easier to troubleshoot any electrical issues that may arise.
The fuse box diagram for the 2000 Ford F650 is divided into several categories, including instrument panel fuse, power distribution box, and central junction box. Each category contains different fuses that are responsible for various systems and components of the vehicle.
Instrument Panel Fuse: This section of the fuse box diagram includes fuses for components related to the instrument panel, such as the gauges, radio, and climate control. By referring to this diagram, you can quickly locate the specific fuse associated with a particular function.
Power Distribution Box: The power distribution box houses high-current fuses that are responsible for powering various electrical systems, such as the alternator and powertrain control module. This section of the fuse box diagram provides information on the fuses’ amperage rating and the systems they protect.
Central Junction Box: The central junction box contains fuses and relays that control essential functions, including the headlights, turn signals, and windshield wipers. The fuse box diagram for this section will help you identify the fuse responsible for a specific electrical component and allow for easy troubleshooting.
In addition to the fuse box diagram, it’s crucial to have a fuse puller tool. A fuse puller makes it easier to remove and inspect a fuse if it’s suspected to be faulty. This tool allows for safe removal without damaging the fuse or the surrounding components.
To ensure the correct fuse replacement, it’s essential to use the proper amp rating and type specified in the vehicle’s manual or the fuse box diagram. Using the wrong fuse can lead to electrical malfunctions or even damage to the vehicle’s electrical system.
In conclusion, understanding the fuse box diagram for your 2000 Ford F650 is crucial for troubleshooting electrical issues effectively. By referencing the diagram and using the appropriate fuse puller tool, you can quickly identify and replace any faulty fuses. This knowledge will help keep your vehicle running smoothly and ensure the proper operation of its electrical systems.
Understanding the Fuse Box in a 2000 Ford F650
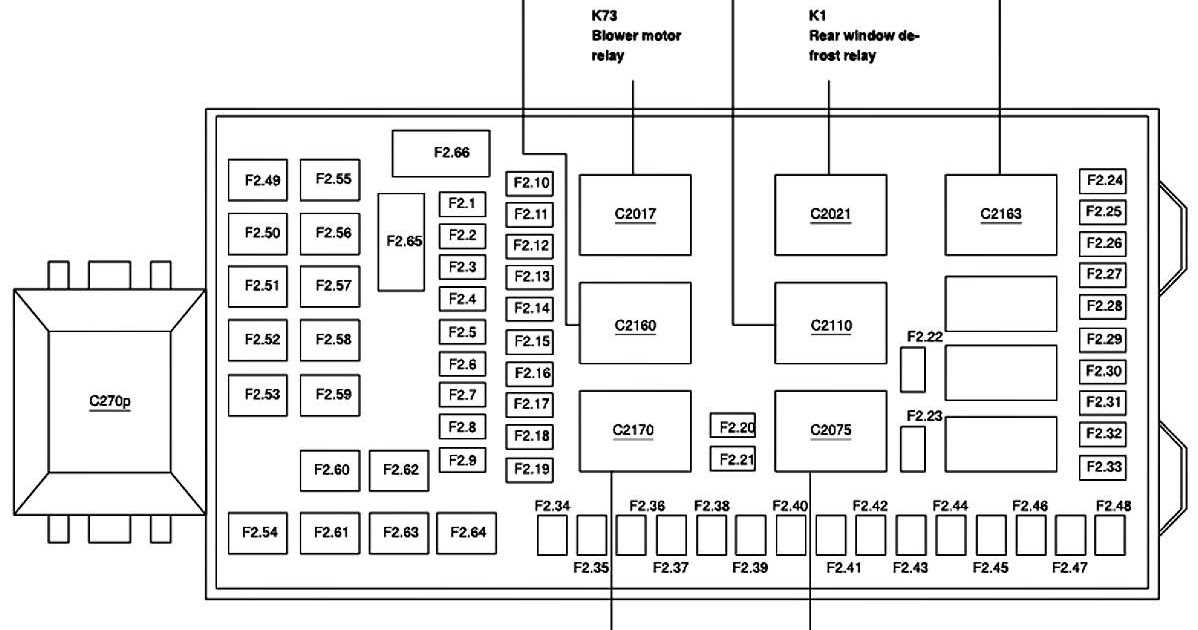
When it comes to finding the right fuses for your 2000 Ford F650, it’s essential to understand the functionality of the fuse box. The fuse box in this truck is responsible for protecting the various electrical circuits by housing the fuses that control them. Each fuse within the box is labeled according to its function, making it easy to identify and replace if necessary.
A 2000 Ford F650 fuse box diagram can be a useful tool in understanding the layout and location of the fuses. The diagram provides a visual representation of each fuse’s position and function within the box. It can help you quickly identify which fuse is responsible for a specific circuit, such as the headlights or the radio.
Some key phrases related to the fuse box in a 2000 Ford F650 include:
- Fuse box diagram: This diagram provides a visual representation of the fuse box’s layout and the location of each fuse within it.
- Fuse function: Each fuse within the box has a specific function, such as controlling the headlights, radio, or interior lights. The fuse box diagram can help identify which fuse is responsible for a certain function.
- Fuse replacement: If a fuse in the 2000 Ford F650 needs to be replaced, the fuse box diagram can help you easily locate the correct fuse and ensure the correct replacement is used.
- Fuse protection: The fuse box is designed to protect the electrical circuits in the truck. If a circuit is experiencing an overload or short circuit, the corresponding fuse will blow, preventing damage to the circuit.
Overall, understanding the fuse box in a 2000 Ford F650 is crucial for maintaining and troubleshooting the vehicle’s electrical system. By referring to the fuse box diagram and familiarizing yourself with the various fuses and their functions, you can quickly address any electrical issues and keep your truck running smoothly.
Locating the Fuse Box
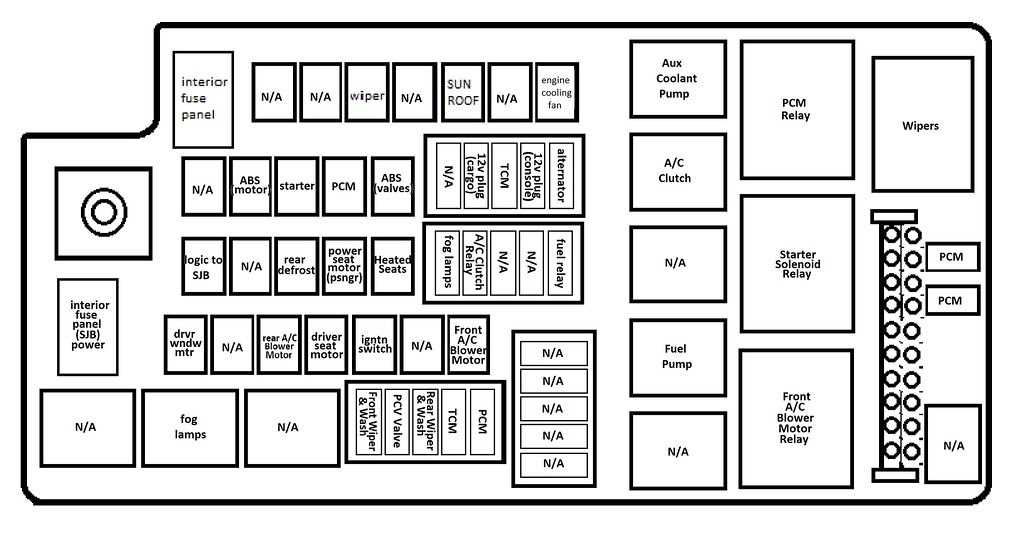
If you are experiencing electrical issues with your 2000 Ford F650, it may be necessary to locate and check the fuse box. The fuse box houses the fuses and relays that control various electrical components in your vehicle. Finding the fuse box is the first step in troubleshooting any electrical problem.
To locate the fuse box in your 2000 Ford F650, you will need to consult your owner’s manual. The manual will provide you with the exact location of the fuse box and a diagram of the fuses and relays inside. The fuse box is usually located in one of three places: under the dashboard, under the hood, or in the trunk. Be sure to check all possible locations if you are unable to find it initially.
Once you have located the fuse box, carefully remove the cover to access the fuses and relays. The cover may have tabs or screws that need to be removed before it can be taken off. Inside the fuse box, you will see a diagram that identifies each fuse and relay and what component it controls. Use this diagram to determine which fuse corresponds to the electrical issue you are experiencing.
When checking the fuses, it is important to use a fuse tester or multimeter to ensure that they are not blown. A blown fuse will have a broken wire inside and will need to be replaced. If you are unsure about the condition of a fuse, it is best to replace it with a new one to be safe. Once you have replaced any blown fuses, reassemble the fuse box cover and test the electrical component to see if the issue has been resolved.
Fuse Box Diagram for a 2000 Ford F650
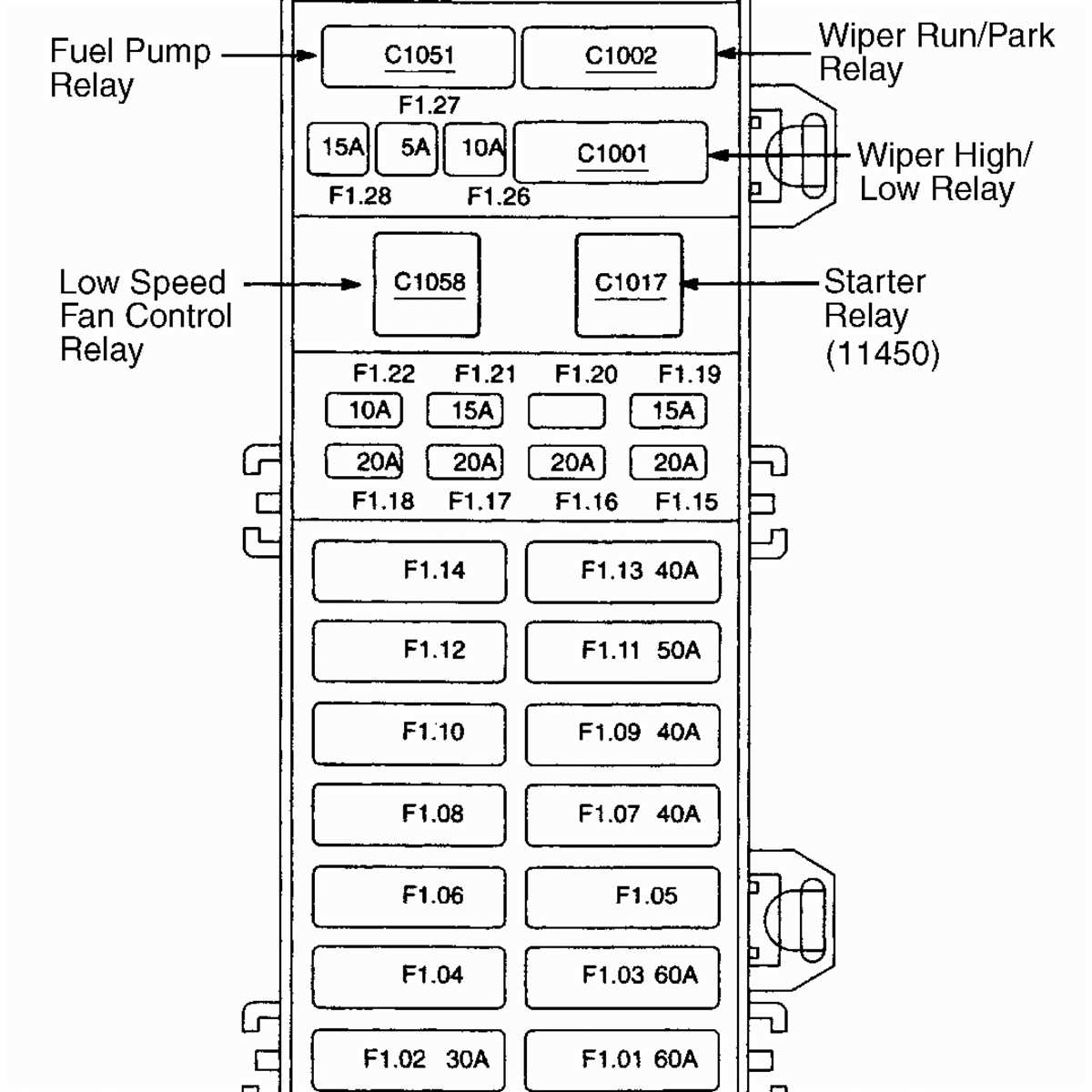
The 2000 Ford F650 is equipped with a fuse box located in the engine compartment. This fuse box contains various fuses and relays that control different electrical components of the vehicle. It is important to know the location and purpose of each fuse in case of a malfunction or electrical issue.
The fuse box diagram for a 2000 Ford F650 can be found on the inside cover of the box. It provides information about the fuse’s number, rating, and the electrical system it controls. The diagram is typically divided into sections, such as lighting, ignition, cooling, and accessories, making it easier to locate a specific fuse.
Here is a general overview of the fuse box diagram for a 2000 Ford F650:
- Fuse 1: Ignition Switch, Starter Relay
- Fuse 2: Powertrain Control Module (PCM) Relay
- Fuse 3: Fuel Pump Relay
- Fuse 4: Anti-Lock Brakes (ABS) Module
- Fuse 5: Trailer Tow Electric Brake Controller
- Fuse 6: Air Conditioner Compressor Clutch Relay
- Fuse 7: Trailer Turn Signals
- Fuse 8: Trailer Battery Charging Relay
These are just a few examples of the fuses and relays that can be found in the fuse box of a 2000 Ford F650. It is highly recommended to refer to the specific fuse box diagram for the accurate information related to your vehicle’s electrical system. In case of any doubts or issues, it is always best to consult the owner’s manual or seek professional assistance.
Common Fuse Box Issues and How to Troubleshoot
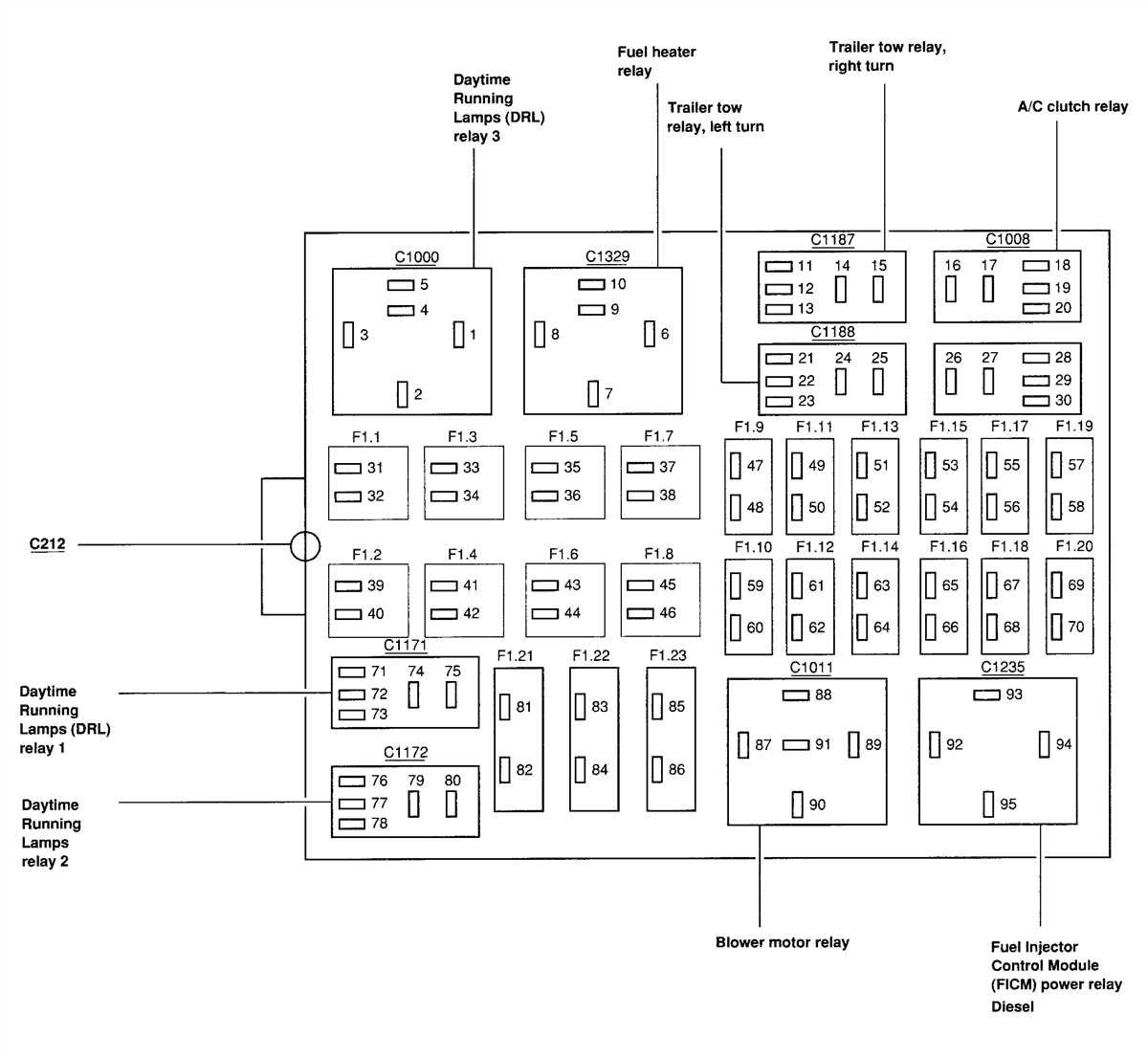
Fuse boxes play an important role in protecting the electrical system of your vehicle from damage caused by electrical overloads. However, over time, issues with the fuse box can arise, leading to electrical problems that can be frustrating and potentially dangerous. Understanding common fuse box issues and how to troubleshoot them can help you resolve these problems quickly and efficiently.
Blown Fuses: One of the most common issues with fuse boxes is blown fuses. When a fuse blows, it interrupts the flow of electrical current to the corresponding component or system. To troubleshoot this issue, start by identifying the fuse that has blown by referring to the fuse box diagram. Once you have identified the fuse, carefully remove it using fuse pullers or pliers. Inspect the fuse to see if the metal strip inside is broken. If it is, replace the fuse with one of the same amperage rating.
Loose Connections: Another common problem with fuse boxes is loose connections. Over time, the connections between the fuses and the terminals can become loose, leading to intermittent electrical issues. To troubleshoot this issue, turn off the ignition and carefully remove each fuse one by one. Inspect the terminals for any signs of corrosion or loose connections. Clean the terminals using a wire brush or sandpaper and tighten any loose connections. Reinstall the fuses and check if the electrical issues have resolved.
Corrosion: Corrosion can also affect the functionality of the fuse box. When corrosion builds up on the terminals and connectors, it can disrupt the flow of electrical current. To troubleshoot this issue, remove the affected fuses and inspect the terminals for any signs of corrosion. Clean the terminals using a baking soda and water solution or a specialized electrical contact cleaner. Ensure that the terminals are completely dry before reinstalling the fuses.
Overloaded Circuits: If you are experiencing frequent blown fuses, it may indicate that your circuits are overloaded. An overloaded circuit occurs when too many electrical devices are powered simultaneously, exceeding the ampere rating of the fuse. To troubleshoot this issue, identify the devices that are consuming excessive power and try using them one at a time to see if they are the cause of the problem. Consider redistributing the load or installing a higher ampere fuse if necessary.
By understanding these common fuse box issues and how to troubleshoot them, you can keep your vehicle’s electrical system running smoothly. However, if you are unsure or uncomfortable with handling electrical components, it is always best to consult a professional mechanic for assistance.
Maintenance Tips for the Fuse Box
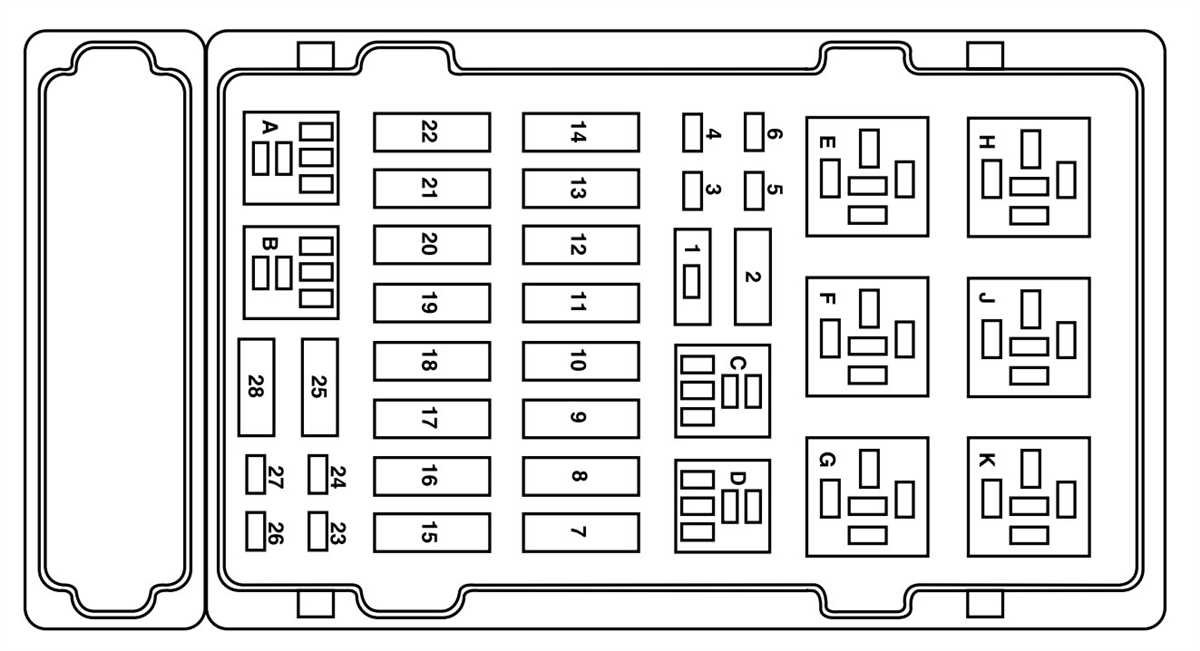
The fuse box is an essential component of your vehicle’s electrical system. It protects your vehicle from electrical surges and prevents damage to critical components. To ensure the proper functioning of your fuse box and avoid potential issues, here are some maintenance tips:
- Regular Inspection: Periodically check the fuse box for any signs of damage, such as corrosion, loose connections, or burnt fuses. Replace any damaged fuses immediately.
- Clean Connections: Over time, dirt and debris can accumulate on the fuse box connections, causing poor electrical contact. Use a gentle brush or compressed air to clean the connections and ensure optimal performance.
- Proper Fuse Usage: Always use the correct amperage rating for each fuse. Using a higher amp fuse can lead to electrical system damage, while a lower amp fuse may not provide sufficient protection.
- Waterproofing: If your fuse box is located in an area exposed to moisture, such as the engine compartment, consider using a waterproof sealant or wrapping the box with protective tape to prevent water damage.
- Emergency Kit: Keep a spare set of fuses of different amperages in your vehicle’s emergency kit. These can come in handy in case of a blown fuse and ensure you’re prepared for any electrical issues.
By following these maintenance tips, you can extend the lifespan of your fuse box and maintain the electrical integrity of your vehicle. Remember, if you’re unsure about any maintenance tasks, it’s always best to consult a professional mechanic or refer to your vehicle’s manual for guidance.