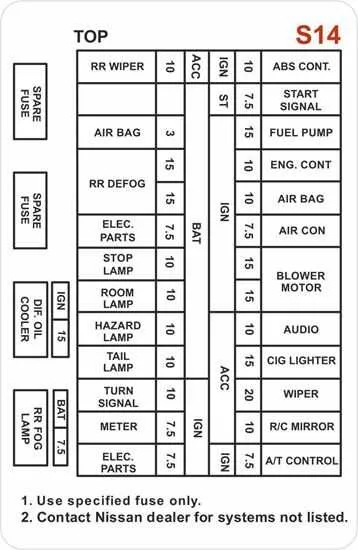
For optimal performance, locate and inspect the central power distribution system within your car. Knowing the exact arrangement of relays and circuits is vital for quick troubleshooting or component replacement. The primary electrical connections are organized in a clear grid, ensuring that each part of the car functions seamlessly. Always begin by identifying the main section, usually positioned within the driver’s side footwell or engine compartment.
It is important to check the precise placement of each relay and connection. The grid will indicate the power sources for essential systems like headlights, ignition, and air conditioning. A thorough understanding of where each component resides can save time when diagnosing issues or replacing malfunctioning parts. Consult your vehicle’s manual for the exact positioning and layout to ensure you’re working with the correct setup.
Make sure to maintain a careful approach while working with the electrical system. Disconnect the power supply before handling any components to avoid accidental short circuits. For a more accurate understanding, use a multimeter to check the status of individual connections. Familiarity with the vehicle’s electrical infrastructure will empower you to quickly identify and address potential issues, ensuring the reliability of key functions.
Electrical Component Layout for 2001 GT
The central unit located inside the engine compartment houses several relays and electrical connections essential for vehicle operation. Start by checking the primary power distribution board located near the driver’s side for the main connections. For interior components, such as the air conditioning system and lighting, focus on the secondary unit positioned under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Ensure all connections are secure and inspect the labels for each section to identify circuits linked to critical components like the ignition and fuel system.
If electrical issues arise, test individual connectors and relays using a multimeter. Pay attention to the clearly marked circuits for critical systems such as wipers, headlights, and brakes. Faulty connections in this area may disrupt power flow, causing malfunction in essential vehicle functions.
For repair or replacement, always use components that match the specifications found in the vehicle manual. When replacing relays or connectors, ensure the new parts are firmly installed to avoid short circuits or power loss in the future. Consider using dielectric grease on connectors to prevent corrosion and ensure longevity.
Understanding the Electrical System Layout for the 2001 GT Model
For efficient troubleshooting and maintenance of your vehicle’s electrical components, it’s crucial to familiarize yourself with the layout of its power distribution components. Here’s a detailed guide on how to identify and interpret the essential sections of the system in your GT model.
- Under the hood, locate the primary power management section near the engine bay. This is where critical electrical components like the ignition and charging systems are connected.
- Inside the cabin, check the secondary power panel located near the driver’s side. It controls interior systems such as lights, sensors, and entertainment features.
- The layout of the sections is divided into several sections, with each one corresponding to a particular set of electrical units. The configuration allows for easy identification of faulty circuits or blown relays.
Each section of the layout has its own designation. Pay attention to the specific labeling of components like relays, fuses, and control units for precise diagnostics. If any part of the electrical setup becomes nonfunctional, start by inspecting the corresponding units from the chart.
- When troubleshooting, it is essential to follow the labeled instructions, especially when replacing a malfunctioning part. Ensure all connections are tight and secure before reassembling any covers.
- Pay particular attention to any sections related to the air conditioning, brake lights, or power steering, as these are common areas where issues arise.
Having a clear understanding of the electrical layout will simplify any maintenance tasks and make diagnosing problems much quicker. Regular inspections of the connections and components will extend the lifespan of your vehicle’s electrical system.
Locating and Identifying Fuses in the 2001 Mustang GT Fuse Box
Start by opening the panel located near the driver’s side, beneath the dashboard. Once accessed, you will find a set of small, rectangular components, each assigned to a specific function within the electrical system. For ease of identification, a label or legend is often printed directly inside the cover or nearby. This guide will help you navigate through the various circuits, such as those for lights, radio, or power windows, making it easier to pinpoint the issue.
If you are looking to replace or check for a blown unit, make sure to have a multimeter handy. For visual checks, inspect each component for any signs of damage, such as discoloration or a broken filament. These are the most common indicators of malfunction. Additionally, some components may be located in a secondary area near the engine compartment; refer to the owner’s manual to confirm their exact placement for specific troubleshooting.
Be cautious when handling these units, as incorrect placement or damage could lead to further electrical issues. If you’re unfamiliar with the process, consulting a professional mechanic might save you time and effort in resolving the problem quickly.
Common Electrical Problems and How to Diagnose the 2001 Mustang GT Fuse System
Start by checking for blown relays or fuses when facing electrical issues in the vehicle. A sudden loss of power to certain components may indicate that a relay has failed or a fuse is damaged. Use a multimeter to inspect the individual components in the system to confirm if they’re operating correctly.
Corroded connections are another frequent cause of malfunction. Clean any dirty or rusted terminals and ensure all contacts are firmly in place. Sometimes, corrosion near the terminals can cause intermittent power loss, so thorough cleaning is essential for restoring proper function.
Check for signs of overheating in the panel where the relays and circuits are located. Overheating can cause components to fail and may even lead to wire damage. Look for discoloration or melted areas, which indicate a possible short circuit. If such damage is found, immediate replacement of affected parts is necessary.
If multiple systems are malfunctioning at once, it could be an issue with a central ground point. Make sure all grounding points are secure and free from rust. Loose or poor connections can prevent components from receiving the necessary voltage, causing them to malfunction.
Test continuity to rule out issues with individual circuits. If there’s no continuity, there may be a break in the wire or a damaged connection somewhere along the path. Identifying these breaks can save time in narrowing down the source of the issue.
Always keep a replacement set of relays and fuses on hand. Since they are prone to wear and tear, having spares can help address issues quickly without waiting for parts to arrive.