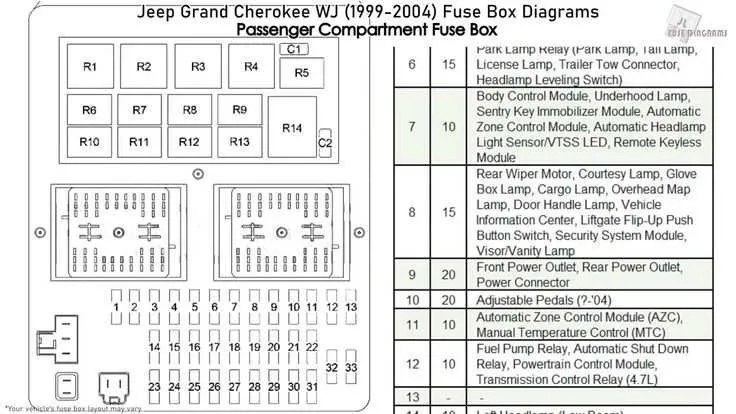
When troubleshooting electrical issues in a 2004 SUV model, understanding the power distribution and circuit layout is essential. To prevent misdiagnosis, it’s crucial to pinpoint the exact location of fuses and relays. This guide provides a clear representation of the electrical component layout to help you identify any faulty connections and restore the vehicle’s electrical functionality quickly.
Key areas to check include: the main power distribution block, secondary fuse panels, and individual relay slots. These components control everything from headlights to interior electronics, so knowing the exact configuration is vital for any repair. Always refer to a well-organized chart that clearly labels each fuse’s purpose and amperage to avoid unnecessary replacements.
For detailed repairs, it’s advised to consult the power layout chart in your owner’s manual or a trusted online resource. This will offer a more precise breakdown of the circuit connections and allow you to quickly isolate potential problems.
Electrical System Layout for Vehicle
If your vehicle’s electrical components are malfunctioning, checking the power distribution system is essential. Each circuit is powered through a set of relays and connections that should be tested if there’s an issue with lights, radio, or other accessories. It’s important to locate the main block, typically found under the dashboard or near the engine compartment, to identify which circuit controls which function.
The system uses color-coded fuses and specific amperage values to ensure proper operation. Check the position of each fuse to confirm it corresponds to the correct function. For example, the main engine components are usually powered through a higher amperage unit, while accessories use lower amperage units.
Make sure to always replace a blown unit with a fuse of the same amperage rating to avoid any potential electrical damage. In some cases, a blown unit could point to an underlying issue in the circuit that needs to be addressed. Therefore, consider using a multimeter to test the integrity of the power distribution lines if the problem persists after replacing the unit.
Understanding the Layout of Electrical Components in the Vehicle
To ensure proper functionality of the electrical system, it’s crucial to familiarize yourself with the location and organization of the power distribution box in the vehicle. The layout is designed to separate circuits based on their functions, allowing for easy identification and troubleshooting.
- Main Power Distribution Box: Located under the hood, this box houses components responsible for high-power circuits such as the engine control, headlights, and air conditioning. It’s essential to check the condition of the connections periodically to avoid system failures.
- Interior Panel: Inside the cabin, you’ll find a secondary box, usually beneath the dashboard. It handles low-power circuits, including interior lights, radio, and window motors. The design ensures that these circuits are protected from high-voltage surges.
- Labeling and Marking: Components within both boxes are clearly marked with labels indicating their respective functions. These labels should be checked against the user manual for precise identification.
If a component stops working, start by checking the related section in the power distribution layout. Replacing a faulty unit is a straightforward process, but always ensure the system is powered down before replacing any part.
- Locate the correct unit: Refer to the manual or the panel’s markings.
- Ensure no power is flowing: Disconnect the battery if necessary.
- Replace with correct part: Only use parts that match the recommended specifications.
Proper maintenance of these electrical boxes will prolong the lifespan of the vehicle’s electronic components and ensure they perform at their best.
Common Electrical Issues and Troubleshooting Tips
Check the Electrical Components Regularly: Start by inspecting all power distribution modules for signs of damage or corrosion. Make sure connectors are tight and free from rust. Corroded terminals are a common cause of electrical malfunctions, leading to intermittent issues in circuits.
Verify the Integrity of Wires: Frayed or damaged wires can short-circuit, causing loss of power to essential components. Check for any visible wear and replace any compromised cables to restore functionality.
Inspect Relays and Switches: Faulty relays and switches often go unnoticed. Test each component with a multimeter to ensure they are sending the correct signals. If one is malfunctioning, replace it immediately to prevent further electrical breakdowns.
Replace Burnt-Out Connections: If a circuit suddenly loses power, a burnt-out connector or terminal could be the culprit. Examine all connection points, particularly those related to high-power components, and replace any damaged areas to prevent further problems.
Use Correct Replacement Parts: When replacing any electrical component, ensure that the new part matches the vehicle’s specifications. Incorrect replacements can lead to short circuits or mismatched power distribution, making the issue worse.
Test the Battery Condition: A weak or dead battery can cause power inconsistencies in various systems. Use a voltmeter to check the battery’s charge level. If the voltage is low, recharge or replace the battery to maintain reliable electrical performance.
Reboot the Electrical System: In some cases, performing a reset by disconnecting the vehicle’s battery for 10-15 minutes can resolve temporary electrical malfunctions. This can help clear any system errors or glitches.
How to Replace Fuses in a 2004 Jeep Cherokee

To replace the electrical components in your vehicle, start by identifying the faulty part. First, locate the fuse panel under the dashboard or in the engine compartment. Use the owner’s manual to find the exact location of the specific circuit you’re targeting.
Once located, turn off the ignition and remove the negative battery terminal to avoid accidental shorts. Use a fuse puller or a pair of needle-nose pliers to gently extract the damaged component from its holder.
Before inserting the new part, ensure it matches the amperage rating of the original. Never substitute with a higher-rated unit, as it can lead to overheating or fire risks. Insert the replacement firmly and check the electrical system to ensure proper functionality.
If the new part blows immediately, there’s likely an underlying electrical issue that requires further diagnosis, such as a short circuit or damaged wiring. It’s essential to address the root cause to prevent repeated failures.
Tip: Always keep a set of spare components in your vehicle for emergencies. Having the right tools, like a multimeter, can help you quickly diagnose any electrical issues that arise.