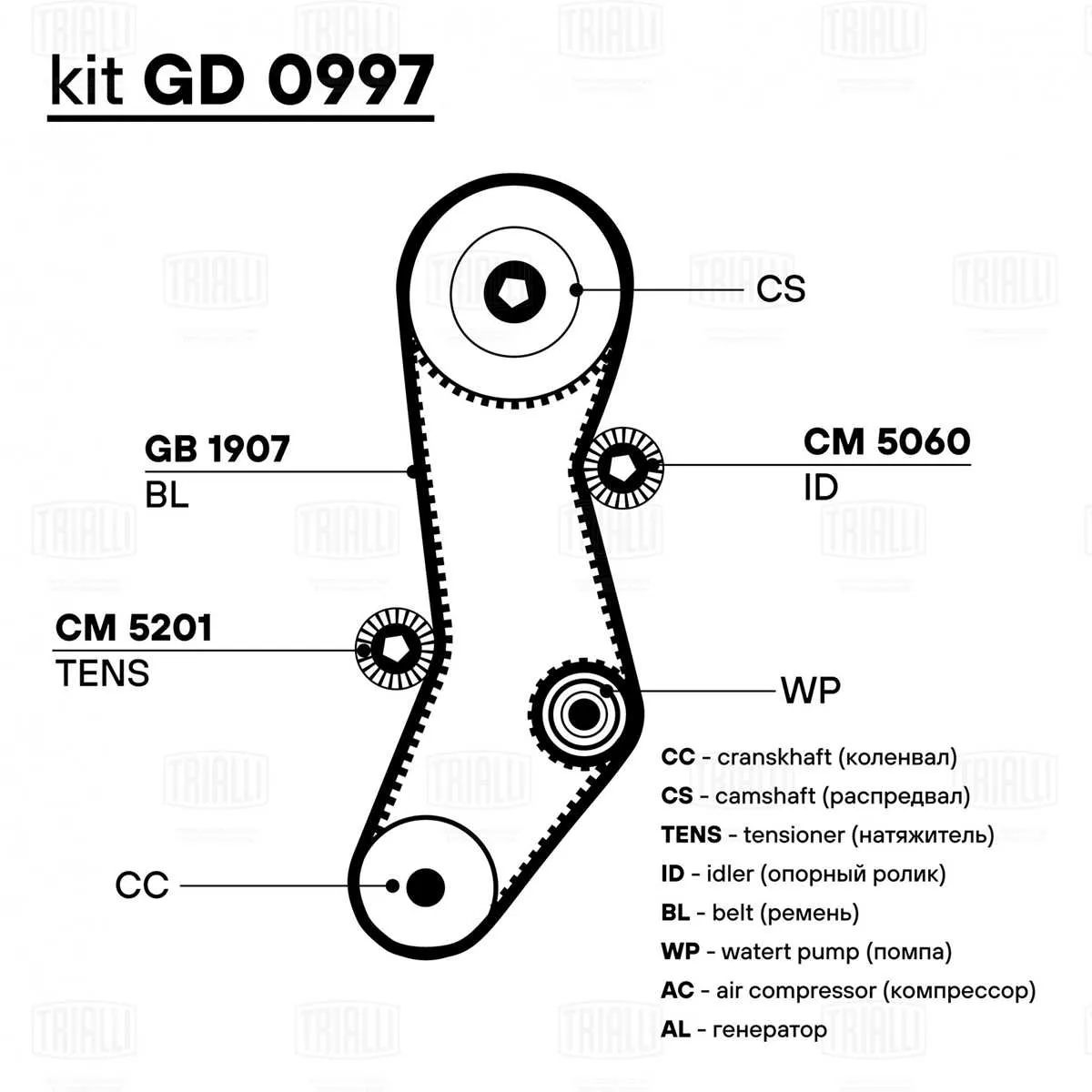
When replacing or inspecting the serpentine system of your vehicle, it is crucial to ensure the proper routing of each component to avoid unnecessary wear and potential failures. A misaligned or incorrectly routed component can lead to the malfunction of critical engine parts, including the alternator, power steering pump, or air conditioning compressor. Follow the manufacturer’s specified routing sequence for accurate installation.
1. Identify the Key Components: Start by identifying the key elements in the system. Typically, the main components include the alternator, tensioner, water pump, air conditioning compressor, and power steering pump. Pay close attention to the position of the tensioner as it is often spring-loaded, allowing it to maintain the appropriate amount of slack in the loop.
2. Proper Routing and Installation: The installation starts by securing the largest pulley (often the crankshaft) as the primary point. Ensure that the belt follows the proper sequence of smaller pulleys without excessive slack. It is important that the belt moves in a smooth, unbroken loop, without twisting or creating tension on any individual component.
3. Testing the Installation: Once the system is correctly routed, manually rotate the engine via the crankshaft pulley to ensure the belt runs smoothly across all pulleys. Check for any signs of irregular tension or noise, and ensure that each pulley is properly aligned with its corresponding component.
Correctly following these steps will help maintain the reliability of the system and reduce the risk of premature failure. Regular inspection and timely replacement of any damaged parts can save you from expensive repairs in the future.
Drive System Configuration
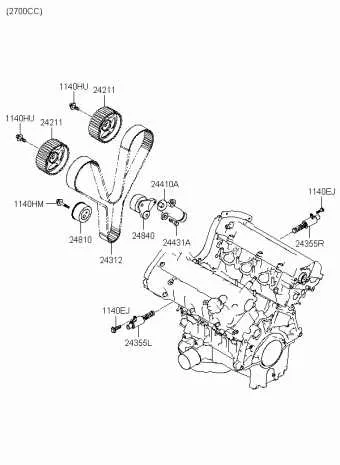
For proper engine performance, ensure all accessory pulleys are correctly aligned and the tension on the system is optimal. A loose or improperly routed mechanism can lead to slipping or failure, impacting key components such as the alternator, compressor, and power steering pump.
- Ensure the routing follows the manufacturer’s recommended layout, where the main crankshaft pulley drives the system, with each component in the correct sequential position.
- Use only high-quality components for replacement to maintain correct functionality and avoid premature wear or damage to other parts.
- Check the condition of the tensioners and pulleys regularly to ensure they are not worn or misaligned.
Before making replacements, verify the length and profile of the components to match the original specifications for proper fitment. This is crucial to avoid misalignment or inadequate tensioning.
- Inspect the routing for clearance, ensuring no components come into contact with surrounding parts, which could cause damage or operational issues.
- For a more efficient setup, consider replacing worn components such as idler pulleys and tensioners to restore proper function and extend the service life of the system.
In case of component failure, it is recommended to address the issue promptly to prevent further damage to the engine or related systems.
How to Read the 2007 Hyundai Santa Fe Belt Routing Diagram

Start by identifying the main components that the drive components interact with, such as the crankshaft pulley, alternator, air conditioning compressor, and power steering pump. Follow the path of the serpentine component, noting how it loops around each component. Pay close attention to the tensioner and idler pulleys, which maintain the appropriate tension and direction. The tensioner must be placed in the correct position to allow for smooth operation and prevent slippage.
Locate the specific grooves and notches in each pulley to match the correct routing pattern. Ensure that the ribbed side of the belt aligns with the grooved pulleys. Confirm the direction of the spin indicated on the diagram and make sure the belt follows the same direction to avoid improper function. This is crucial for the power transmission to all accessories.
Before reinstallation or replacement, double-check the overall path on the visual map, verifying the belt path aligns with each pulley’s markings. Remember that incorrect placement or routing can cause excessive wear, leading to premature failure. Refer to the vehicle’s maintenance guide for any specific notes regarding adjustments to the components or belt positioning, especially if there are newer updates or revisions.
Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing the Serpentine Belt

Start by ensuring the engine is turned off and the vehicle is on a stable, level surface. Disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent electrical accidents during the process.
Locate the tensioner pulley and use a ratchet or a wrench to relieve the tension. This will allow you to remove the existing drive component from the system. Take note of the routing path of the component before removing it, as proper installation depends on this information.
Carefully slide the component out of its position, making sure not to damage surrounding parts. Inspect the new component for any defects, ensuring it matches the required specifications for the vehicle.
Install the new component by aligning it along the same path. Ensure it fits properly into the grooves and securely onto the pulleys. Once in place, use the ratchet or wrench to tighten the tensioner back into position, applying the correct tension to avoid over-tightening.
Double-check the routing one more time before starting the engine. Turn on the vehicle and observe the operation, ensuring everything runs smoothly without any unusual noises or friction.
If everything looks good, reconnect the negative terminal of the battery and test the vehicle again for functionality before completing the task.
Common Issues with the Belt System in 2007 Hyundai Santa Fe
Ensure proper tension and alignment when replacing or inspecting any components in the drive system. A misaligned or overly tight component can result in premature wear or failure of related parts.
One common issue involves the wear of the tensioner pulley. Over time, it can lose its ability to maintain the correct pressure on the driving components, leading to slippage or unusual noise. Regular inspection of the tensioner’s functionality can help identify issues before they cause damage to the system.
Another problem to look out for is cracked or worn-out pulleys. Any damage to pulleys can cause instability, which might lead to the improper functioning of the entire assembly. Replace damaged pulleys promptly to avoid further complications.
Friction between parts may also result in premature wear of the auxiliary components. Ensure that there are no foreign objects causing obstruction between the pulleys and surrounding parts. Lubrication of moving components will reduce wear and extend the lifespan of the system.
Finally, the age of the driving components should not be overlooked. If the system has been in use for an extended period, even with proper maintenance, it may begin to show signs of degradation. Plan for periodic replacements of these parts as part of a long-term maintenance schedule.