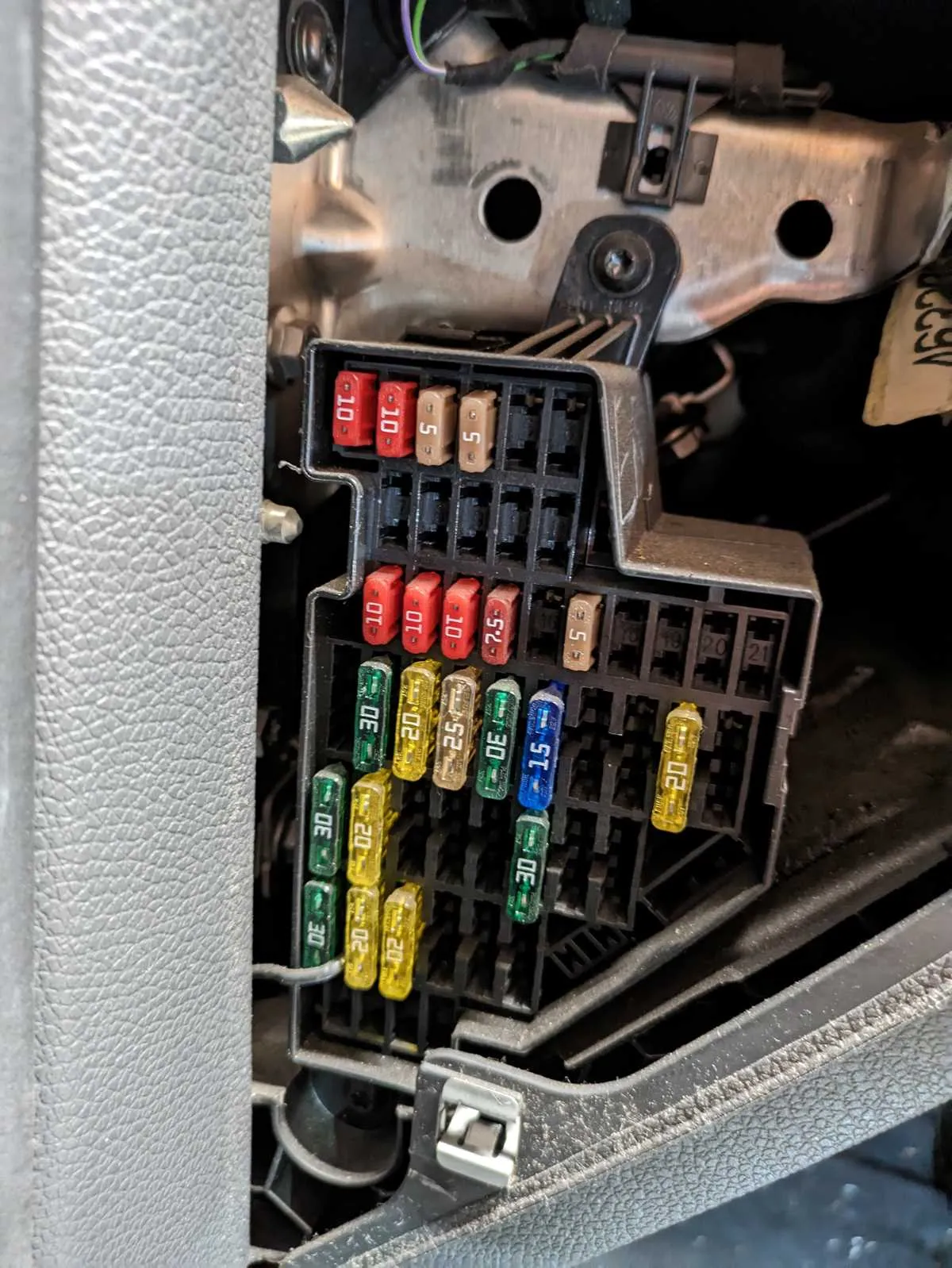
If you’re having issues with the electrical system in your vehicle, start by checking the component panel. It is the most common area for troubleshooting problems related to power distribution and circuit malfunctions. Whether you’re dealing with malfunctioning lights, non-working accessories, or a complete power failure, locating the specific panel and understanding its connections will help resolve the issue faster.
First, identify the location of the power distribution area inside your vehicle. In most cases, this panel is found beneath the dashboard or under the hood. Refer to the owner’s manual for precise details on where to find this section, as the position can vary based on the model and year.
Once you’ve located the panel, check for a legend or guide that explains the function of each connection. Each terminal corresponds to specific electrical components like the engine, interior lights, or climate control systems. A clear understanding of these associations helps when replacing or inspecting faulty connections.
Keep track of fuse ratings to avoid installing incorrect replacements. Overpowering a circuit can cause further damage to electrical components, so always match the rating provided in the reference guide. If you’re unsure about the amperage, it’s safest to consult a professional for guidance.
For more detailed troubleshooting, use the reference chart for pin configurations and component identification to pinpoint which circuit is malfunctioning. This approach saves time and ensures that no part of the system is overlooked when diagnosing faults.
Electrical Layout Overview
For quick access to the vehicle’s electrical components, always check the under-hood panel and the interior location. You’ll find the necessary relays and circuits clearly marked for various systems like lighting, HVAC, and ignition. Each area will have its own set of connections and will follow a color-coded standard to help you identify the appropriate fuses and relays for specific parts of the vehicle.
Start by verifying the connection status of the main terminal in the engine compartment, which supplies power to critical functions. For interior elements, inspect the central cabin setup near the driver’s side panel to troubleshoot any interior electrical concerns like the radio or power windows.
When replacing, ensure that you are using the exact amperage rating indicated in the manual to avoid overloading circuits. Different components may require higher or lower ratings, and using the wrong type can lead to further electrical issues or malfunctions. Keep a set of spares handy for quick replacements during a malfunction.
Be aware of the possibility of faulty connections, especially in areas exposed to heat and moisture, which can cause corrosion over time. Regularly check the terminals for any signs of wear or discoloration, as this could indicate an underlying issue that might require professional attention.
How to Locate the Fuse Box in Your Vehicle
Start by checking the driver’s side dashboard. Look to the left of the steering wheel near the door frame. There should be a small panel that can be removed to reveal the electrical components inside.
If you’re unable to find it there, open the hood and inspect the engine compartment. Near the battery, there’s often a larger enclosure with a cover. This is another common location for power distribution components.
Lastly, check the trunk area. In some models, you’ll find a compartment on the right side, behind a panel. It’s typically near the spare tire or along the side wall.
Understanding the Layout and Its Components
To ensure efficient operation, it’s important to recognize the placement and function of each component in your vehicle’s electrical system. Here’s what you need to know:
- Relays: Control high-power circuits by using a low-power signal. They are essential for systems like headlights, horn, and air conditioning.
- Electrical Connectors: These provide a secure interface for wiring, ensuring stable connections for various components.
- Fuses: Protect individual circuits by breaking the connection when there’s an overload, preventing damage to sensitive components.
- Power Distribution: The layout directs electrical current to different components, helping to prevent overloading and ensure proper function.
Here are some tips for troubleshooting:
- Check for any blown fuses. A blown fuse often indicates an issue with the associated circuit.
- Inspect the relays for damage, as these components control multiple systems in your car.
- Ensure connectors are free of corrosion to maintain good conductivity.
- Use a multimeter to measure the voltage and current flow to identify issues with power distribution.
Understanding these elements can simplify diagnostics and help prevent electrical failures in the future. Be sure to consult your vehicle’s specific manual for exact placement details of these components.
Common Electrical Issues and How to Troubleshoot Them
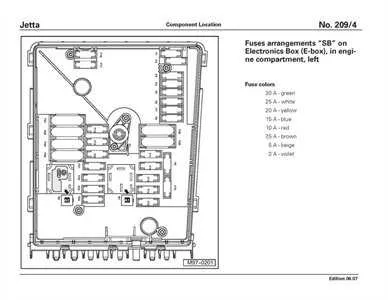
When experiencing power loss or malfunctioning components, the first step is to check the main electrical panel under the dashboard. A blown relay or tripped circuit is often the root cause. Inspect each connector carefully for signs of damage or corrosion. If any terminal appears worn out or rusty, clean it with a wire brush and re-tighten it securely.
Identifying a Faulty Relay
A non-functioning component often points to a faulty relay. To verify this, use a multimeter to test the continuity of the relay in question. If the reading shows no continuity, replace the relay with one of the same rating and specifications.
Tripped Circuit Breakers
In some cases, a circuit breaker may trip due to excessive power draw. Reset the breaker by flipping it to the off position, then back to on. If the issue persists, check for wiring issues such as a short circuit, particularly in the affected area.
Corroded Terminals
Corrosion is a common culprit behind electrical failures. Use a contact cleaner and a soft brush to remove any corrosion from terminals. Always ensure that the connections are tight and free from any foreign material that may cause a short.
Loose or Broken Wires
Inspect the wiring thoroughly. If any wires are loose or show signs of fraying, it is essential to repair or replace them immediately. Ensure that all wires are properly secured to their respective terminals and connectors.
Blown Fuses
If a component stops working, a blown fuse could be the cause. Always verify the fuse rating and replace it with a new one of the same type and amperage. Never bypass a fuse, as this can lead to more severe damage.
Testing Electrical Components
To test whether an electrical part is functioning, use a multimeter to check for voltage at the connectors. If no voltage is present, trace the wires back to their source, ensuring there are no breaks or interruptions along the path.