For optimal engine performance, ensuring the proper function of the thermal regulation components is essential. Regularly inspect components like the radiator, water pump, thermostats, and coolant hoses to maintain efficient heat dissipation. A detailed overview of fluid circulation and component interconnectivity helps prevent overheating and ensures the longevity of your engine.
Check the coolant circulation path: Coolant fluid should travel seamlessly from the radiator through the engine block, absorbing heat before returning to the radiator. If any parts of this circuit experience blockages or leaks, it may lead to excessive engine temperatures, reducing efficiency.
Be sure to monitor the thermostat operation: It plays a key role in regulating fluid flow. A malfunctioning thermostat can either cause the engine to overheat or not warm up properly, compromising fuel efficiency and engine health.
Regular inspections of the fan and water pump should be conducted. These components ensure consistent fluid flow and heat dissipation when the vehicle is in motion or idling. Any irregularity could result in inconsistent engine temperatures, leading to potential damage over time.
Engine Heat Management Layout
Ensure proper coolant flow by checking the radiator, water pump, and thermostat regularly. Inspect the hoses for any cracks or leaks that could disrupt fluid circulation. Make sure the coolant is at the right level and of the correct type to maintain optimal engine temperature.
Verify the function of the radiator fan and the shroud, as any obstruction can lead to overheating. The radiator cap should be tightly sealed to maintain pressure and prevent fluid loss. Regularly flush the radiator to remove debris or sediment that may hinder heat dissipation.
Pay attention to the coolant reservoir to avoid overfilling, which can lead to excess pressure. Ensure the water pump operates efficiently by listening for unusual sounds and checking for leaks. The thermostat must open and close at the correct temperatures to regulate engine heat properly.
Examine the coolant temperature sensor to ensure accurate readings for proper engine control management. Use quality fluids and parts when replacing any components to guarantee the longevity and efficiency of the heat dissipation process.
Understanding the Main Components of the Engine Temperature Regulation in 2017 Powertrain
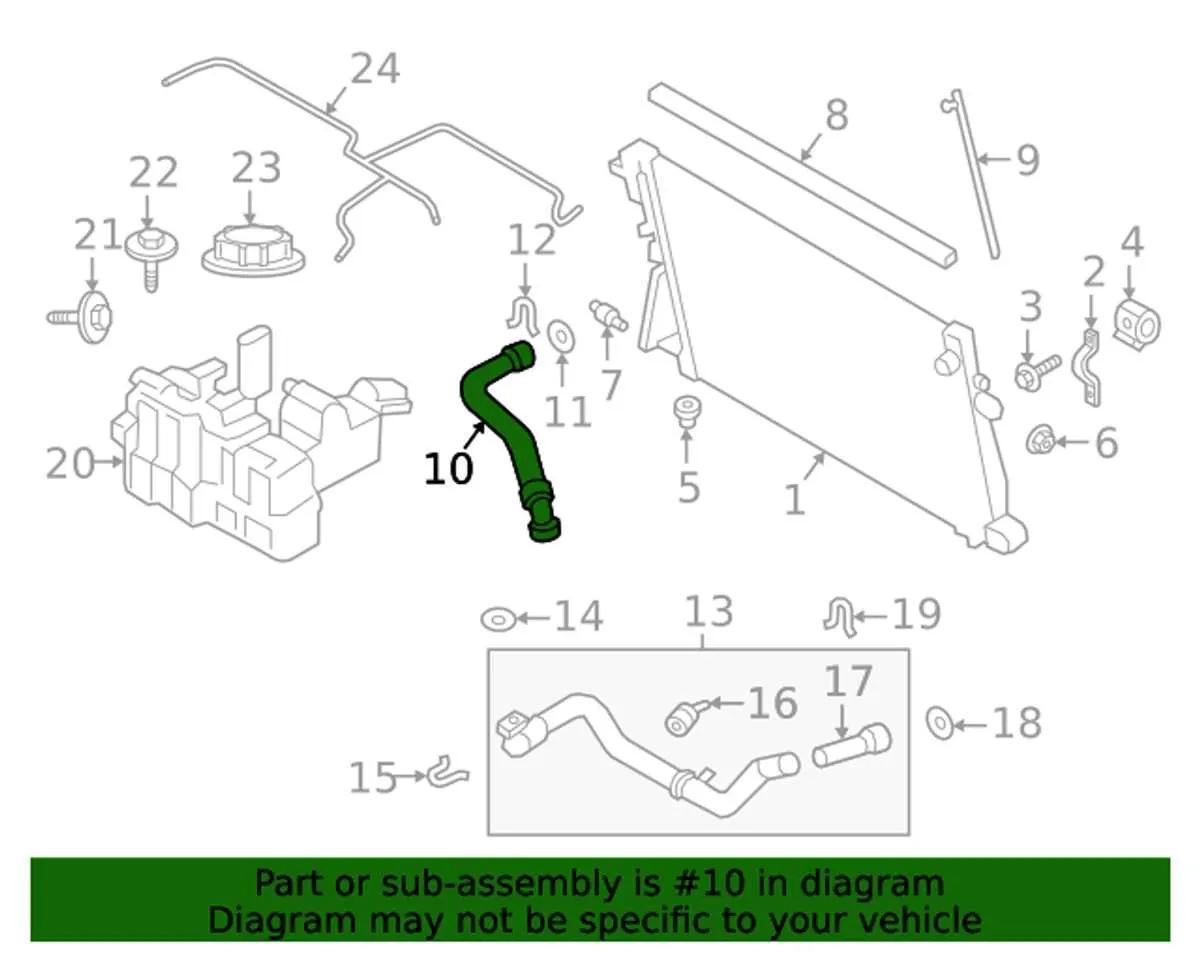
To ensure optimal engine performance and longevity, it’s critical to grasp the function of key elements in the thermal management unit. Below is a detailed look at each component and its role in maintaining appropriate operating temperatures.
The primary unit for managing excess heat is the radiator. This part plays a pivotal role in releasing heat absorbed by the engine. A high-efficiency radiator is essential for preventing overheating, especially in high-load conditions.
Another crucial element is the thermostat. This valve controls coolant flow to ensure that the engine reaches the optimal temperature quickly and prevents excessive heat buildup. A malfunctioning thermostat can cause the engine to run too cold or too hot, compromising performance and efficiency.
The water pump ensures that the fluid circulates properly throughout the engine and radiator. It’s vital to ensure that the pump is functioning well to maintain consistent cooling and prevent the system from becoming air-locked, which would impair its efficiency.
The hoses connecting various components carry the liquid to and from critical areas. Inspecting hoses for wear and tear can prevent leaks and other cooling inefficiencies. It’s important to replace these parts as they age to avoid sudden failures.
| Component | Function | Maintenance Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Radiator | Absorbs heat from engine and releases it into the environment. | Check for leaks and debris regularly. Flush periodically to maintain efficiency. |
| Thermostat | Regulates coolant flow to maintain optimal engine temperature. | Replace if engine fluctuates between hot and cold temperatures unexpectedly. |
| Water Pump | Pumps coolant through the engine and radiator for heat dissipation. | Inspect for leaks and listen for unusual noises. Replace if inefficient. |
| Hoses | Transport coolant between components. | Check for cracks or wear and replace as necessary to prevent leaks. |
Regular inspection and maintenance of these components are necessary to prevent overheating, ensure longevity, and maintain performance. Addressing small issues early can prevent costly repairs in the future.
How to Diagnose Engine Temperature Regulation Problems
To effectively identify issues related to temperature control in your vehicle, start by checking the coolant fluid levels. Low fluid can indicate a leak or poor circulation. Ensure the reservoir is filled to the appropriate level, as outlined in your vehicle’s manual.
If the engine overheats or takes longer than usual to reach normal operating temperature, inspect the radiator for blockages. Dirt, debris, or corrosion can reduce airflow, which compromises heat dissipation. Clean the exterior of the radiator, checking for any visual signs of damage or leaks.
- Thermostat malfunction: A faulty thermostat can prevent the engine from reaching optimal operating temperature. Test it by measuring the coolant temperature as the engine warms up. If the temperature doesn’t rise steadily, the thermostat may be stuck open or closed.
- Water pump inspection: A malfunctioning pump can reduce the circulation of coolant. Look for leaks around the water pump area or unusual noises during operation. If there’s a loss of fluid or visible wear, the pump may need replacement.
- Fan operation: Check if the cooling fan operates properly when the temperature gauge rises. If it doesn’t engage, it could be an issue with the fan motor, the fan clutch, or the associated relay. Test the fan functionality and replace any faulty parts.
Next, check the radiator cap. A defective cap can cause pressure loss, leading to overheating. Replace the cap if it appears damaged or is not sealing correctly.
- Leaks: Carefully inspect hoses for signs of leakage, cracks, or bulging. Pay attention to areas around hose connections and clamps, ensuring they are tight and secure.
- Coolant temperature sensor: A malfunctioning sensor can send incorrect readings to the engine control unit. Verify the sensor’s accuracy with a diagnostic tool and replace if necessary.
Lastly, perform a pressure test on the entire cooling circuit. This can help detect any hidden leaks or weaknesses that may not be visible during a visual inspection.
Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing Cooling System Parts
1. Start with Disconnecting the Battery: Before working on any engine components, disconnect the negative terminal to avoid electrical hazards. This step is critical for your safety.
2. Drain the Fluids: Use a drain pan to collect any antifreeze or coolant. Open the radiator valve or lower hose to completely empty the reservoir. Proper disposal of fluids is essential to protect the environment.
3. Remove the Old Radiator: Loosen and detach the radiator hoses. Depending on your setup, you may also need to unbolt the radiator mounts. Lift out the old radiator carefully to prevent damage to surrounding parts.
4. Inspect the Water Pump: Check for leaks or excessive wear. A failing pump can cause poor circulation and overheating. If it’s damaged, remove the bolts securing it and replace it with a new one. Ensure that the new unit is properly aligned and tightened.
5. Replace the Thermostat: The thermostat regulates fluid flow and keeps temperatures in check. If your engine has trouble reaching optimal operating temperature or overheats, it’s time for a replacement. Remove the housing and install a new thermostat, making sure the gasket is intact.
6. Inspect and Replace Hoses: Check all hoses for signs of cracking or wear. Replace any that appear compromised. Use high-quality, heat-resistant hoses to avoid future issues. Tighten the clamps securely to prevent leaks.
7. Check and Replace the Radiator Cap: The radiator cap maintains pressure within the system. A faulty cap can lead to overheating. Replace it with a new one to maintain the correct pressure.
8. Install the New Components: Position the new radiator and secure it with bolts. Attach all hoses and ensure proper alignment. Double-check the water pump and thermostat installations. Tighten all fasteners to the manufacturer’s specifications.
9. Refill with Fluid: Fill the reservoir with the recommended antifreeze mixture. Use a funnel to avoid spills. Don’t forget to check for air pockets during the process–burp the system by running the engine for a short time while monitoring fluid levels.
10. Perform a Test Run: Start the engine and allow it to warm up. Keep an eye on the temperature gauge to ensure the system is functioning properly. Look for leaks around the hoses, pump, and radiator, and confirm that the fluid levels remain stable.
11. Final Checks: After the engine has cooled down, check the fluid levels again and top off if necessary. Also, inspect all components one more time to ensure everything is secured.