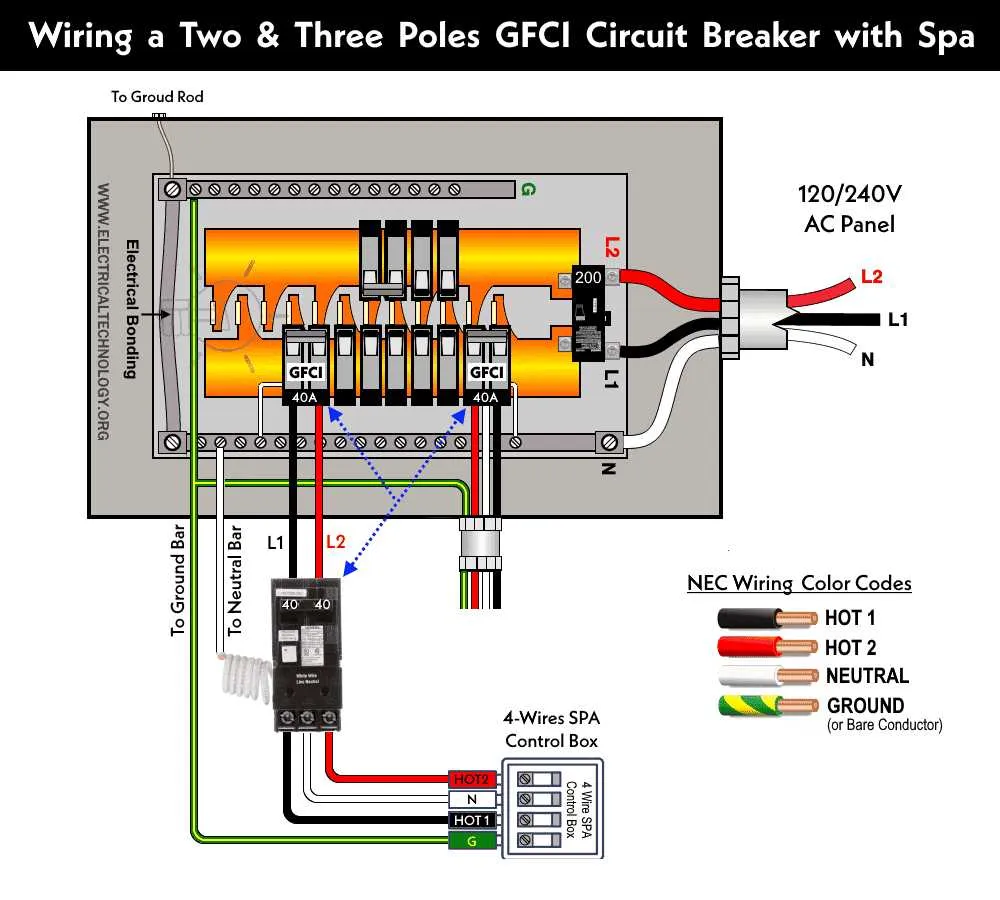
When installing a 50-amp electrical circuit, ensure you’re using the right gauge of wire and properly connecting it to the electrical panel. The correct wire size for this setup is typically 6 AWG copper or 4 AWG aluminum, depending on the distance from the power source. It’s critical to use appropriate connectors and secure each wire to avoid any risk of overheating or damage.
Start by identifying the power supply and ensuring it matches the required voltage for your setup. For most applications, this will be 240 volts. Then, attach the live wires to the terminals that correspond to your load requirements. The neutral wire should be routed separately to the neutral bus bar in the panel, while the ground wire connects to the ground bar.
Before you begin, turn off all power to the system to avoid any electrical shock. Ensure all connections are tight and properly insulated. It’s essential to check the connection for integrity before powering up the system to ensure a safe, efficient operation.
Important: Always double-check local electrical codes before proceeding with installation. If unsure, consult a licensed electrician to guarantee compliance with regulations and to prevent potential hazards.
50 Amp Electrical Panel Connection Guide
Ensure that the circuit is connected with a wire capable of handling at least 6 AWG copper or 4 AWG aluminum. This will prevent overheating and provide adequate power flow.
Start by linking the live wire to the top terminal of the switch. The neutral wire should be connected to the separate neutral bar, ensuring it doesn’t touch the live terminal. Grounding is crucial–attach the ground wire to the metal box or grounding bar of the panel.
Double-check the connections before securing everything. Tighten the terminals firmly to avoid loose contacts that could cause power interruptions or sparks. Use a torque wrench for accuracy if available.
For optimal safety, verify that all components are rated for the voltage and current you plan to use. Consider using a lockout/tagout procedure while working to prevent accidental energization.
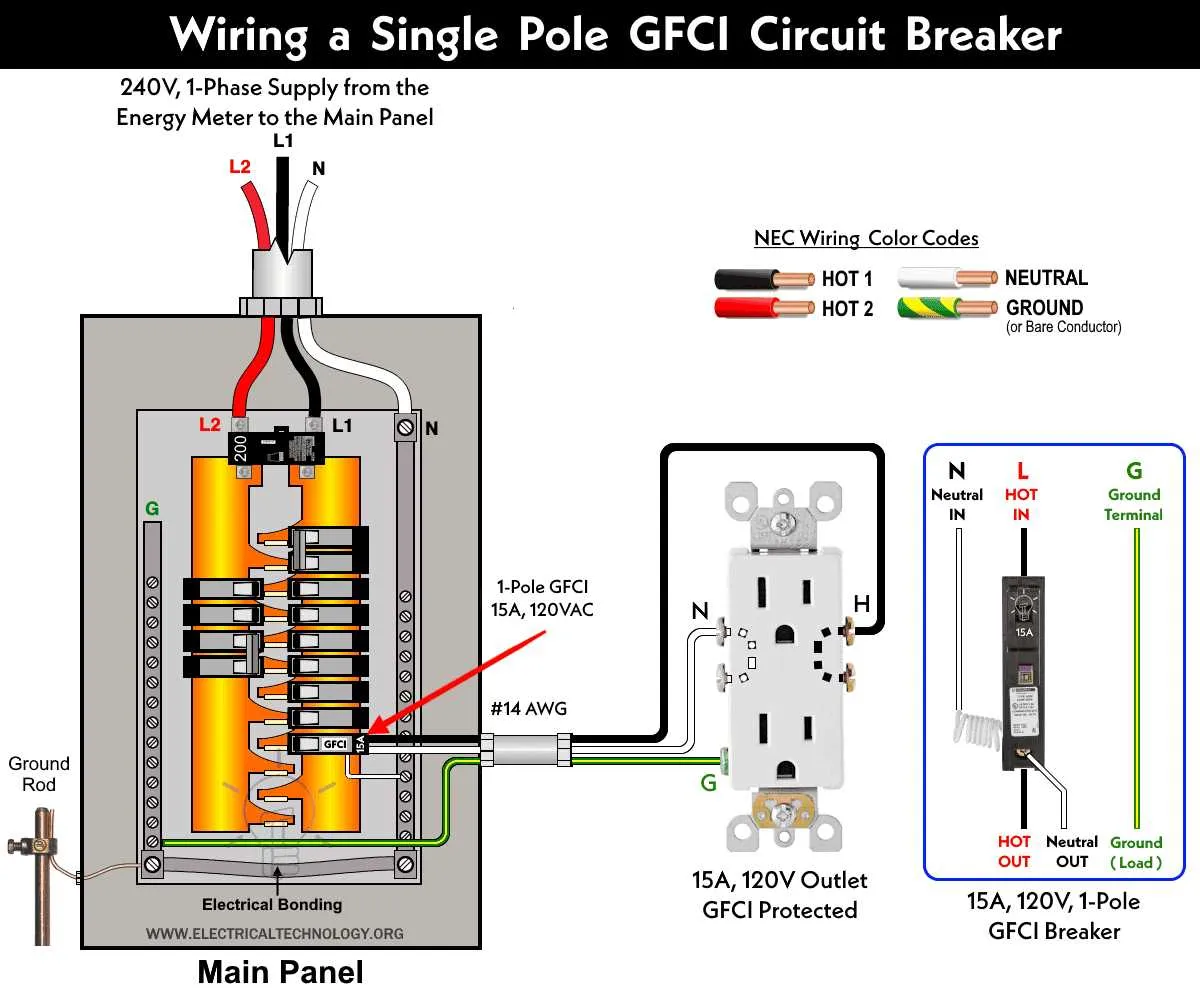
How to Properly Wire a 50 Amp Breaker in a Panel
Start by turning off the main power supply to ensure safety during installation. Use a voltage tester to confirm no current is present in the panel.
Choose a 6 AWG copper or 4 AWG aluminum conductor for the connection. Ensure the wire insulation is rated for the expected voltage and temperature. Cut the wire to an appropriate length, allowing enough slack for secure connections and future adjustments.
Connect the black (hot) wire to the terminal on the device, securing it tightly with a screwdriver. Use the torque specifications from the manufacturer to avoid over-tightening.
Attach the white (neutral) wire to the neutral bus bar in the panel. Ensure the connection is firm and the wire is adequately stripped at the end to make good contact.
Connect the green or bare (ground) wire to the ground bus bar. This wire should be free of any damage, and all exposed metal should be securely grounded.
After the connections are made, check the tightness of all terminals to prevent any potential loosening during operation. Use a torque wrench if required by the manufacturer.
Once everything is connected, close the panel cover and turn the power back on. Test the system with a multimeter to ensure proper function.
Choosing the Right Wire Gauge for 50 Amp Circuit
For circuits rated for 50 units of electrical capacity, use 6 AWG copper or 4 AWG aluminum conductor. This ensures safe operation and prevents overheating. Copper wires handle the load more efficiently, whereas aluminum requires a thicker gauge to provide the same performance.
Always select wire that matches the total load demand and installation environment. For instance, if the wiring will run through conduit or be exposed to high temperatures, consider using a higher-rated insulation type, such as THHN, to improve safety and longevity.
Ensure that connections and terminals are rated for the selected wire gauge. Undersized wires can lead to excessive heating, increasing the risk of electrical fires or damage to appliances.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Installing a 50-Amp Circuit
Ensure correct conductor size for your setup. Using wires that are too thin can lead to overheating and potential fire hazards. A minimum of 6 AWG copper or 4 AWG aluminum is recommended for this level of power flow.
Do not ignore the correct positioning of the connection terminals. Improper tightening of the terminals can result in loose connections, causing arcing and heat buildup over time.
- Check that the wire insulation is intact before making any connections.
- Ensure all copper wire ends are properly stripped before insertion.
Incorrectly choosing the connection type can cause major issues. Always opt for the manufacturer’s recommended configuration to avoid excessive heat and improper power distribution.
- Double-check the load requirements and match them precisely to the breaker’s capacity.
- Avoid overloading circuits by maintaining a proper balance of the total electrical load.
Do not skip the grounding procedure. Grounding the setup correctly prevents electrical shock risks and ensures the system operates safely during faults.
Finally, test the installation thoroughly before use. Running a quick check can identify issues that could otherwise go unnoticed, such as faulty connections or improper configurations.