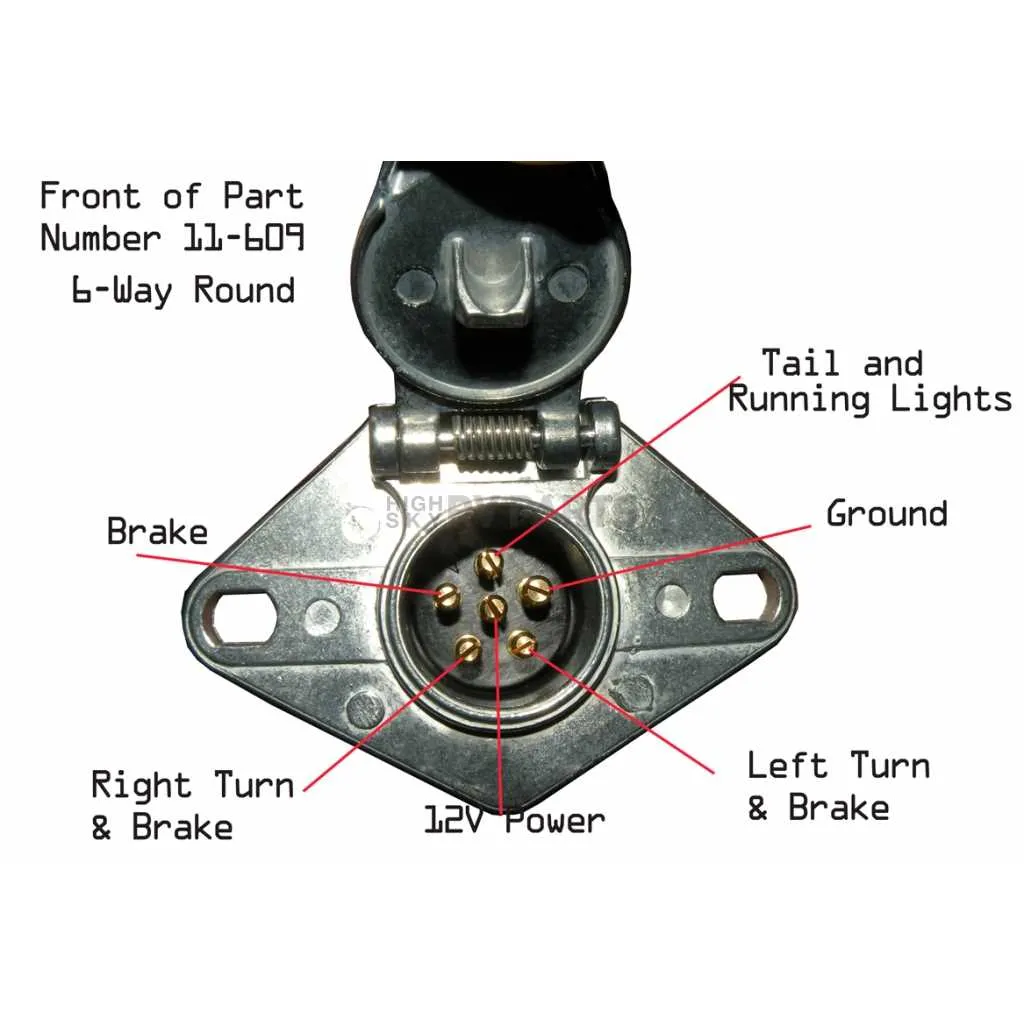
If you’re planning to tow or connect an electrical system, ensure that you understand the wiring for a six-pin setup. This configuration is essential for transmitting signals such as brake lights, turn signals, and electric braking functions from your vehicle to the towed unit. Proper wiring prevents malfunction and reduces risks during operation. Accurate pin mapping is key to achieving a safe and effective connection.
The six-pole setup typically involves specific connections for power, ground, and lighting functions. The standard arrangement is usually designed to ensure a stable flow of electrical signals for different purposes, including the operation of tail lights and brake indicators. Consult the manual for exact pin locations and corresponding color codes to avoid confusion during installation.
For those unfamiliar with the process, verifying wire placement and ensuring a secure, corrosion-resistant connection is vital. You can use a multimeter to test continuity and confirm that each wire is appropriately connected to its respective pin. This step minimizes the chances of electrical faults while ensuring compatibility across different vehicles and units.
6-Pin Wiring Overview
For efficient and secure electrical connections between your vehicle and external equipment, follow this detailed pin configuration. Proper wiring ensures reliable operation and prevents damage to circuits.
The first pin should handle the ground function, providing a safe return path for the electrical current. This connection is essential for avoiding electrical surges or failures.
The second pin is for the left turn signal. It controls the activation of the left indicator light and should be connected to the appropriate vehicle system. Incorrect wiring can lead to malfunctioning signals.
Next, the third pin is assigned to the right turn signal. Similar to the left signal, it controls the right indicator. Ensure the connection is tight and free from corrosion to maintain visibility.
The fourth pin carries the brake lights signal. It’s vital for activating the brake lamps of the connected device. A consistent signal is necessary for ensuring safety during braking.
For powering auxiliary devices, the fifth pin provides 12V power to the external unit. This is typically used for powering lights or electric systems. Ensure the wiring is rated for the required current to avoid overheating.
Lastly, the sixth pin delivers the reverse lights signal. It activates reverse lighting on the external unit when the vehicle shifts into reverse gear. Proper connection ensures visibility during reversing maneuvers.
Be sure to verify each connection before usage, testing for continuity and proper grounding. Regular maintenance and inspection of the wiring will ensure long-term reliability.
Understanding the Pinout Configuration for a 6-Wire Plug
To correctly wire a 6-pin plug, follow this precise pinout configuration:
- Pin 1: Ground (White) – This is the common ground wire, typically color-coded white. It connects to the chassis of both the vehicle and the attached equipment.
- Pin 2: Left Turn Signal (Yellow) – The yellow wire controls the left turn signal, ensuring proper lighting functionality when turning left.
- Pin 3: Right Turn Signal (Green) – The green wire is responsible for the right turn signal, enabling the correct indicator to light up during a right turn.
- Pin 4: Tail Lights (Brown) – This pin powers the running lights, providing visibility for the equipment during low light conditions.
- Pin 5: Electric Brakes (Blue) – The blue wire is crucial for electric brake operation, allowing the vehicle’s braking system to engage and decelerate the attached load.
- Pin 6: 12V Power (Red) – The red wire supplies 12V power to auxiliary equipment, such as charging batteries or powering an electric winch.
Ensure each pin is correctly wired to avoid malfunction. A reliable connection will guarantee smooth operation of all necessary functions during towing.
How to Wire a 6-Pin Plug: Step-by-Step Guide
1. Prepare the Cables – Begin by stripping the insulation from the ends of your wires. Expose about 1 inch of copper on each wire to ensure a solid connection with the terminals.
2. Identify the Pins – Refer to the manufacturer’s color guide to determine the correct order for each wire. Typically, you’ll have a combination of white (ground), black (brake), yellow (left turn signal), green (right turn signal), brown (tail light), and blue (electric brake).
3. Connect the Wires – Insert each wire into the appropriate pin hole and tighten it securely. For a strong connection, use a crimping tool or screw terminal to attach the wires to the metal terminals inside the plug.
4. Secure the Wires – Ensure all wires are tightly fastened. If needed, use a small amount of electrical tape to prevent movement and to avoid any potential short circuits.
5. Test the Connections – After wiring, connect the plug to your vehicle’s socket and check each function, such as brake lights, turn signals, and tail lights. Verify everything is working as intended before use.
6. Final Check – Double-check for any exposed wires or loose connections. Ensure that all components are insulated and securely positioned to avoid interference while driving.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting with 6-Pin Electrical Systems
Check for corrosion on the pins and sockets. Corrosion often causes poor electrical contact, leading to malfunctions. Use a wire brush or electrical contact cleaner to remove it. After cleaning, apply dielectric grease to prevent future buildup.
If lights aren’t working, test the fuse for the system. A blown fuse will disrupt the flow of power to the lighting circuit. Replace the fuse with the appropriate amperage to restore functionality.
Ensure the wiring is secure and not damaged. Inspect the cable for cuts, abrasions, or fraying, which can lead to shorts or disconnected circuits. If the wire is compromised, replace it with a similar gauge and length.
Verify that the power is reaching the correct pins. Use a multimeter to check for continuity across the contacts. If there is no voltage, the issue may be a malfunctioning power source or a faulty wire connection.
Double-check the ground connection. A loose or broken ground can cause erratic performance, including intermittent or no light operation. Tighten or replace the ground wire as needed to restore proper function.
If certain functions are not activating, check for crossed wires or miswiring. Refer to the manufacturer’s guide for the correct pin configuration. Incorrect wiring can lead to malfunctioning circuits, such as the brake light being linked to the turn signal.
Test the system under load conditions. Sometimes, an issue only becomes apparent when the lights or brakes are in use. By checking the system while operating the connected vehicle, you can identify whether the problem is intermittent or constant.