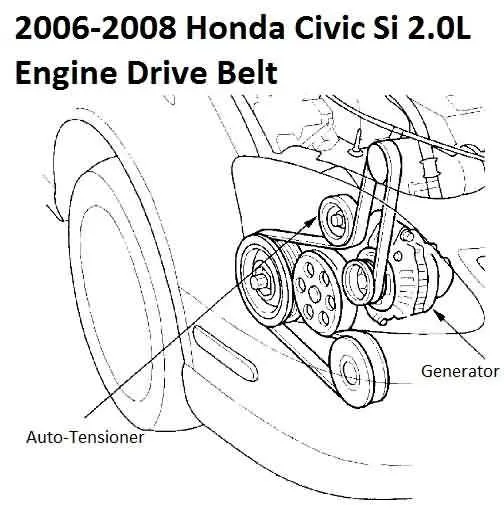
Refer directly to the detailed schematic for the serpentine routing in this model year midsize sedan to ensure accurate belt placement and tension. Understanding the exact path of the multi-ribbed accessory loop helps prevent premature wear and guarantees optimal performance of the alternator, power steering, and air conditioning systems.
Key points include correct alignment over tensioners and pulleys, as well as proper sequencing of the auxiliary loops. Use the factory-recommended reference to avoid misrouting that can lead to slippage or noise issues.
Visual aids for this configuration clearly indicate the position of idler wheels, tensioning devices, and the crankshaft pulley, enabling precise reassembly or replacement without guesswork. Accurate mapping is essential when performing maintenance or diagnosing related engine accessory problems.
Engine Pulley Layout for the 2009 Model
Locate the serpentine routing by following these steps to ensure proper installation and tension:
- The main drive loop starts at the crankshaft pulley, powering multiple components.
- It wraps around the alternator, providing electrical charge.
- Next, the tensioner pulley maintains correct tightness throughout the system.
- The routing continues over the water pump pulley to regulate coolant flow.
- It then passes the power steering pulley for hydraulic assistance.
- Lastly, the air conditioning compressor pulley completes the circuit.
Use the following tips to verify the alignment and tension:
- Inspect all grooves for wear or damage before fitting the new loop.
- Adjust the tensioner arm to eliminate slack but avoid over-tightening.
- Ensure each pulley spins freely without wobble or noise.
- Refer to the vehicle’s service manual for torque specifications on tensioner bolts.
- Double-check the routing path matches the outlined pulley sequence to prevent malfunction.
Locating and Identifying Each Belt on the Engine

To locate the primary drive components on the engine, start by identifying the alternator and power steering pump. The long serpentine component runs over pulleys connected to both the alternator and the pump. Check the positioning of the water pump, which is typically driven by a separate component, located slightly lower. The air conditioning compressor is also connected by a distinct, shorter component. Pay attention to the tensioner pulley, a small round part designed to maintain the correct tension on the system, often located near the bottom of the engine. The auxiliary drive component, used for various accessories, is routed differently depending on the model.
Ensure the routing path is aligned with the engine’s specific configuration. The crankshaft pulley serves as the central point of movement, and from there, the power is distributed to the various components. Double-check each pulley for wear signs, as misalignment can cause premature wear on the drive system. Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines for the correct installation and maintenance of these components to avoid damage.
Step-by-Step Guide to Removing and Installing the Serpentine Belt
1. Prepare Your Tools: Gather a socket wrench, ratchet, and a torque wrench. A serpentine belt tool can also be helpful for tension adjustment.
2. Locate the Tensioner Pulley: Identify the tensioner that holds the belt in place. It usually requires a wrench or tool to relieve pressure.
3. Release Tension: Position your wrench or serpentine tool on the tensioner bolt and rotate it counterclockwise to release tension from the system. Once tension is relieved, remove the belt from the pulleys.
4. Inspect the Pulley System: Before installing the new component, check for any damage or wear on the pulleys. If necessary, replace any worn parts.
5. Install the New Serpentine Belt: Start by routing the new piece around the pulleys, following the correct path indicated by the pulley system. Ensure it’s securely seated in all grooves.
6. Reapply Tension: Using your wrench, rotate the tensioner back into position to secure the new component. Ensure it’s tightly in place.
7. Test Functionality: Start the engine and observe the belt’s operation. Listen for any unusual sounds and make sure the belt is running smoothly over all pulleys.
8. Final Check: After running the engine for a few minutes, recheck the tension on the belt. If necessary, adjust it again to ensure optimal operation.
Troubleshooting Common Belt Issues Using the Diagram
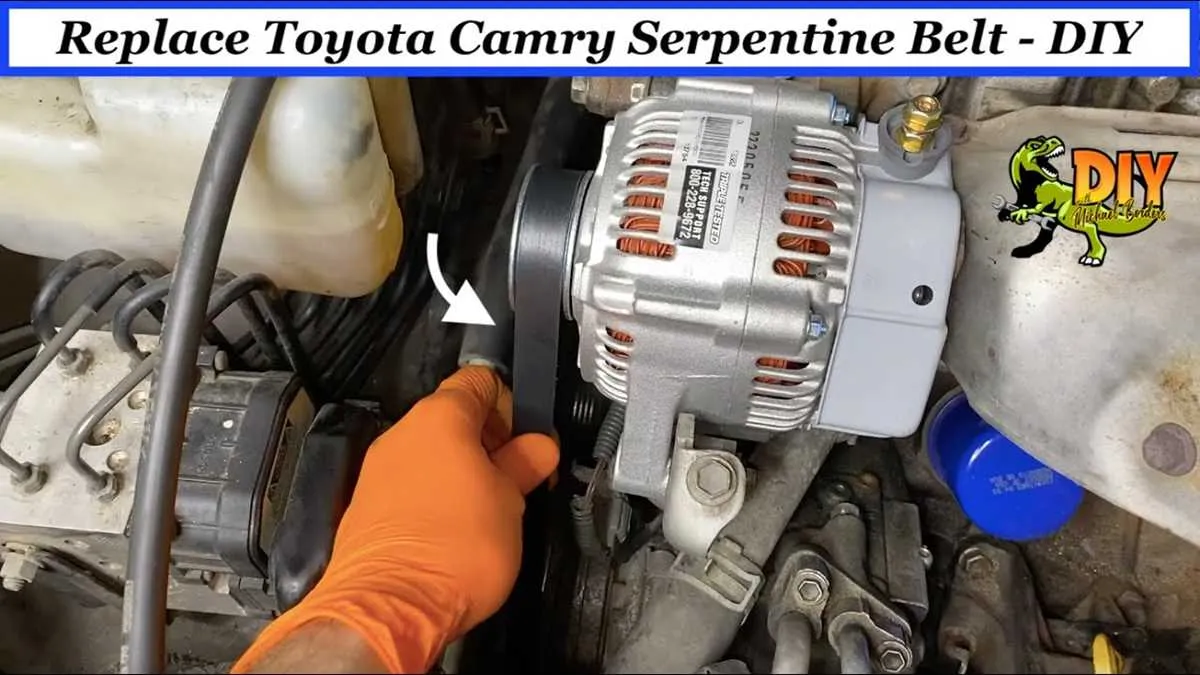
Check for proper tension: A loose or over-tightened component drive can cause slippage or excessive wear. Inspect the path as shown in the illustration to ensure each pulley is properly aligned and the components are tight enough to function optimally. Insufficient tension can lead to irregular operation of the engine accessories.
Examine wear patterns: Uneven or damaged grooves indicate poor alignment or an underlying issue with one of the pulleys. Follow the routing guide to confirm the positioning of each part. Pay close attention to any signs of friction or cracks along the length.
Identify unusual noise sources: Squealing sounds often signal friction between the pulley and the accessory, which may result from misalignment or incorrect routing. Listen for any unusual sounds while the engine is running and cross-reference with the alignment positions as indicated in the schematic.
Look for signs of contamination: Oil or coolant leaks can deteriorate the integrity of the drive system. Ensure that no fluids are dripping onto any of the components. Refer to the visual reference to check if any parts are near fluid lines or gaskets that may fail and contaminate the drive.
Inspect for cracks or tears: Any damage to the rubber or material along the serpentine should be addressed immediately. Refer to the outlined sections to ensure that no portion of the system is fraying or showing visible damage. Replace any affected parts as soon as they are identified.