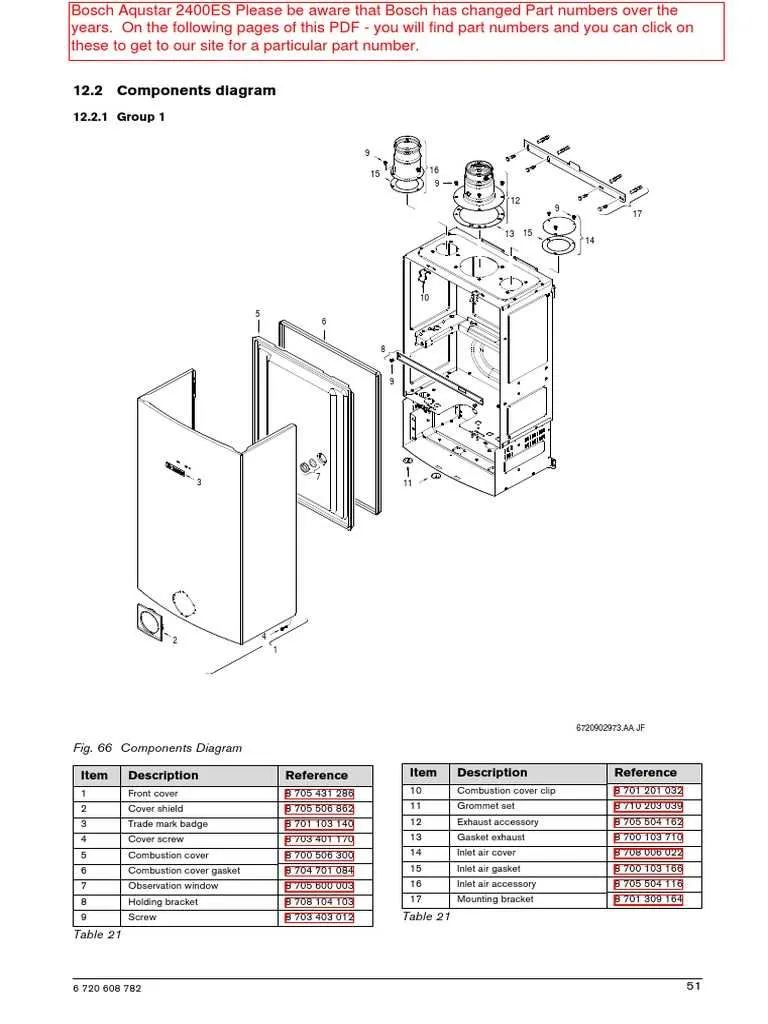
Understanding the key elements of a hot liquid system is crucial for anyone maintaining or repairing these units. First and foremost, ensure you are familiar with the heating element–the core component that converts electrical energy into heat. This is typically located at the bottom or the side of the appliance, depending on the model.
Next, check the thermal sensor or thermocouple, which regulates temperature by detecting changes in heat levels. A malfunctioning sensor can lead to overheating or underheating, rendering the system inefficient. It’s vital to regularly inspect this component to ensure optimal performance.
Additionally, the control valve serves as the system’s brain, regulating the flow and distribution of the heated substance. If this component is faulty, it can lead to irregular heat levels or complete system failure.
Finally, do not overlook the insulation materials around the storage tank. These layers help to retain heat, improving energy efficiency. Inadequate insulation can significantly increase energy consumption, making the system more costly to operate.
Key Components of a Home Heating System
To ensure optimal performance and longevity, it is crucial to understand the key elements of a home temperature control unit. Each component plays a specific role in converting energy into usable warmth, and malfunctioning parts can lead to inefficiency or system failure.
The primary element responsible for heat generation is the heating element itself, which directly converts electrical energy into thermal output. This unit must be monitored for wear, as mineral buildup can significantly reduce efficiency over time.
The temperature sensor is essential for maintaining the desired environment. It constantly measures the unit’s internal temperature and communicates with the control system to adjust the heat level accordingly.
The tank is another critical feature, as it stores the heated fluid. Its insulation is key in preventing heat loss, which directly impacts the energy efficiency of the system. Leaks or damage to this area can cause significant heat wastage.
Pressure relief valves are vital for safety, ensuring that excessive internal pressure is safely released, preventing dangerous situations. Regular inspection is recommended to avoid blockages or corrosion that may compromise their function.
The control unit allows for temperature adjustments and may include a digital interface for precise regulation. It also serves to monitor energy consumption and alert users to system anomalies.
Finally, the anode rod, often overlooked, plays a crucial role in preventing corrosion inside the tank by attracting corrosive particles before they can damage the inner lining.
Understanding the Role of Heating Elements in Water Heaters
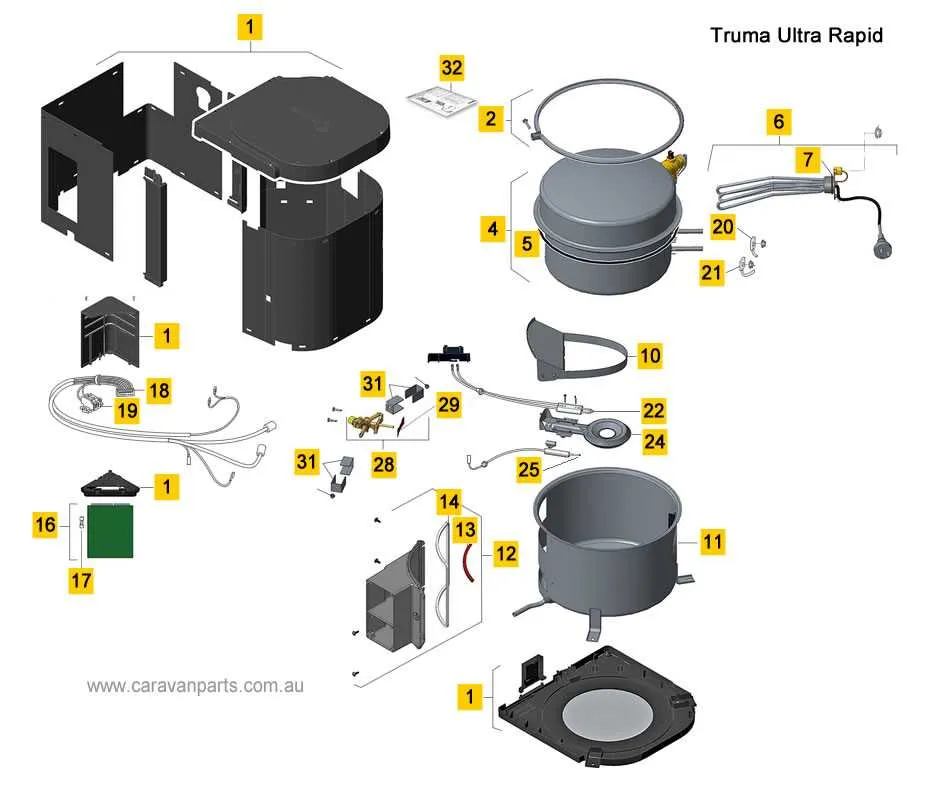
The heating elements are crucial components responsible for warming up liquids in any thermal system. Their performance directly impacts efficiency and energy consumption. Here’s what you need to know:
- Function: Heating elements convert electrical energy into heat, which is transferred to the liquid. This process occurs through resistance, where the element generates heat as current flows through it.
- Material: Most elements are made from materials like copper or stainless steel, chosen for their durability and high thermal conductivity.
- Types:
- Immersion elements: These are fully submerged in the liquid and provide direct heat transfer.
- Flange-mounted elements: Positioned on the exterior, these work by indirect heating and are more common in larger systems.
- Installation: Proper installation is essential for optimal function. Incorrect positioning or poor connections can lead to inefficient heating or even malfunction.
- Maintenance: Periodic inspection of the heating element is necessary to prevent mineral buildup, which can decrease performance and shorten lifespan.
For optimal performance, ensure the element is designed for your specific system’s requirements. Regularly check for signs of wear or corrosion and replace components when necessary to avoid disruptions in heating efficiency.
Identifying Key Safety Features in Heating System Components
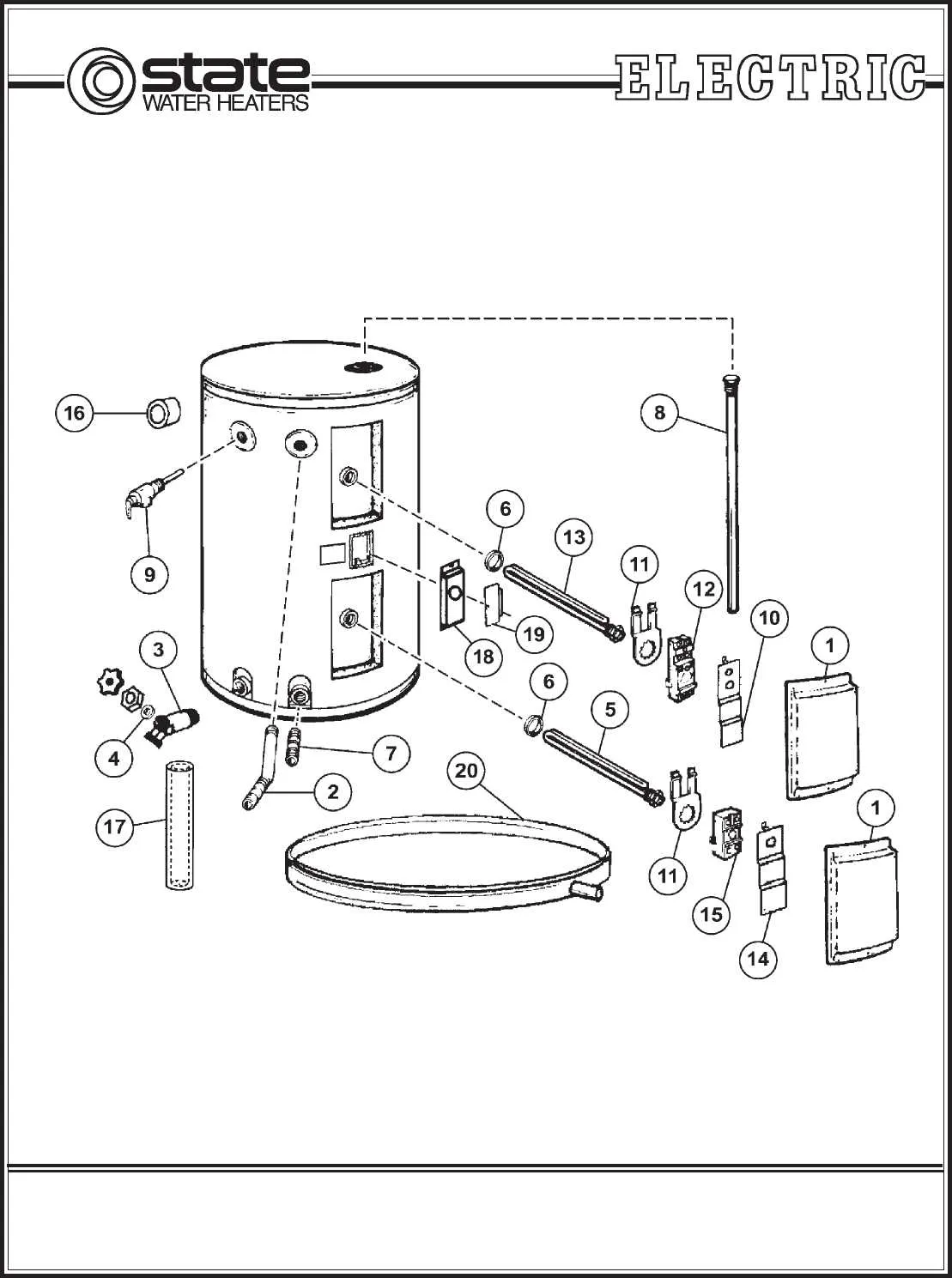
Ensure the presence of a thermal cutoff switch to prevent overheating and damage. This component automatically disconnects the system once a certain temperature threshold is reached, protecting both the appliance and surrounding areas.
Check for pressure relief valves. These are critical for maintaining safe operational conditions, as they release excess pressure, preventing potential explosions or structural failure.
Verify the insulation quality around wiring and electrical connections. Proper insulation minimizes the risk of short circuits or electric shocks, ensuring safety during operation.
Look for a properly functioning grounding mechanism. Grounding ensures that electrical currents are safely redirected, reducing the risk of fire or electrical injuries.
Examine the anode rod. This feature protects metal components from corrosion by attracting corrosive elements, extending the lifespan of the system and reducing the risk of leaks or failures.
Inspect the presence of a high-limit switch. This safety mechanism cuts off power when the system’s temperature exceeds a safe limit, preventing overheating and potential hazards.
How to Maintain and Replace Common Water Heater Components
Start by regularly checking the anode rod. This metal component prevents corrosion inside the tank. Replace it every 2-5 years, or sooner if you notice significant wear. A worn anode rod will lead to rusting and reduced lifespan of your system.
Heating elements should be inspected annually for scale buildup or damage. If you notice insufficient heat production or inconsistent temperatures, these may need replacement. To replace, shut off the power, drain the tank, and unscrew the old element before installing a new one. Always verify the element’s wattage before buying a replacement.
Ensure the temperature and pressure relief valve is functioning correctly. Test it by lifting the lever to release some water. If it doesn’t operate smoothly or shows signs of leakage, replace it immediately to prevent potential rupture of the tank.
The thermostat controls the temperature and should be recalibrated if the water is too hot or too cold. Check for consistent readings with a thermometer and adjust the settings accordingly. If calibration does not fix the issue, replace the thermostat.
Finally, if your unit has a drain valve, ensure it remains free from sediment buildup. Periodically flush the tank by opening the valve and allowing the water to run out. This keeps the system running efficiently and helps prevent clogs.