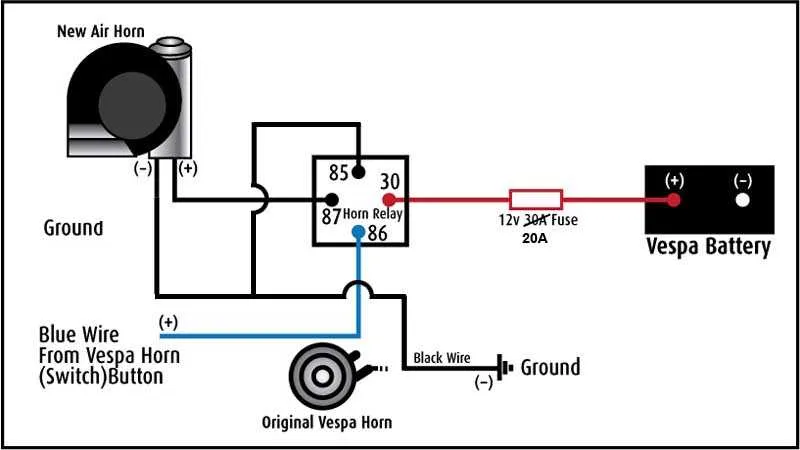
To successfully install your sound signaling device, ensure a proper connection between the power source and the triggering mechanism. First, connect the positive terminal of the power supply to the input terminal of the signal emitter. This is essential to maintain a continuous flow of electricity when activated.
Next, attach the negative terminal to the ground connection, ensuring a stable circuit. A direct link to the vehicle’s chassis often provides an optimal grounding point. Use a secure, corrosion-resistant connector for this step to prevent any electrical failures.
For the activation system, integrate a switch that can handle the electrical load. A relay might be necessary to manage the higher current flow required by the signaling unit. Position the switch where it’s easily accessible for the user and ensure all connections are tight to avoid short circuits.
Finally, check the connections and ensure that the system is properly sealed to prevent water or dirt from compromising the integrity of the electrical components. Regular maintenance of the connections will prolong the lifespan of the entire setup and ensure reliability in its operation.
Installation Guide for Electric Sound Devices
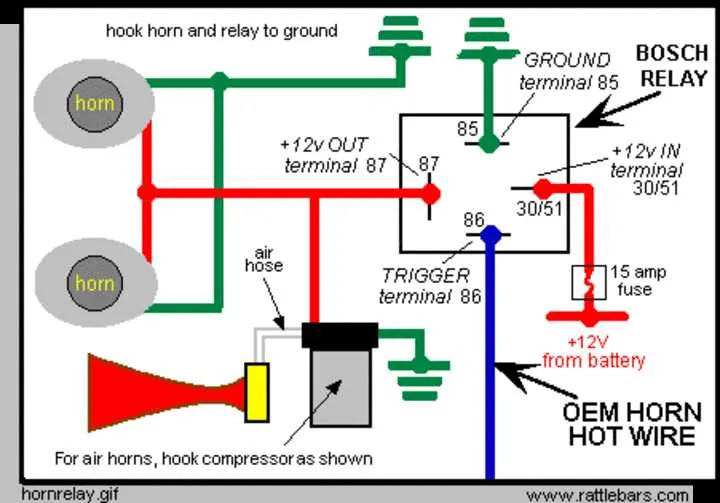
For proper installation, begin by ensuring you have the correct gauge wire for the setup. Typically, a 14-16 AWG wire will be sufficient for most systems.
- Step 1: Connect the positive terminal of your power source to the relay’s input pin.
- Step 2: Attach the negative terminal to the ground location on the vehicle chassis or another secure metal part.
- Step 3: The activation switch should be connected to the relay’s control pin. This switch will complete the circuit when pressed.
- Step 4: Use a fuse between the power source and the relay for protection against overloads.
- Step 5: Make sure to verify all connections are secure before testing the system.
Proper grounding and securing of all components will ensure optimal function and safety.
Step-by-Step Guide to Connecting a Loud Signal Device

Start by ensuring you have the necessary tools: wire cutters, electrical tape, a fuse, and a relay. Make sure the power source is turned off to prevent any accidents during installation.
First, connect the positive terminal of the device to the relay using a thick gauge wire. This connection should be made securely to handle the current required by the loud signal unit. The other end of this wire should be attached to the battery’s positive terminal.
Next, run a smaller gauge wire from the relay’s ground terminal to the chassis of the vehicle to establish a reliable ground connection. This step is crucial for the proper functioning of the circuit.
Link the activation switch to the relay. This can be done by connecting one wire from the switch to the relay’s control terminal. The other wire should go to the vehicle’s ignition circuit or another source of 12V that will trigger the relay when you press the switch.
After connecting the activation switch, install the fuse in line with the positive power wire to prevent potential damage from power surges. The fuse should be rated slightly higher than the expected load of the signal device.
Once all connections are made, test the system by powering on the vehicle and pressing the activation switch. Ensure the device emits the desired sound and there are no issues with the wiring.
Finally, secure any exposed wires using electrical tape or cable ties to prevent them from coming loose or being damaged while driving.
Choosing the Right Fuse and Relay for Loud Sound Systems
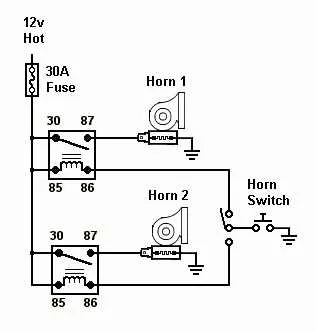
Use a fuse rated 30 amps or higher to ensure protection for high-power components. For 12V setups, a 40-amp fuse is commonly recommended, depending on the power consumption of the device. A fuse of this capacity will prevent overheating or fire hazards if there’s a short circuit or overload.
Opt for a 5-pin relay to manage the current efficiently. These relays provide a secure method to control the activation of your sound system, allowing the circuit to handle a much higher amperage than a typical switch would. The 5-pin configuration ensures that both the power and trigger signals are properly routed.
Match fuse size to amperage draw. For a system drawing 20 amps, a 25-30 amp fuse is appropriate. If the setup is consuming 15 amps or less, a 20-amp fuse will suffice. Ensure the fuse is installed as close to the power source as possible to prevent damage in case of a malfunction.
Install the relay in a dry location to prevent moisture damage. A location near the power supply but away from excessive heat or direct water exposure is ideal for optimal performance and longevity of the components.
Consider using a heavy-duty relay for systems with higher current requirements. This ensures that the relay can handle the increased load without risking burnout, which is common in substandard relays when they are used in high-demand applications.
Common Electrical Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Incorrectly sizing fuses can lead to damaging the system or fire hazards. Always select a fuse with the correct amperage based on the components’ power rating. Refer to the manufacturer’s specifications for proper fuse size to ensure safety and longevity.
Failing to use the correct gauge of wire often results in overheating and voltage drops. Ensure that the wire you use can handle the current required by the device. Use thicker wire for higher current applications to avoid damage and improve performance.
Improper grounding can cause the system to malfunction or even damage other electrical components. Always ensure a solid connection to a clean, unpainted metal surface for the ground wire. This will prevent erratic behavior and potential failure of the entire system.
Connecting multiple components to the same power source without considering their power requirements can overload the circuit. If you need to power several devices, use a separate circuit or ensure that the power source can handle the combined load to avoid failures.
Using cheap or poor-quality connectors can lead to weak connections and increased resistance. Invest in quality connectors that are rated for the intended current. Make sure they are tightly secured to ensure a reliable and safe connection over time.
Neglecting to check for proper insulation of wires can result in short circuits and other electrical hazards. Always inspect wires for wear or cuts in the insulation, and replace any damaged sections to maintain a safe system.