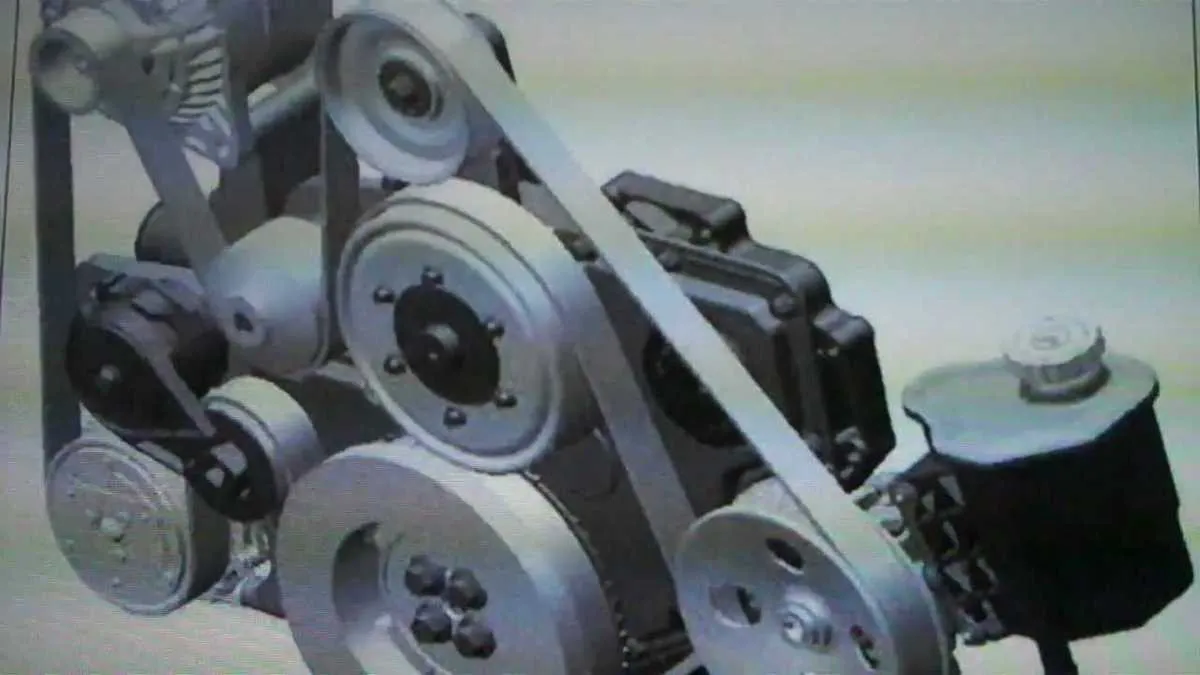
To ensure optimal performance and avoid unnecessary wear in your vehicle’s powertrain, it’s crucial to understand the specific arrangement of the rotating elements. The accessory drive system connects several components, including the alternator, water pump, and power steering pump, to the engine’s main shaft. Each element must be carefully aligned to prevent slippage or over-tension, which could lead to system failures.
Proper routing and tension management are key to maintaining system efficiency. Always check the manufacturer’s specifications for recommended tension levels, as improper settings can cause excessive stress on both the components and the belt. Over-tightening is a common issue that leads to premature wear of the accessories and their respective bearings.
The sequence of pulleys and the order in which they interact with the drive system play an important role in ensuring reliable operation. It’s essential to follow a step-by-step approach when adjusting or replacing any part of the system. Be sure to inspect each component for any signs of damage or misalignment, as these could disrupt the entire drive train and lead to costly repairs.
By maintaining a clean, well-lubricated system and replacing worn-out parts promptly, you can extend the life of your engine’s accessory drive system. Regular maintenance checks and a proactive approach will help avoid major disruptions and keep your vehicle running smoothly.
Serpentine System Layout for 6.7L Diesel Engine
For optimal engine performance, ensure proper routing of the drive components, such as the alternator, water pump, and AC compressor. The main accessory drive path is crucial for balanced load distribution and system efficiency.
Start by installing the tensioner pulley in its designated position to maintain proper slack in the system. The alternator is positioned to the left, while the water pump sits directly in front. The AC compressor should be mounted adjacent to the power steering pump. Pay attention to the sequence to avoid overloading the components.
It’s critical to use the correct torque when securing each component. Double-check the routing path, ensuring that there is no interference with the engine block or other moving parts. Misalignment can cause rapid wear and lead to premature failure.
Ensure the tensioner is working properly by manually adjusting the slack before installation. Afterward, run the engine for a short period and inspect all components for unusual vibrations or sounds.
For replacement, use a high-quality belt suited for the engine’s specific needs. Avoid cheap aftermarket products that might compromise longevity and performance. Periodically inspect the system for signs of wear, cracks, or stretching, especially if you notice any drop in engine performance.
Understanding the Layout for Cummins 6.7 Engines

For optimal engine performance, follow the recommended routing for the accessory drive system. This ensures correct tensioning and alignment of components such as the alternator, air conditioning compressor, and power steering pump. Proper placement of the components will avoid undue stress on the engine’s parts and increase their lifespan.
- Ensure the correct tension is applied to each pulley to avoid slippage, which can lead to premature wear or overheating.
- Align the serpentine loop in accordance with the factory instructions to maintain proper rotation direction for the various engine-driven accessories.
- Verify that all components are securely mounted, and check for any looseness or misalignment that could cause failure during operation.
For a smooth and efficient operation, pay special attention to the routing near the alternator and the tensioner pulley. The tensioner should be adjusted properly to maintain the right pressure across all parts, which will reduce the risk of vibrations and noise.
- Inspect the pulley alignment regularly to prevent any deviation that could lead to frictional losses or overheating.
- Consider replacing the tensioner after a set number of miles or operating hours to avoid unexpected breakdowns.
In case of repairs, always double-check the routing and make sure to replace any worn or damaged components immediately to avoid costly engine failures.
Step-by-Step Guide to Pulley and Tensioner Replacement on a 6.7L Diesel Engine
1. Before starting, ensure the engine is cool and the ignition is off. Disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to avoid electrical mishaps.
2. Remove any components obstructing access to the front of the engine, such as the air intake ducts, coolant reservoir, or engine covers.
3. Locate the tensioner assembly and use a suitable wrench to relieve tension from the pulley system. This will allow you to easily slide the unit off the system.
4. Using a socket wrench, remove any bolts securing the pulley brackets to the engine. Pay attention to bolt sizes and locations for reinstallation.
5. Carefully detach the drive component from its position. If necessary, use a rubber mallet to gently tap the unit for loosening.
6. Clean any surfaces where the new pulley or tensioner will be mounted to ensure a secure fit. Check the condition of the surrounding components for wear or damage, replacing them if needed.
7. Install the new pulley, ensuring it is aligned properly with the other components. Tighten the bolts to the manufacturer’s specified torque settings.
8. Reattach the tensioner, making sure it operates smoothly and without resistance. Double-check the system for any misalignment.
9. Reinstall any components you removed earlier and reconnect the battery. Start the engine and verify that the system runs quietly and without irregular sounds.
10. Perform a visual inspection to ensure everything is securely in place, and monitor the system during the next few hours of operation for any signs of irregularities.
Troubleshooting Common Pulley System Issues in Diesel Engines
When encountering irregular noise or malfunction in the pulley system, check for wear on the tensioner and idler pulleys. A faulty tensioner can lead to improper adjustment, causing excessive slack or tightness in the rotating system. If a whining sound or vibration is present, inspect the pulley alignment and ensure no misalignment has occurred. Misalignment can lead to uneven wear and reduced efficiency in power transmission.
Inspect the condition of the drive components regularly. Any visible cracks or fraying on the components may indicate improper usage or excessive load, requiring immediate replacement. Additionally, verify the tightness of fasteners that hold these components in place. Loose components can cause vibrations that might accelerate the wear process, leading to eventual system failure.
Another common issue involves overheating. Excessive temperatures can warp or damage the components, affecting their ability to function smoothly. Ensure the cooling system is functioning properly and that there are no obstructions or leaks causing reduced airflow around the components. Overheating may also indicate an issue with the water pump or thermostat, requiring inspection for proper operation.
Check for any excessive noise coming from the auxiliary power system. This could be a sign of improper installation or misalignment between the components, such as the alternator or power steering pump. Verify the mounting bolts for tightness and inspect the condition of bearings. A worn bearing can cause unnecessary friction, leading to further damage and premature failure of other parts.
In cases of power loss or reduced engine efficiency, inspect the tension and overall condition of the system’s components. Reduced performance could be caused by a poorly adjusted system or degraded parts, which can no longer transfer power efficiently. Always ensure that the system is properly calibrated according to the manufacturer’s specifications.