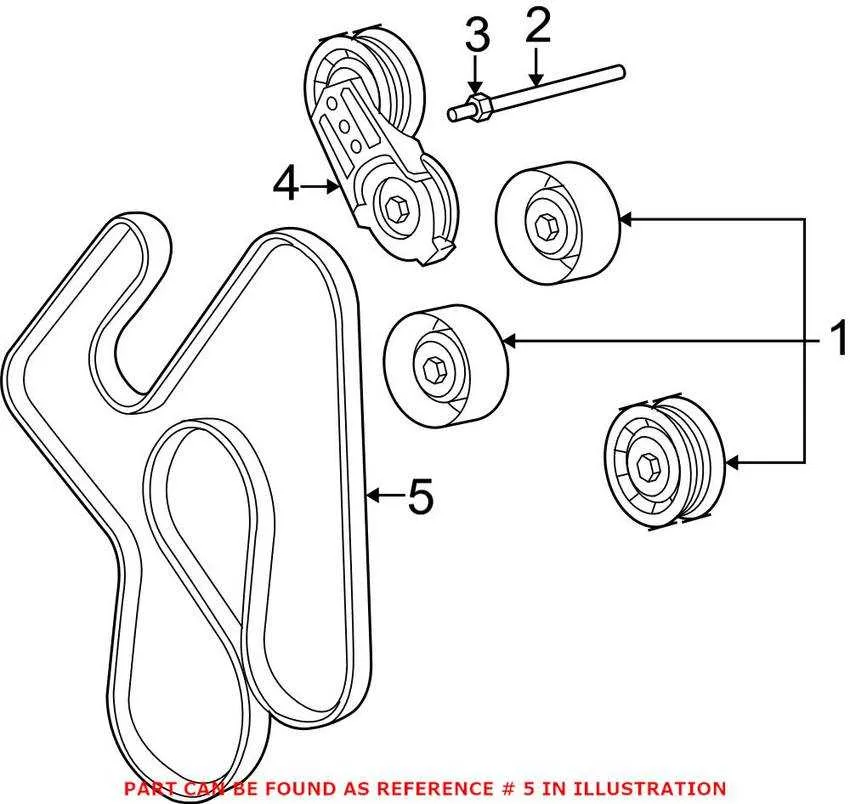
When performing maintenance or modifications to the 5.7L powerplant, accurate positioning of the rotating components is crucial. Ensure that the pulleys, tensioners, and associated hardware are aligned according to the manufacturer’s specifications to avoid unnecessary wear or engine performance issues.
Precise alignment of the timing components will prevent incorrect operation, reducing the risk of component damage. If misaligned, tension can cause premature failure of the drive system, leading to costly repairs. Double-check the orientation of each part before assembly.
Regular inspection of the tensioning system is recommended to maintain optimal engine function. Over time, the rotating assembly experiences natural wear. Pay special attention to the condition of the idler pulleys and the drive belts, which may require replacement every 60,000 miles or as specified in the maintenance guide.
Additionally, always verify that the proper torque specifications are applied to prevent slipping or over-tightening. Using a torque wrench ensures each bolt is set accurately, which is essential for long-term reliability and performance. Correct installation is the foundation for smooth operation and minimal maintenance needs.
Serpentine Layout on 5.7L Engine

Ensure the correct routing of the drive components to avoid misalignment or premature wear. The primary route should start from the crankshaft pulley, moving clockwise around each accessory, securing proper tension at every point. The alternator, power steering pump, and water pump are the key components connected by this system.
Start by aligning the tensioner pulley at the right side of the assembly, ensuring it is placed correctly. Next, check the positioning of the idler pulleys, which guide the belt with precise angles. These parts must be located with accuracy to avoid slippage or irregular wear on the system.
Double-check the path across the A/C compressor, verifying that the routing matches the expected configuration. Ensure there is enough slack on the tensioner to allow for proper stretching, but not too much to create excessive movement in the system.
Finally, confirm the alignment of all pulleys. Misalignment of even one can cause operational issues and potentially damage the accessories. Perform a visual inspection to confirm that the belt runs in a straight line across all components. Avoid twists or any sharp angles that could reduce efficiency or lead to failure.
Understanding the Timing Mechanism Configuration in the 5.7L Hemi Engine
Ensure correct alignment of all components to avoid misfires or engine performance issues. This system directly influences valve synchronization with crankshaft rotation, making accurate setup crucial.
- Confirm the alignment of the camshaft sprockets with the timing marks on the engine block. Incorrect positioning leads to improper valve timing.
- Verify that the crankshaft pulley and camshaft sprockets are positioned at top dead center (TDC) for the engine’s specific configuration.
- Use precise torque specifications when securing camshaft sprockets and other associated components to prevent slippage during operation.
- Inspect the system periodically to ensure that tension remains optimal, especially after high-mileage usage or engine disassembly.
Do not skip the step of replacing worn or damaged components in the timing mechanism. A slight deviation can result in a significant reduction in engine efficiency or permanent damage.
- Check the condition of all associated seals and gaskets to prevent oil leaks, which could affect timing accuracy.
- Ensure all components are free of debris and contaminants during reassembly.
Utilize proper alignment tools and consult the factory service manual for the exact positioning procedures and torque requirements. Any deviation from factory specs can negatively affect engine longevity and performance.
Step-by-Step Process for Replacing the Timing Belt on 5.7 Hemi
Start by disconnecting the negative battery cable to prevent electrical hazards. Remove the engine cover and any accessories that obstruct access to the components, including air intake parts and hoses.
Lift the front end of the vehicle and securely support it with jack stands. Remove the front wheels to gain better access to the timing chain assembly.
Next, remove the crankshaft pulley by loosening the central bolt. This often requires a special tool to prevent the engine from rotating. Once the pulley is off, proceed to remove the lower engine shield or covers.
With the engine exposed, loosen the tensioner and remove any necessary fasteners securing the chain guides. Mark the positions of the camshaft and crankshaft sprockets for reassembly. Use a ratchet or impact wrench to carefully take out the timing components.
Inspect the sprockets and other related parts for wear and replace if necessary. Position the new set of components, ensuring the alignment marks are properly matched to the engine’s timing specifications.
Install the new guides and tensioner. Tighten the fasteners to the manufacturer’s torque specifications. Reinstall the crankshaft pulley, ensuring it is torqued correctly.
Double-check all components for proper alignment, then reassemble any parts that were removed earlier. Lower the vehicle and reconnect the negative battery terminal.
Finally, start the engine and listen for any abnormal noises. If everything sounds good, perform a test drive to verify the work.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting with 5.7 Hemi Serpentine System

When the serpentine system on the 5.7L engine malfunctions, it can lead to a series of issues. Start by checking for abnormal wear or cracking in the components that connect to the tensioner pulley. These parts often degrade over time due to heat and friction. If the serpentine is misaligned or slipping, ensure the routing is correct and confirm the proper tension on the unit.
Examine the pulleys closely for signs of wear, as they are prone to seizing or excessive play. This can prevent proper operation of connected accessories like the alternator, power steering, and air conditioning. Replacing a faulty pulley immediately can save further engine damage and reduce the risk of overheating.
Another common issue occurs when the tensioner fails. If there is insufficient tension or if the unit becomes stuck, it will cause the components to underperform. Checking the tensioner spring for damage and replacing it when necessary will ensure optimal system functionality.
In some cases, even with correctly installed parts, improper torque can affect the system’s performance. Over-tightening or under-tightening the accessories or idler pulleys can lead to premature failure. Ensure that each component is tightened to the specified torque settings to avoid unnecessary wear.
If unusual noises such as squealing or grinding persist, it’s likely that the idler pulley or tensioner is failing. Diagnosing early through sound can prevent further complications and part breakdowns. Regular inspection of the system’s integrity will help maintain engine efficiency and prevent costly repairs.