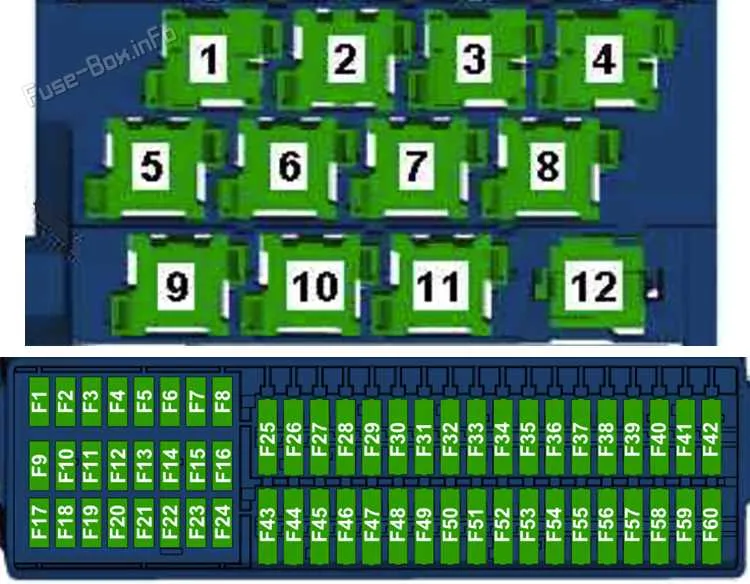
If you’re experiencing issues with your vehicle’s electrical components, it’s crucial to first inspect the central connection points that distribute power throughout the system. These critical nodes are located in two main compartments within the car: the engine and passenger areas. Each compartment houses essential relays and connectors that play a vital role in the overall performance.
Start by identifying the exact location of the power distribution panels. The rear section, typically under the dashboard, is where most of the fuses for the internal systems are found. The front area, near the engine, houses the high-current connections that manage power for critical components like lights, the ignition system, and other high-power electronics.
For a thorough inspection, you’ll need to identify the proper symbols and labels. Make sure to match the positions of each relay and connector to their corresponding systems–knowing which component powers what will save time and prevent unnecessary part replacements. It’s essential to use a detailed visual reference when examining these power panels to ensure the connections are intact and functional.
Tip: If a particular function isn’t working, such as lighting or power to the cabin accessories, refer to the corresponding location on your vehicle’s manual to pinpoint which relay or connector is responsible. This helps to quickly identify which part may need replacement or servicing.
Understanding the layout can also be useful when adding aftermarket accessories. You can safely tap into existing power sources, ensuring that you do not overload circuits and maintain the vehicle’s electrical integrity.
Electrical System Layout and Component Placement
For optimal performance, always consult the correct reference for each electrical connection and its corresponding protection unit. Start by locating the main power distribution panel under the dashboard. Here, you will find various circuits that supply energy to critical systems such as lighting, airbags, and entertainment units.
Each circuit is linked to a specific relay or protective device. These elements can be identified based on their color coding and the number of pins, which often correspond to their function. For example, a component responsible for air conditioning will have a unique identifier distinct from that of the headlights or central locking system.
The engine compartment also houses another set of protective units for high-power systems like the alternator and the cooling fan. Carefully examine the connections, ensuring no corrosion or loose wires, as these could lead to short circuits or system failure.
For troubleshooting, always use a multimeter to verify continuity and voltage in each circuit. This method will help you quickly identify any faults in the current flow, allowing for more efficient repairs or replacements of damaged components.
Tip: When replacing any protective units, ensure that the replacement is rated correctly for the amperage and voltage of the circuit it is protecting. Incorrect replacements can lead to overheating or component damage.
Important: Make sure all connections are secure and that the system is properly grounded to avoid electrical hazards.
Identifying Electrical Component Locations in a 2012 VW Beetle
The main power distribution center can be found beneath the dashboard, on the driver’s side. Look behind the panel below the steering wheel, which houses critical connections for several circuits.
An additional distribution unit is located in the engine compartment. It’s positioned near the vehicle’s battery, accessible by removing a cover or panel that shields it from dirt and moisture.
In some cases, a smaller power control unit is found within the cabin, near the door or glove compartment, depending on the vehicle’s specific configuration. Always check the owner’s manual for precise locations if you encounter any difficulty locating these components.
Ensure that the car is turned off and the battery is disconnected before inspecting or working with any of these electrical systems to avoid electrical shock or short circuits.
Common Electrical Component Issues and Troubleshooting Tips
Inspect the connectors regularly for any signs of corrosion or dirt buildup, as these can cause intermittent connections and power loss. Clean any dirty terminals with a specialized electrical cleaner to ensure proper conductivity.
If certain systems fail to function, check the relay and circuit pathways for breaks or damage. A malfunctioning relay can be a hidden cause behind non-responsive components, such as the lighting system or windshield wipers.
Test the voltage: Use a multimeter to confirm the voltage supply is consistent. If there’s a significant drop, you might be dealing with an underlying issue in the electrical wiring or an overtaxed circuit.
Loose or damaged wiring: Inspect the wiring for signs of fraying or disconnections. Tighten any loose connections or replace any wires that show visible damage to prevent shorts or electrical hazards.
Overloaded circuits: If electrical components stop working after a certain accessory is used, check for any overdrawn current. Adding extra accessories without considering the system’s capacity can lead to tripped circuits.
Lastly, make sure to replace faulty elements promptly with the correct ratings. Using incorrect components can cause cascading electrical failures or even risk fire hazards. Always follow manufacturer specifications when replacing parts.
How to Replace Fuses in the 2012 VW Beetle Fuse Box
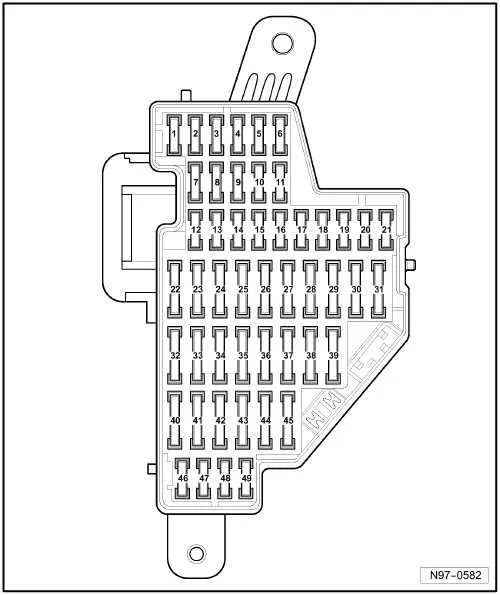
To replace a blown fuse in the electrical system of your vehicle, follow these steps:
- Locate the main electrical panel in the cabin, typically near the driver’s side beneath the dashboard or inside the glove compartment.
- Ensure the ignition is turned off before proceeding.
- Use a fuse puller or a pair of needle-nose pliers to carefully remove the damaged component. If you don’t have a puller, a small flathead screwdriver can also help.
- Inspect the fuse for visible damage, such as a broken wire or a blackened appearance.
- Choose a replacement with the exact same amperage rating, which is crucial to prevent electrical overload. The correct fuse rating is usually marked on the panel or in the owner’s manual.
- Insert the new fuse into the empty slot, ensuring it is fully seated and snug.
- Turn on the vehicle and check the system to confirm that everything is working as expected.
Common fuses that may need replacement include those for headlights, air conditioning, and interior lights. Always keep a small supply of various amperages in your vehicle for quick fixes.
- For the front passenger compartment, fuses for interior lights, AC, and radio are frequently replaced.
- For the rear compartment, check fuses related to the trunk and rear lights.
If the replacement fuse blows again, there may be an underlying electrical issue that requires professional diagnosis.