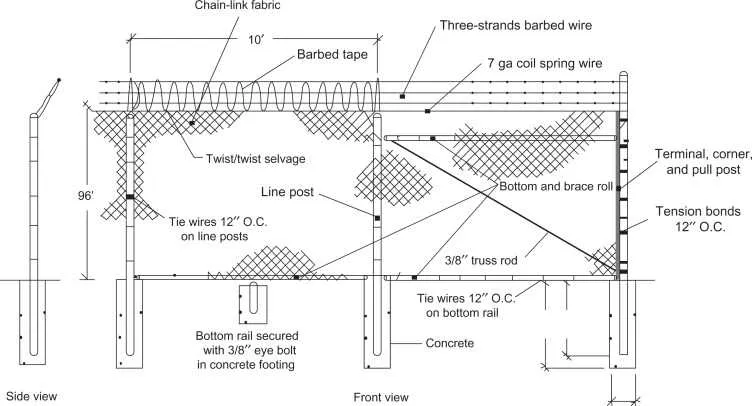
When planning a secure boundary, understanding the structure is crucial for proper installation. The vertical elements should be aligned securely to provide optimal support, while the horizontal rods must be tightened correctly to ensure the system remains intact for long-term use.
Make sure to invest in high-quality posts, as they provide the necessary foundation. These posts should be firmly placed in the ground, offering stability to the entire setup. Horizontal bars, also known as rails, work together with these posts, forming a rigid skeleton. They support the mesh, allowing it to stretch and remain taut.
The mesh, made of twisted wire strands, should be durable and corrosion-resistant to withstand external forces. Tensioning devices will help maintain the mesh’s integrity by keeping it tight across the structure. Pay attention to the connectors used to join various sections; they must be robust to prevent sagging or loosening over time.
Additionally, select fasteners that are weather-resistant, as outdoor conditions can weaken them quickly. Regular inspections and maintenance will ensure everything stays functional, and any issues can be addressed before they compromise the setup’s strength.
Understanding the Components of a Wire Barrier Structure
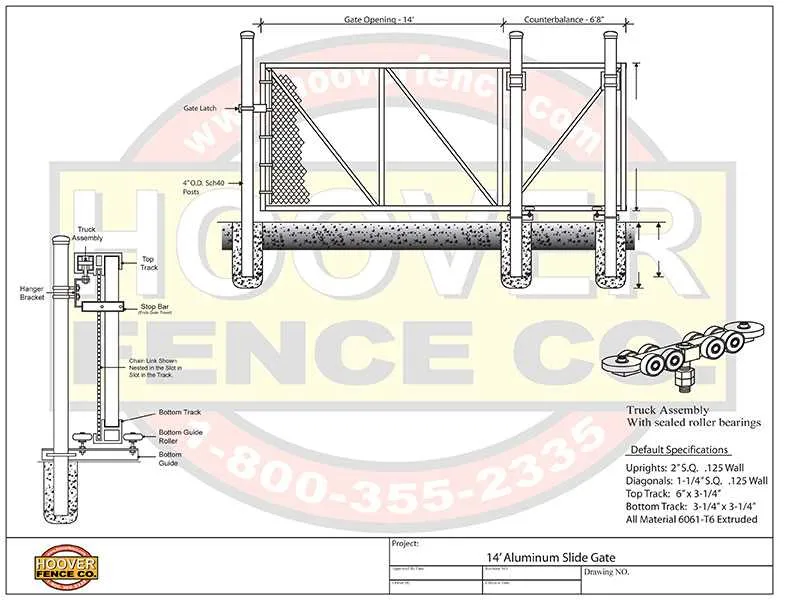
For effective assembly, identify the key components involved in constructing a wire barrier. Start with the framework, which is supported by vertical posts, commonly made from steel or aluminum. These posts should be anchored securely into the ground, ensuring stability for the entire system. Use horizontal rails to connect the posts, which provide additional support for the mesh.
The mesh itself is attached to the horizontal supports using specialized fasteners, often clips or ties. Ensure these fasteners are tightly secured to maintain the integrity of the structure. For added durability, a top rail may be installed to prevent sagging over time.
Consider using tension wires to keep the material taut. This is especially useful in areas with high winds, as it prevents the mesh from loosening. At the base, ensure proper tensioning of the material to avoid any gaps that could weaken the barrier’s effectiveness.
Understanding the Key Components of a Mesh Barrier
Start by ensuring you select high-quality steel posts, as these form the core structure for securing the netting. Opt for terminal posts for corners and gates, as these provide added strength and support. For intermediate stretches, use line posts, spaced about 6-10 feet apart, depending on the height and purpose of the enclosure.
The wire mesh should be tightly woven to prevent gaps. Choose a gauge of wire that suits your security needs; thicker wire offers more durability but can be harder to work with. Ensure it’s attached to posts using tie wires, which should be twisted securely to hold the mesh in place.
For a smooth and tensioned appearance, utilize tension bars at the end of the netting. These are inserted through the last row of mesh openings and connect to the posts, ensuring the net remains taut. Don’t forget to secure everything with tension bands, which wrap around posts and hold the tension bars in place.
Lastly, consider adding a top rail for extra rigidity, especially in areas with high wind or potential strain. This horizontal support stabilizes the entire system and keeps the posts aligned. For additional security, a gate frame with hinges and a latch mechanism will complete your installation, allowing easy access while maintaining a robust perimeter.
How to Properly Install Each Component of the Enclosure
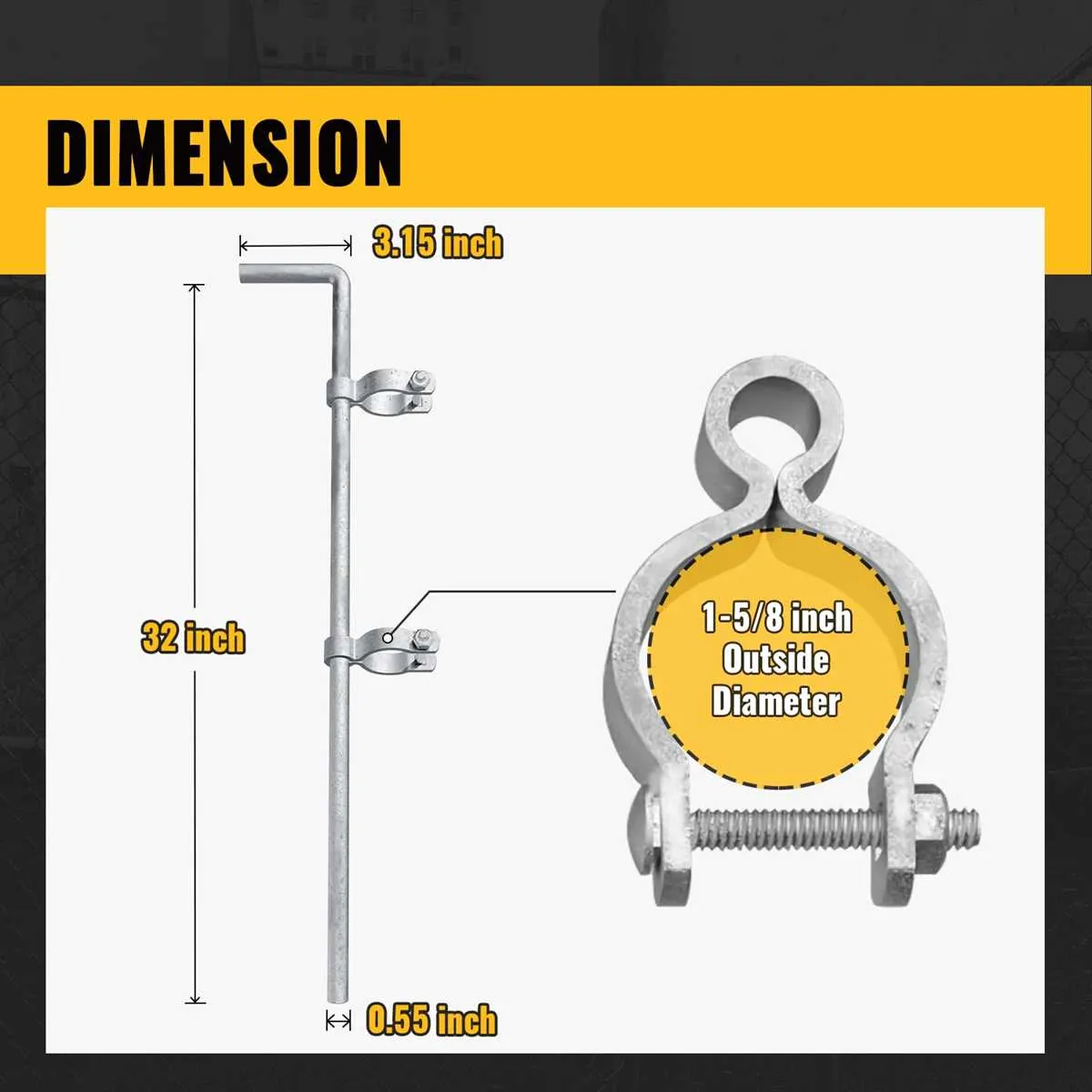
Start by securing the posts into the ground. Use concrete to set them firmly, ensuring they are level and spaced according to your layout. Each post should be about 6 to 8 feet apart, depending on the material used for the mesh and the environment.
Next, attach the horizontal rails to the posts. Secure them at appropriate heights, usually two or three, to provide strength and support. The rails should be fixed tightly using brackets or screws to prevent any shifting.
When preparing the mesh, unroll it slowly to prevent tangling. Begin attaching it at one end, stretching it tightly across the span. Use tension bands and wire ties at regular intervals (every 12-24 inches) to attach the mesh to the posts and rails. Make sure it’s taut, but not overly stretched to avoid damage over time.
- Install tension bands around the posts to hold the wire securely in place.
- Use wire cutters to trim excess mesh after it’s secured, ensuring a clean finish.
- Double-check the overall tension; it should be firm but flexible enough to withstand winds.
Lastly, add caps to the posts to seal them and prevent water damage. These caps also offer a finished appearance and prevent rust formation at the tops of the posts.
Maintenance Tips for Metal Enclosure Components
Regularly inspect the structure for rust and corrosion. Apply a rust-resistant coating or paint to prevent deterioration of the framework, especially in areas exposed to moisture.
Ensure all tensioning wires and supports are securely fastened. Tighten any loose connections using appropriate tools to avoid sagging or instability. Replace any worn-out fasteners with high-quality, durable replacements.
Check the vertical posts for signs of leaning or shifting. If necessary, reinforce the posts by adding concrete around the base or adjusting the ground stakes to ensure proper alignment.
Periodically clean the mesh to remove dirt, debris, and algae buildup. Use a mild detergent solution and a soft brush to scrub the surface without damaging the material.
Inspect any gate hardware for smooth operation. Lubricate hinges, locks, and latches to prevent sticking or rust. Replace any faulty components immediately to maintain functionality.
For wooden supports, treat the timber with a protective sealant to prevent rot and decay, particularly in regions with high humidity or exposure to rain.