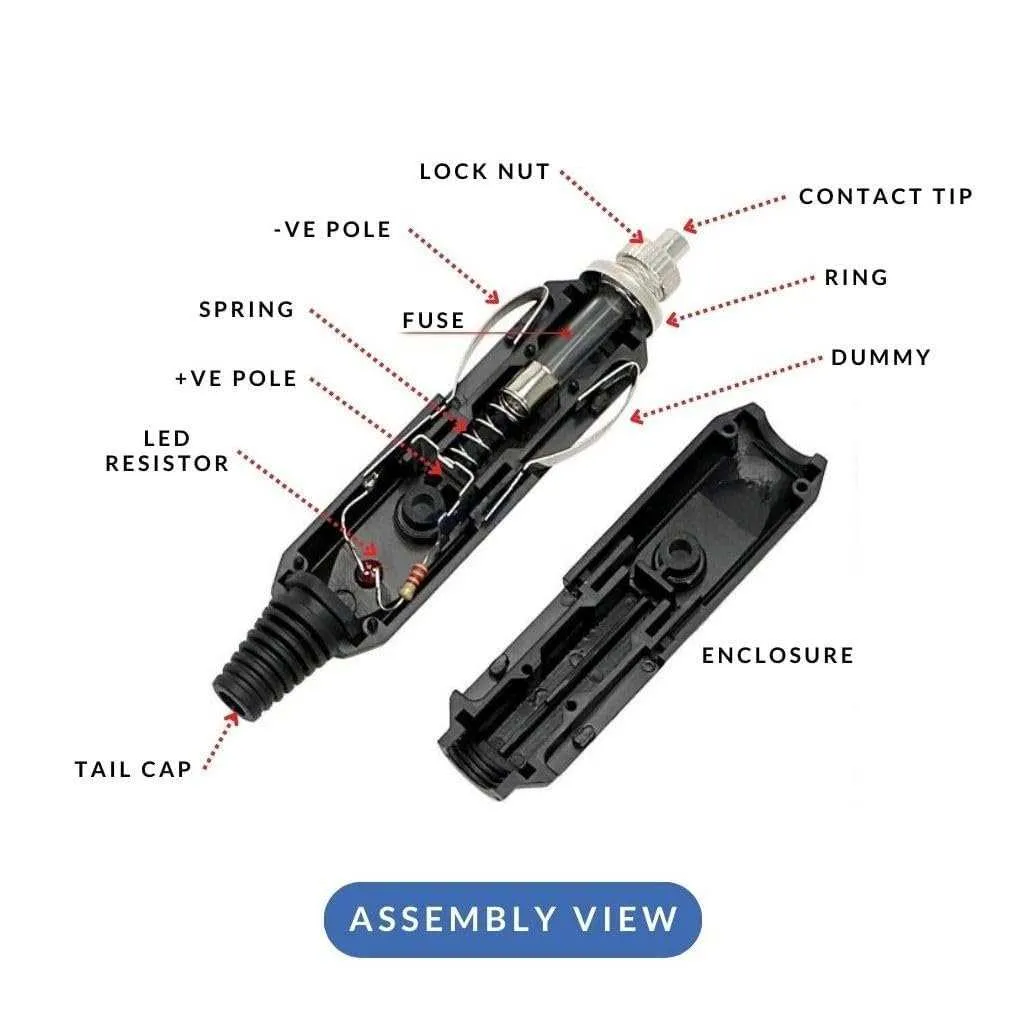
For reliable connections to the vehicle’s auxiliary power source, it’s crucial to have a clear understanding of the proper setup. Follow this guide to ensure each component is correctly installed for optimal functionality and safety. Focus on the terminals, ensuring proper polarity–this prevents damage to your devices and ensures stable power flow.
Identifying Terminal Positions: Each connection type requires a consistent approach for wiring. Make sure to identify the positive and negative terminals before proceeding. Failure to follow this step may result in short circuits or malfunctioning equipment. Ensure that the wiring is securely fixed, with no exposed areas that could cause a potential hazard.
Wire Gauge Selection: Choose the appropriate wire gauge to support the required current flow. A wire that’s too thin may overheat, while one that’s too thick could be harder to manage. Aim for a balanced option that allows safe power transfer without the risk of overheating or voltage drops.
Securing Connections: Use reliable connectors to prevent accidental disconnections or loose contacts. These connections should be tight but not over-tightened, which can cause wire damage. Make sure the setup is clean and free from corrosion to ensure longevity.
Safety Tip: Always test the installation before relying on it for regular use. Check for any signs of instability or faulty connections, which could compromise the system’s reliability and your devices.
Power Connector Circuit Overview

Ensure the connection is done with proper polarity to avoid malfunction. The positive terminal connects to the central metal, while the negative terminal is attached to the surrounding outer metal. Both terminals should have secure contacts to prevent any power loss or short circuits.
Use a fuse rated for the device to protect against overcurrent situations. Typically, a 15A fuse is sufficient for most applications, but check the device’s power requirements. Place the fuse as close to the source as possible to limit potential damage.
The power delivery wire should be of appropriate gauge based on the total current consumption. For devices drawing up to 10A, a 14 AWG wire is recommended. For higher currents, consider using thicker cables to minimize voltage drop and heating.
When connecting, avoid using loose or corroded contacts. These can lead to poor performance and even create sparks. Clean the terminals regularly and make sure they are free from rust or debris.
For a secure connection, crimp the wire ends into the terminals tightly. Soldering can also be used for additional stability, especially in environments where the connection is subject to vibrations.
Lastly, ensure all exposed wires are insulated or shielded to prevent accidental short circuits. Proper insulation will enhance safety and durability over time.
Understanding the Basic Setup for a Vehicle Power Connector
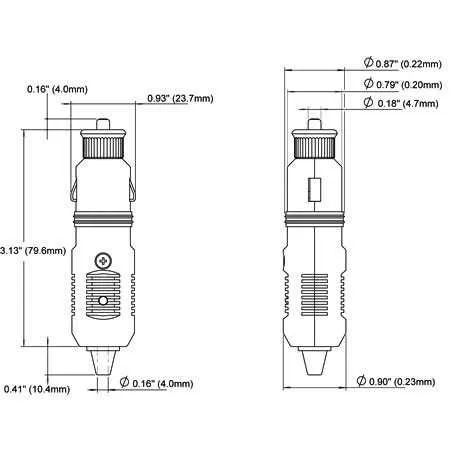
Ensure proper connections and safety when installing a vehicle power connector. The correct assembly of these components is crucial to avoid power issues or even accidents.
- Red wire: This typically serves as the positive connection. It should be securely connected to the positive terminal of the power source.
- Black wire: Acts as the ground or negative connection. Ensure it is properly attached to the vehicle’s ground system to avoid electrical malfunctions.
- Fuse: A fuse is necessary to protect the circuit from overcurrent. Select a fuse rated slightly higher than the expected current draw to prevent damage without unnecessary tripping.
- Insulation: Proper insulation is essential to prevent short circuits. Make sure all exposed wires are wrapped or covered with an insulated material.
- Connector Terminals: Use reliable terminals that securely clamp onto the wires. Poor connections can lead to heat buildup and potential fire hazards.
When setting up the power connection, always double-check that the positive and negative wires are correctly oriented. A reverse connection can lead to electrical failure or damage to connected devices.
Verify that the wires are properly sized for the expected power load. Overestimating the size can be unnecessary, but undersized wiring could cause overheating.
- Ensure that all components are rated for the correct voltage and current.
- Test the setup before fully installing it to avoid troubleshooting later.
By following these guidelines, you ensure a secure and effective setup that will provide reliable power for your devices.
Common Electrical Issues and How to Resolve Them
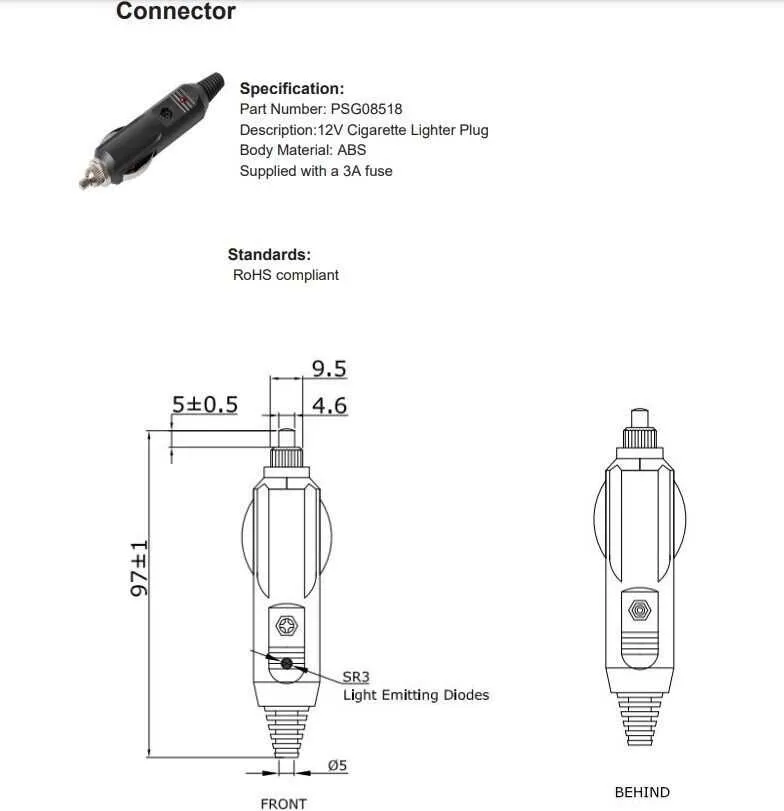
One common problem with power connectors is a poor electrical connection. Check for loose or corroded terminals. If the metal contacts inside the connector are dirty, clean them with a fine abrasive cloth. Make sure both the metal parts of the connector and the device it’s inserted into are free from rust or residue.
Another issue is a faulty fuse. Over time, fuses can burn out due to electrical surges or consistent use. Replace the fuse with one of the same rating to ensure proper functionality. Check the device’s manual to confirm the correct fuse type.
Short circuits are another frequent problem. If the connection is exposed or wires are damaged, the circuit might short out. Inspect the cable for any visible cuts or abrasions, and replace any damaged sections of the wire. Use proper insulation tape to ensure safety and prevent further damage.
Sometimes, overheating can cause the connector to fail. If the system operates with high power demands, the temperature might exceed the capacity of the connector, causing it to overheat. Ensure that the connector is rated for the required power load and consider using a connector with a higher temperature tolerance if needed.
Lastly, check for incorrect installation. Sometimes the connector might be inserted in a way that doesn’t establish a solid connection, which can lead to intermittent power loss. Verify the connection is secure and aligned according to the device’s specifications.
Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing a Vehicle Power Socket Connection
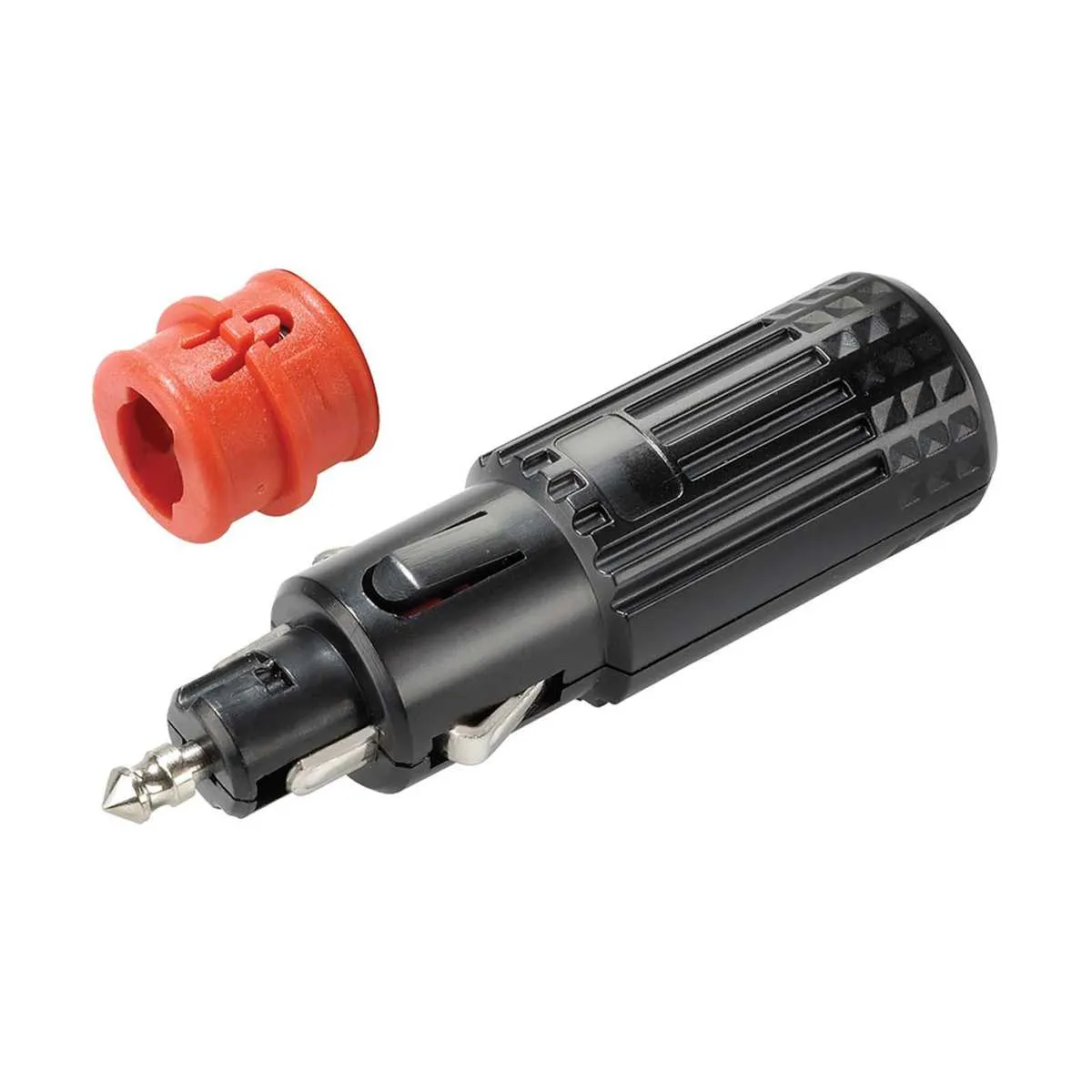

First, disconnect the battery to avoid any electrical hazards. Then, locate the faulty socket and assess its condition. If the socket is attached to a panel, remove any screws or fasteners to access the area.
Cut the old connection wires close to the socket. Strip about half an inch of insulation from each wire using a wire stripper. Ensure you do not damage the copper strands inside.
Now, connect the new socket. Match the positive and negative terminals of the socket to the corresponding wires. Use a crimping tool to secure the wire ends onto the socket’s terminals. Ensure the connections are tight and there is no exposed wire that could cause a short circuit.
Reattach the socket to its original mount, ensuring it’s firmly secured in place. Before reinstalling the panel, double-check the connections to make sure they’re correct and free from any errors.
Reconnect the vehicle battery, then test the socket by plugging in a device to confirm it’s working properly. If everything functions as expected, reinstall any panels or covers that were removed earlier.