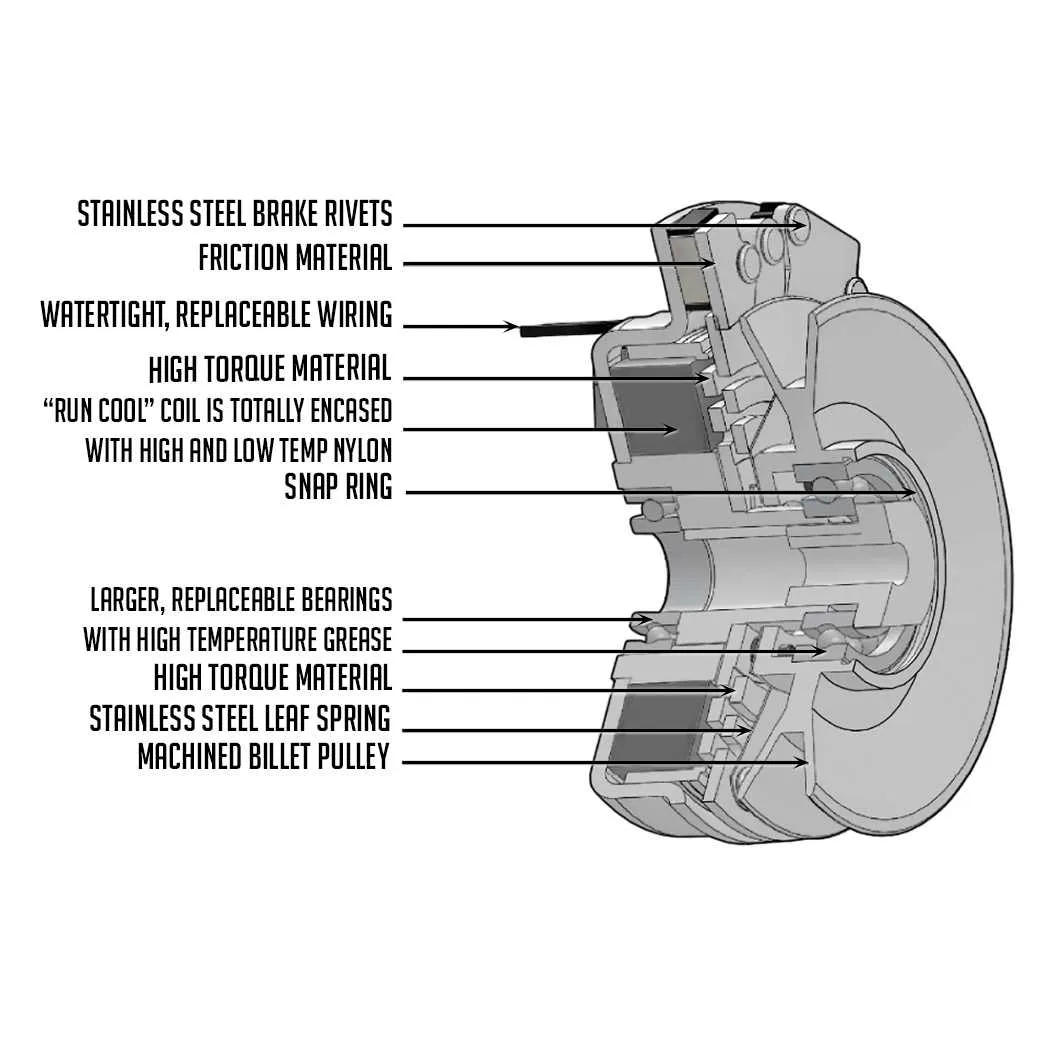
Before troubleshooting or making repairs on your mower, it’s crucial to familiarize yourself with its electrical configuration. Knowing the correct connections and their placement can prevent unnecessary damage and ensure the machine runs smoothly. Focus on identifying the key components, such as the ignition system, motor connections, and safety switches. Ensure that each wire is intact and properly connected to avoid operational failures.
One of the most common issues with outdoor power equipment is poor electrical contact. If you’re experiencing difficulty starting the engine or your mower stalls intermittently, the first place to check is the wiring harness. This network of connections is responsible for powering essential parts of the engine, so ensuring the proper continuity and grounding of these links is vital.
For an effective repair, you’ll want to review the control panel, relays, and fuses. Inspect these elements regularly for corrosion or signs of wear. Remember, even minor wear can disrupt the flow of electricity and compromise functionality. Use a multimeter to confirm voltage at various connection points to identify faults.
When handling repairs or installations, always refer to the manual for precise locations of components. A detailed map of your mower’s electrical system will save you time and minimize errors. Accurate wiring ensures that the mower functions as intended and provides a longer service life.
Electrical System Overview
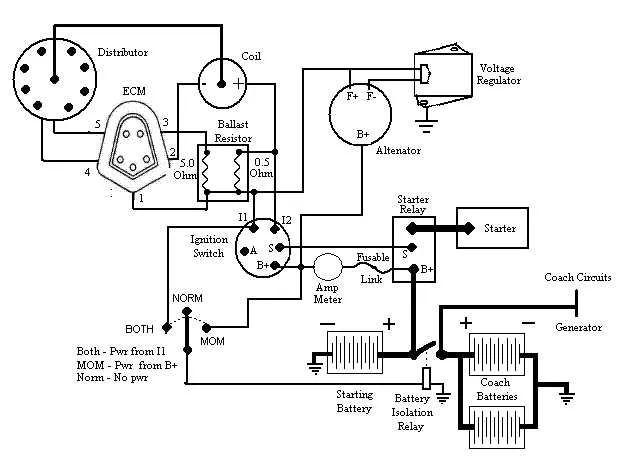
To resolve electrical issues, start by checking the battery’s voltage and ensure all connections are secure. A multimeter will help verify the integrity of the system. If your mower is unresponsive, inspect the solenoid for proper operation. For machines with starter motors, check the starter relay and ensure no corrosion is present on terminals.
Ensure the fuses are intact. If any are blown, replace them with the same rating to avoid further damage. Examine the switch and ignition system thoroughly, as faulty wiring can prevent startup. It’s essential to confirm that all components are receiving proper voltage levels according to the manufacturer’s specifications. If the mower operates intermittently, consider tracing the ground connections and ensuring proper continuity.
Be sure to follow the manufacturer’s color-coded system for each wire type. When in doubt, consult the specific model’s repair guide to prevent any confusion. Isolate potential short circuits by systematically testing each circuit with a voltage tester. This allows you to pinpoint exactly where the issue lies, without unnecessary disassembly.
Understanding the Key Components of the Electrical System
To ensure smooth operation of your mower, it’s essential to understand the main components that make up its electrical setup. Each part plays a crucial role in the functionality and troubleshooting of the system. Here’s what you need to know:
- Battery: Supplies power to all electrical components. Check its charge and condition regularly. A weak or dead battery can cause startup issues.
- Ignition Switch: Allows you to start the engine and control the electrical circuits. A malfunctioning switch can prevent the engine from starting.
- Fuses: Protect the system from overloads. Always replace blown fuses with the correct amperage to prevent further damage.
- Relays: Control high-power circuits such as the starter and ignition system. If your mower fails to start, a faulty relay could be the cause.
- Solenoid: Acts as a switch to start the engine. It’s essential for powering the starter motor, and if it’s defective, the engine won’t turn over.
- Starter Motor: Cranks the engine. If the motor doesn’t engage, check the solenoid and the motor’s connections.
- Safety Switches: Ensure the machine operates safely. These switches cut power to specific components if not engaged properly, such as when the seat or brake isn’t in the correct position.
Familiarize yourself with these components and ensure proper maintenance to avoid downtime and improve reliability. Regular checks and quick fixes can prevent more serious issues down the line.
How to Troubleshoot Common Electrical Issues in Lawn Mowers
Start by inspecting the fuse. If the mower isn’t turning on, check for a blown fuse, which is a common issue. Replace it with one of the same amperage rating. A damaged fuse often indicates a short circuit, so ensure no wires are exposed or frayed.
If the engine cranks but doesn’t start, test the ignition switch. A malfunctioning switch can prevent the mower from starting. Use a multimeter to check for continuity when the switch is in the “on” position. If there’s no continuity, replace the switch.
Check the solenoid. If the engine fails to start and the battery is charged, the solenoid may not be working correctly. Use a voltmeter to measure voltage across the solenoid terminals while cranking the engine. If there’s no voltage, replace the solenoid.
Inspect the starter relay for malfunction. A faulty relay can prevent proper starting. To test, use a multimeter to check the relay’s connections. If the relay fails to engage, it’s time to replace it.
For problems with the mower’s lights, examine the bulbs and the connections. A blown bulb or corroded connector can cause lights to flicker or not work. Clean the terminals and replace the bulbs as necessary.
If the mower’s motor runs intermittently, inspect the ground connections. A loose or corroded ground wire can lead to sporadic power loss. Tighten or clean any ground connections to ensure a stable electrical path.
For issues with the PTO (Power Take-Off) switch, ensure it is operating correctly. A faulty PTO switch may prevent the blades from engaging. Check for continuity across the switch terminals; if there’s none, replace the switch.
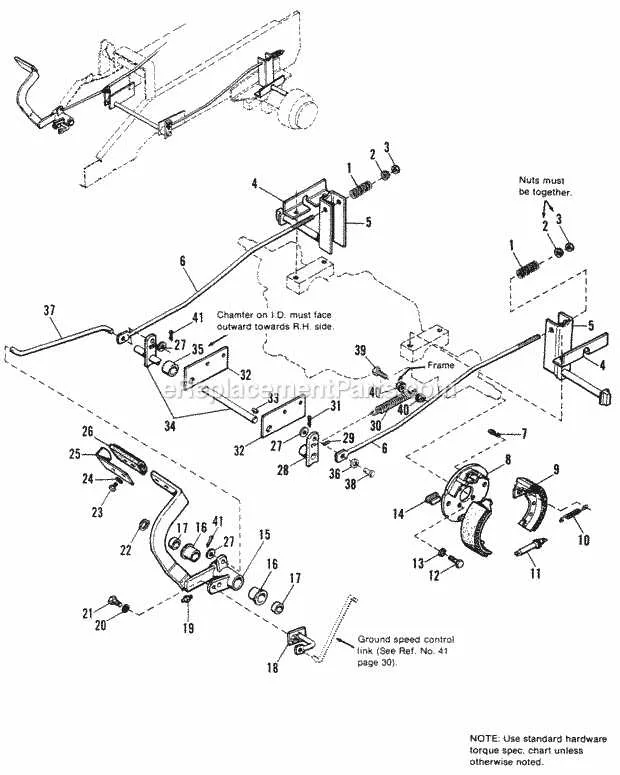
Step-by-Step Guide to Rewiring a Dixie Chopper for Optimal Performance
Start by disconnecting the battery to avoid any electrical hazards. Ensure you have a multimeter, wire strippers, and connectors ready. Examine the existing connections for wear or damage before proceeding.
First, trace the wires from the engine to the ignition system. Check the continuity of each wire to ensure there are no broken circuits or faulty connections. Any damaged wires should be replaced with the same gauge and type of wire. Use a high-quality, weather-resistant wire for outdoor use.
Next, focus on the grounding points. A poor ground connection can cause inconsistent performance. Clean any corroded grounding areas and secure new grounding straps if necessary. The engine block should be tightly grounded to the chassis for maximum performance.
Reinstall or replace any fuses that have blown. Consult the manufacturer’s guide for the correct fuse rating to avoid overloading the circuit. Fuses protect sensitive components from surges, and replacing them with the right type ensures longevity.
Ensure all control switches are connected properly. Examine the starter switch, key switch, and throttle connections. If the controls are not responding as expected, replace the switches and clean any contacts to improve response time.
When routing the new wires, avoid tight bends that may cause them to wear out prematurely. Secure wires with clips or ties to prevent them from touching hot surfaces or moving parts, which could cause shorts.
Finally, check the voltage output from the alternator to ensure it’s within proper specifications. If the voltage is inconsistent, replace the alternator or regulator as needed. Once all connections are secure, reconnect the battery and test the system for proper functionality.