If you’re troubleshooting electrical components or replacing a blown relay in your truck, the primary electrical distribution system is crucial to understand. The first step is to locate the system responsible for managing power flow to essential components such as lights, wipers, and engine controls.
Check the central unit placed near the driver’s side, typically below the dashboard or near the engine compartment. This unit contains multiple connections that supply power to various systems throughout the vehicle. Refer to the labels near the terminals for identifying specific functions like the engine control unit, air conditioning, and power steering.
Be aware of the color codes and numbered slots. Each terminal is marked to show which circuits it manages, making it easier to diagnose issues. For example, the connection near the engine’s cooling system is often linked with the cooling fan relay. Consult the service manual to confirm circuit assignments for a more precise diagnosis.
If you’re replacing or inspecting any component, always double-check the electrical connections to ensure they are secure and free from corrosion. Additionally, ensure the system is powered off to avoid short-circuits while working on it.
For advanced troubleshooting, consider using a multimeter to verify the voltage at various connections to determine if any wiring has worn out or a component is malfunctioning.
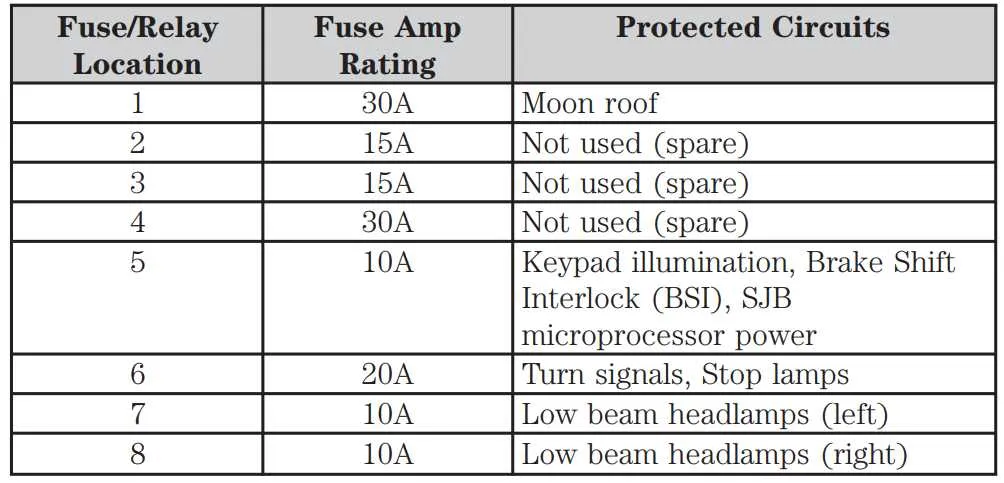
Engine Compartment Electrical Layout
To locate the electrical components and relays in the engine compartment, refer to the schematic for proper identification. This layout includes essential fuses that control various functions like lights, ignition, and auxiliary systems. Ensure that all connections are checked for corrosion or damage to maintain proper functionality.
Key Components: Main relays, ignition relays, lighting fuses, and sensors are all housed in this section. Regular inspection will prevent power failures or component malfunction.
Note: Always consult the vehicle’s manual for detailed placement, as each section is labeled to help in easy identification of each element. Properly replace any damaged or blown fuses with the correct amperage rating to avoid electrical issues.
For a detailed view, locate the reference diagram that matches your vehicle’s model year and specific configuration. This will ensure all electrical circuits remain functional and safe.
Identifying Fuses and Relays in the 2010 Pickup Electrical System
To properly identify the electrical components in the vehicle’s power distribution unit, start by referencing the specific layout guide located in the owner’s manual or a service manual. Each component has a designated number and function, which can be easily cross-referenced with the printed map on the cover of the unit.
Relays are typically situated in the upper portion of the assembly, while individual electrical protection devices are arranged below. These units serve to protect circuits from overloads by cutting off the power when the current exceeds safe levels.
For effective troubleshooting, it’s important to check the condition of each component. Use a multimeter to verify continuity and to determine if the protective elements are working as intended. Additionally, use the color-coded label system to identify each unit quickly without needing to remove it from its housing.
Ensure that you replace any damaged or faulty items with components that match the specified amperage and type for optimal performance. Avoid substituting components with different ratings as this may lead to further electrical issues or even cause damage to other systems in the vehicle.
When replacing a relay or protection unit, always inspect for signs of wear or corrosion on the connectors. Clean them thoroughly before reinserting the new part to maintain solid electrical contact and ensure proper function.
How to Replace a Blown Fuse in the Engine Compartment Electrical Panel

To replace a blown circuit protection component, start by locating the panel in the engine compartment. It is typically on the driver’s side near the battery or fender. Remove the cover by lifting the latch or unscrewing the fasteners, depending on the design.
Identify the faulty component by checking the markings on the back of the panel cover, which indicate the function and location of each element. Once the damaged component is found, carefully pull it out using a pair of needle-nose pliers. Ensure you pull straight to avoid damaging the surrounding components.
Before installing the new one, verify its specifications. The replacement should match the amperage rating of the blown unit. Insert the new piece firmly into the correct slot, ensuring it fits securely. Double-check to confirm it’s seated properly.
After installation, close the panel cover and test the electrical system to verify the repair. If the issue persists, recheck the components or inspect for any underlying electrical issues.
Common Electrical Issues and Troubleshooting with the 2010 Ford F150 Fuse Box
If you’re experiencing electrical malfunctions, it’s often related to the central electrical panel. Below are key issues and how to address them:
- Blown Relays or Fuses: One of the most common problems is a blown fuse or faulty relay. If a specific component, like lights or radio, stops working, check the related fuse first. Always replace with the correct amperage.
- Corrosion or Loose Connections: Corrosion can interfere with electrical flow. Inspect connectors for rust or dirt and clean them with a contact cleaner. Ensure all terminals are tightly secured.
- Short Circuits: A short circuit can cause intermittent power issues or even damage components. This typically occurs due to wiring damage or faulty parts. Use a multimeter to trace the short and replace damaged wiring.
- Overheating of Electrical Components: If any circuit overheats, it may indicate a short, faulty relay, or an overloaded circuit. Make sure the system is not pulling more current than it’s rated for.
- Failed Grounding Connections: A poor grounding connection can cause irregular behavior in electrical components. Inspect ground wires for loose connections or corrosion and tighten or replace them as necessary.
Follow these steps to diagnose and repair electrical problems, ensuring the vehicle’s system remains reliable.