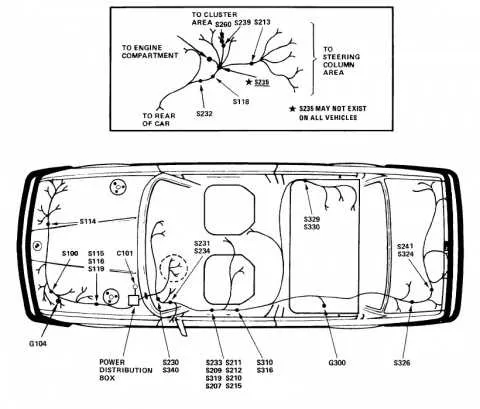
If you’re troubleshooting or upgrading the electrical system in your 3 Series from the ’80s, understanding the internal wiring connections is crucial. The component distribution inside the cabin and engine bay is designed to ensure that all essential functions operate smoothly, from lighting to sensors.
Start by identifying the power routing for each circuit. Pay close attention to the central control unit, which distributes power to various subsystems. The most commonly affected components are the climate control, interior lights, and ignition system. Incorrect wiring or a damaged connection can lead to malfunctioning systems, so ensure each pin is securely connected.
The first step in effective diagnosis is isolating the affected area by following the individual circuit paths. A clear visual of the system helps to understand which components rely on each other. Focus on the areas where critical systems like the alternator or ignition are connected to the primary power network, as these are often the source of issues.
Tip: For those replacing or inspecting any connectors, always ensure the contact points are clean and free from corrosion. For added longevity, use dielectric grease to protect against moisture and oxidation.
Also, when performing checks, be methodical in examining the grounding points. A poor ground connection is often the root cause of erratic behavior in electrical components. A multimeter can help you identify any weak or broken connections that may be causing disruptions.
Electrical Component Layout for the BMW E30
For optimal functionality, always ensure the proper installation of relays and connectors. The main electrical panel should be checked for any signs of wear, such as corrosion or loose terminals, as these can cause malfunctioning of vital systems.
Common issues to watch for: A malfunctioning headlight, non-responsive ignition system, or a failure of the windshield wipers can often be traced back to faulty connections within the electrical hub. Make sure each relay is seated properly and that all connections are tight to prevent these problems.
Step-by-step guide: Start by inspecting the main panel under the dashboard for any visible damage. Check the integrity of the wires leading to the various systems. Use a multimeter to test continuity on each lead to ensure proper functionality. If there is any fluctuation in power, it’s crucial to identify the faulty component before replacing it.
Important notes: Some systems require specific amperage levels to operate correctly. Refer to the vehicle’s manual for the correct ratings to avoid overloading any components. Also, ensure that each fuse matches the prescribed amperage to prevent overheating.
Locating the E30 Fuse Box and Understanding Its Components
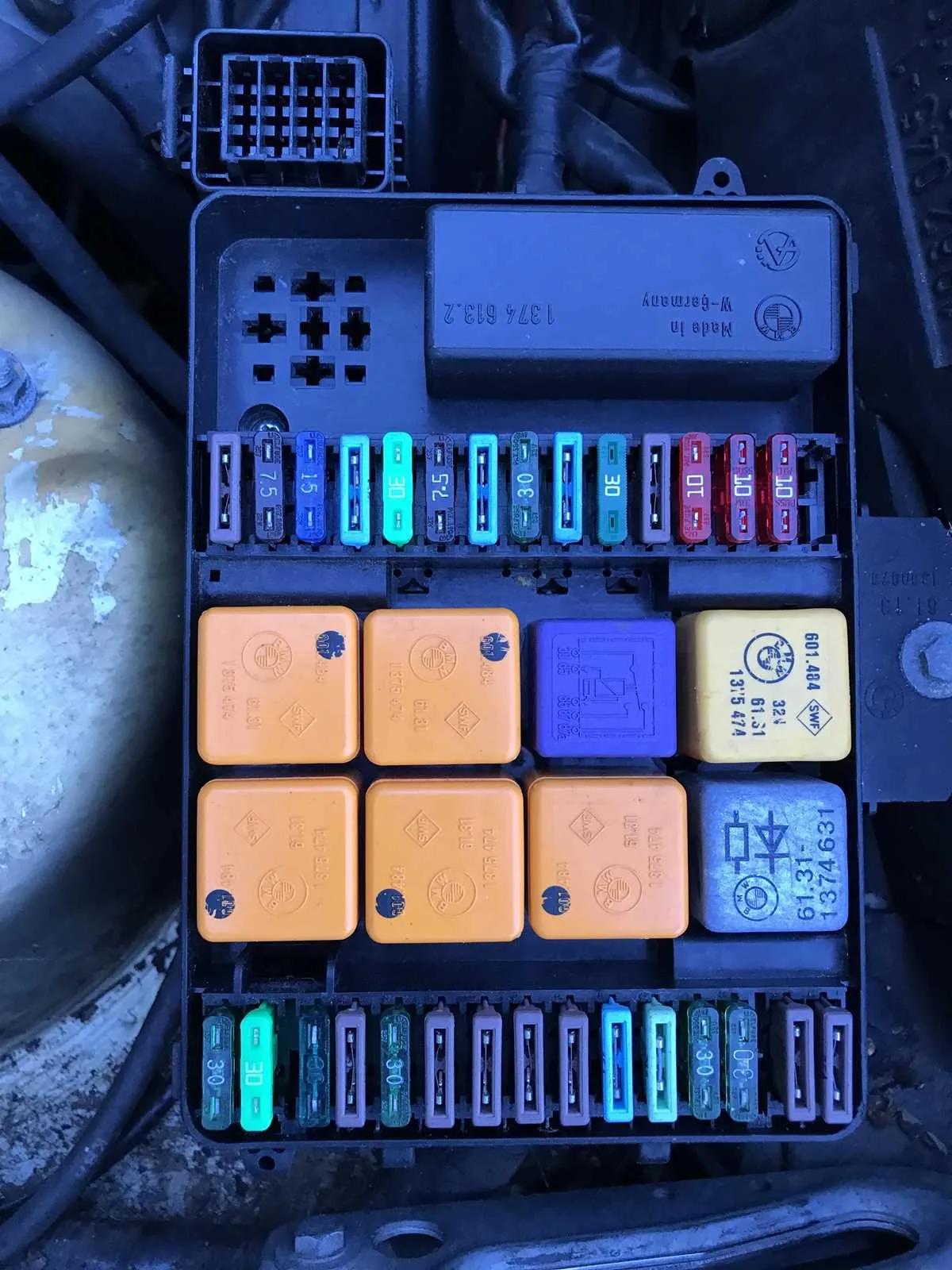

The main electrical distribution panel is located in two places within the vehicle. The primary section is inside the cabin, near the driver’s side. The secondary part is situated in the engine compartment, providing power to essential components under the hood.
- Cabin Placement: Open the driver’s side door and remove the panel located beneath the dashboard, just above the footwell area.
- Engine Compartment Placement: Look on the driver’s side of the engine bay, near the windshield. You will see a protective cover which needs to be removed to access the components.
Each section contains a set of relays and connectors that manage power distribution to different vehicle systems, such as lighting, climate control, and ignition. Understanding their function helps in troubleshooting electrical issues.
Components Breakdown
- Relays: These switch circuits on and off, allowing higher power components to operate safely with the lower power control circuits.
- Terminals: Metal connectors that ensure a solid link between wiring and the central panel. They may become corroded over time, leading to weak or intermittent electrical connections.
- Connectors: Responsible for linking individual wires to the central panel. Inspect them for wear and ensure they are securely fastened to prevent shorts.
Regular inspection of these components is crucial for maintaining the vehicle’s electrical system. It is recommended to perform a check-up every 6 to 12 months, especially if any electrical issues are present.
How to Identify and Replace Fuses in the E30 Fuse Box
Start by turning off the ignition and removing the key to prevent any electrical hazards. Use a flat-head screwdriver or a plastic tool to carefully open the cover, exposing the electrical components. Look for a labeled chart that corresponds to each circuit’s location. If the labels are unclear, refer to the vehicle manual for specific positions.
Check each component by visually inspecting the metal strip inside the component for any signs of breakage or damage. If the strip is intact, the circuit is functioning properly. A broken strip indicates a blown part, which needs to be replaced. Use a multimeter to test the continuity if needed, as this is a more accurate method to identify failure.
To remove a faulty component, gently pull it out using pliers or a fuse puller, making sure not to damage the surrounding area. Take note of the amperage rating printed on the component before replacing it. Always replace with a component of the same rating to avoid damage to the electrical system. Insert the new component firmly in place, ensuring it fits securely.
After installation, check the circuit by turning on the ignition and testing the associated functions. If the issue persists, recheck the installation or consider testing other circuits that may be linked to the problem.
Common Electrical Issues and Troubleshooting Using the Fuse Layout
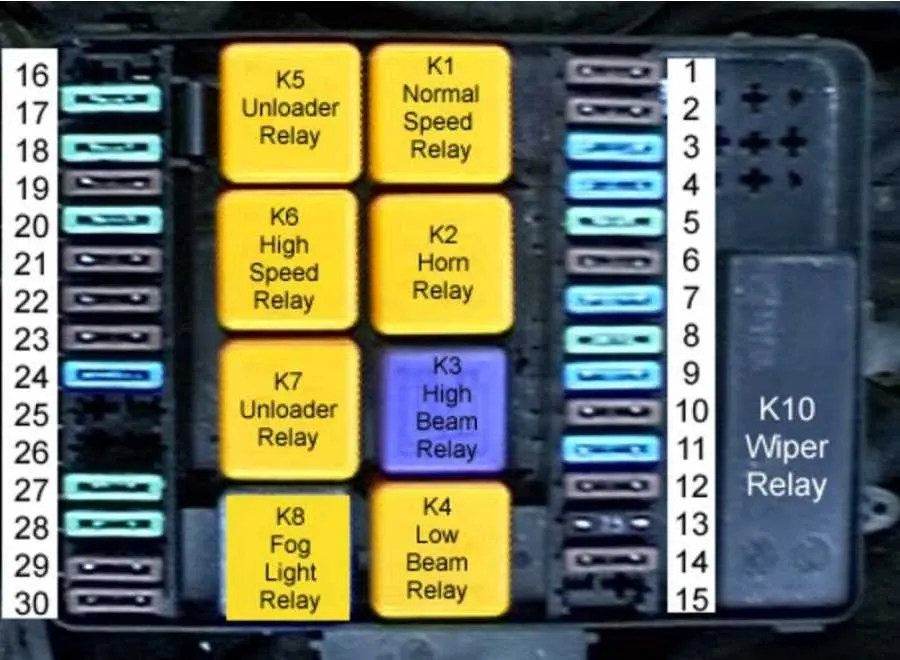
If you experience intermittent electrical malfunctions, start by inspecting the power distribution layout under the dashboard. A blown circuit can cause specific components to lose power while others remain operational. Check the associated relays and terminals for signs of corrosion or damage, as poor connections often lead to unstable functionality.
One of the most frequent problems involves faulty connections at the terminal ends. Inspect the wiring for any visible wear or fraying, particularly in areas where it may come into contact with metal parts of the vehicle. Damaged insulation could lead to short circuits or power loss in certain areas.
If a component such as the lights or windshield wipers fails, locate the corresponding power channel on the layout. Verify that all the necessary paths are intact and that the switch triggering the electrical flow is functioning properly. In some cases, the issue lies in a relay malfunction, where the power flow is not being correctly directed to the component despite the switch being in the active position.
For persistent electrical failures, using a multimeter to check the voltage at various points in the system is crucial. This will help confirm whether power is being adequately delivered or if there’s an issue within the power delivery channels themselves. A voltage drop across specific points can point to weak or broken connections.
Finally, ensure that all ground connections are secure. A loose ground can result in erratic electrical behavior, where components work intermittently or fail entirely. Tighten any loose bolts on the grounding points and inspect for signs of rust or oxidation that could impair the connection.