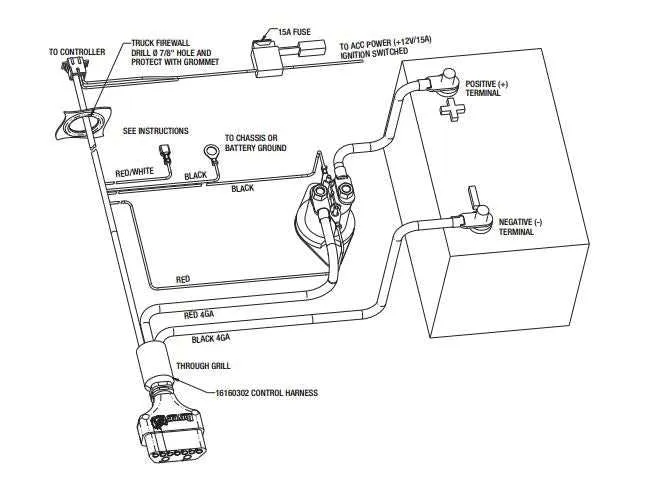
If you’re setting up the electrical components for a plowing attachment, focus on achieving secure, clear, and well-organized connections. Accurate placement of wires will ensure that each part of the system functions properly and avoids potential malfunctions during use. Start by correctly identifying the power source and controlling switches, making sure they are aligned with the respective outputs for optimal performance.
For reliable operation: Begin by connecting the control module to the main battery and ensure that the power leads are of adequate gauge to handle the load. The actuator wiring should be routed in a way that minimizes exposure to external elements, preventing wear over time.
Properly connect the solenoid and ensure that the ground points are securely fastened to the vehicle frame. Use quality connectors to prevent corrosion or unreliable connections that could lead to intermittent failure. Test each component before finalizing the setup to confirm the system operates seamlessly under all conditions.
Proper Connection Setup for Your Vehicle’s Hydraulic System
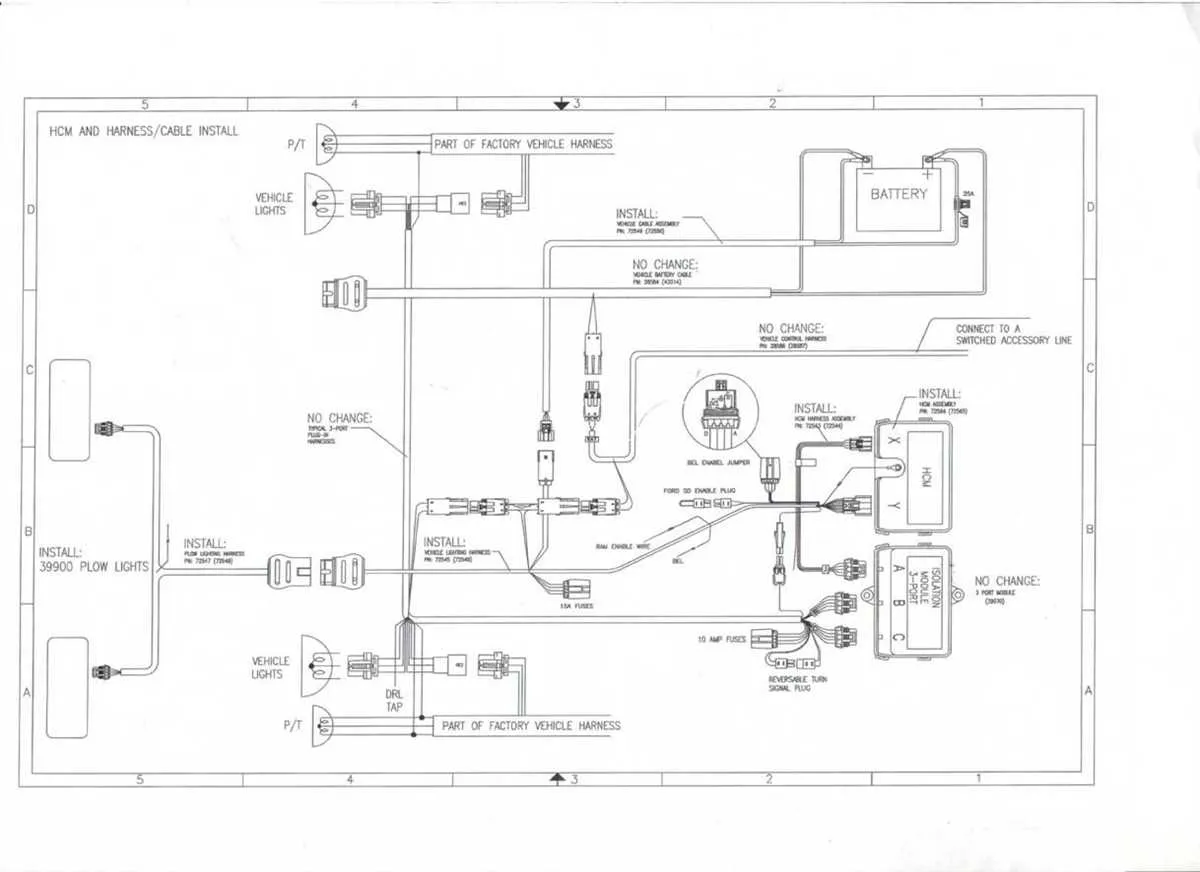
Ensure each component is securely connected to the power source. Use heavy-duty cables capable of handling high amperage without overheating. Start by linking the battery terminals, ensuring they are tightly fastened to avoid power interruptions during operation.
Relay placement is crucial for proper functionality. Position it in a dry, well-protected area to prevent exposure to moisture, which can lead to malfunctions. Make sure to check that the relay contacts are free from corrosion and that all terminals are clean and well-greased.
Grounding is essential for stability. Connect the grounding wires directly to the vehicle’s frame, ensuring a low-resistance path. Never ground to a painted surface; use bare metal for better conductivity.
Verify the hydraulic control lever is properly wired to its respective terminals. Check the harnesses for any signs of wear, and replace them if necessary. Double-check the system’s fuse to make sure it’s rated appropriately for the system’s needs to prevent overloads.
Finally, test the system in a controlled environment before use. Look for any irregularities in the electrical feedback and ensure that all connections are stable, with no signs of flickering or poor performance.
Understanding the Basic Electrical Components of a Snow Removal System
Ensure the power source is reliable. A properly connected battery is essential for consistent operation. Make sure the battery is securely mounted, and terminals are clean and free of corrosion.
Control Unit: This is the interface that allows the operator to control the movement of the blade. Check that the control unit is wired correctly to the solenoids and the actuator. It should be connected directly to the battery to prevent power drops during operation.
Relays and Fuses: These protect your system from overloads. Ensure the relay is properly wired to the battery and the control unit. Fuses should be rated correctly to prevent any risk of circuit damage. Always replace a blown fuse with one of the same rating.
Solenoids: These components manage the direction and force of the hydraulic system. They should be connected to both the power source and the control unit. If the solenoid is not functioning, verify its connection and check for any potential damage or dirt that could interfere with its operation.
Actuator: The actuator drives the mechanical parts. Confirm that the actuator is receiving proper electrical input and is free of mechanical blockages. Check all connections for wear and ensure they are tight.
Grounding: Proper grounding is crucial for electrical stability. Ensure all components are grounded to a common point to avoid electrical interference and potential short circuits.
Wiring Harness: The harness should be inspected regularly to ensure that all wires are insulated and routed to avoid exposure to heat or sharp edges. Any damaged wires should be replaced immediately to prevent shorts.
How to Properly Connect the Power Unit to Your Vehicle

Ensure all components are compatible: Before starting, check that your vehicle’s electrical system matches the requirements of the attachment. Most modern vehicles need a specific connector that matches the power unit’s output. Verify the voltage and amperage specifications to avoid overloading your system.
Connect the power leads: Begin by attaching the main positive cable to the vehicle’s battery terminal, ensuring a tight connection to prevent accidental disconnection. Follow by securing the ground wire to a clean, unpainted metal surface on the vehicle’s chassis.
Install the control wiring: Route the control cables from the power unit to the vehicle’s cab. Choose a path that avoids moving parts or high-temperature areas. Use cable ties to secure the wires, preventing them from coming loose or being damaged.
Test the electrical connections: Before finalizing the setup, check the voltage with a multimeter. The power unit should be receiving the correct voltage to function properly. Activate the system and verify that the power unit responds correctly, such as by moving in the expected directions.
Secure all components: Once the connections are verified, ensure all wires are properly insulated and that connectors are waterproof. Tighten all bolts and fasteners, ensuring no part of the system is loose.
Tip: Double-check that all fuses are in place and rated for the power unit to prevent any electrical issues during use. Keep an eye on cable wear, especially after a season of heavy use.
Troubleshooting Common Electrical Issues in Snow Removal Equipment
If the system fails to operate correctly, check the connections for any signs of corrosion or damage. Corroded terminals or worn-out wires can cause poor conductivity, leading to malfunctioning components. Ensure that all connectors are tight and secure.
- Inconsistent Operation: Often caused by loose or corroded connectors. Inspect the power relay and make sure all pins are intact. Replacing a faulty relay can resolve intermittent functionality.
- Motor Not Responding: Verify the battery voltage with a multimeter. If the voltage is low, charge or replace the battery. Check the fuse and replace any blown fuses to restore proper function.
- Control Switch Issues: If the control panel fails to respond, check the wiring harness leading to the switches. Look for any cuts or pinched cables. Clean the switch contacts for better conductivity.
Ensure all ground connections are solid. A poor ground connection can cause a range of issues, including erratic behavior or complete system failure. Tighten any loose ground terminals and clean them if necessary.
- Start with the power source. Test the battery and fuses to rule out power issues.
- Check the control system and wiring for continuity. A multimeter is a useful tool to trace the flow of electricity.
- Inspect the motors and actuators for signs of wear or damage. Replace parts as necessary.
Finally, always use the correct tools and follow the manufacturer’s guidelines when replacing parts. Avoid using aftermarket parts that may not meet the required specifications, as they can lead to further electrical issues.