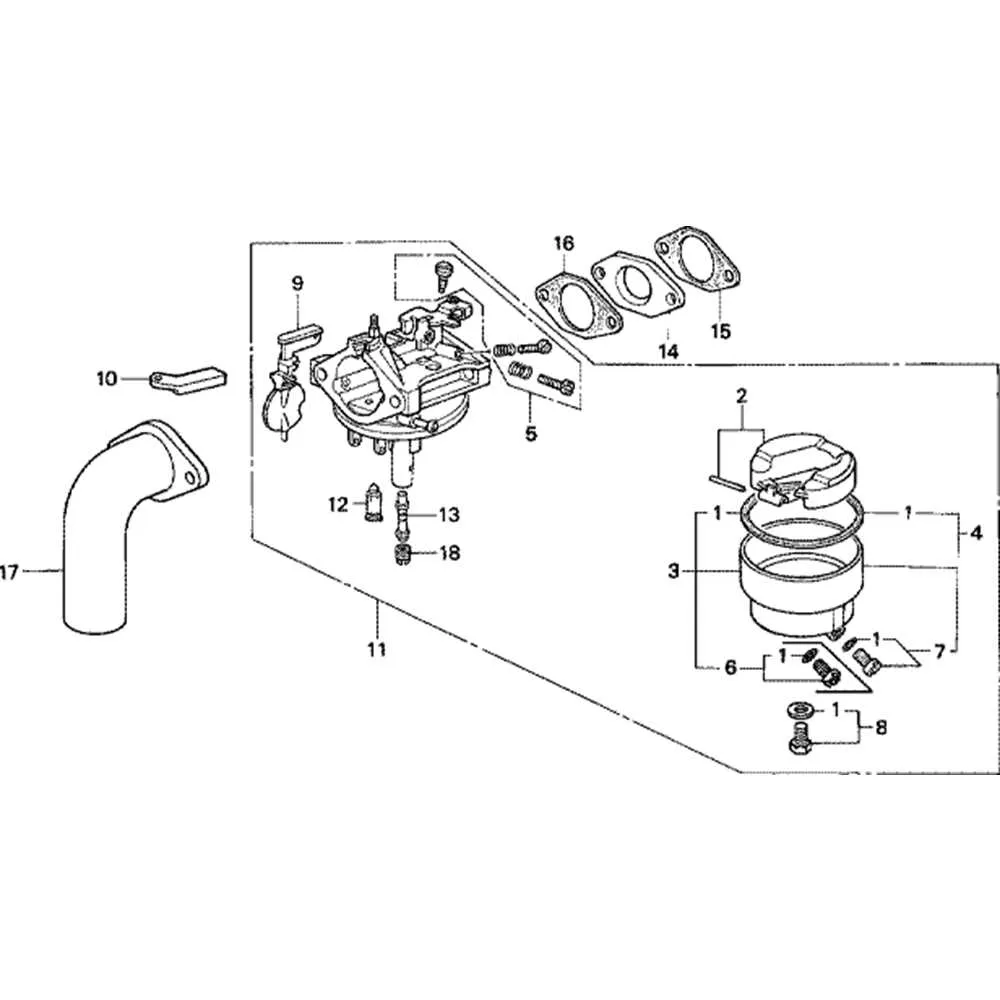
To restore optimal performance, it’s crucial to first identify the components responsible for fuel delivery in small engine systems. If you’re experiencing irregular starting or stalling, the first area to inspect is the fuel system’s intake mechanism, which regulates the flow of gasoline into the engine. Refer to detailed schematics to locate critical parts such as jets, valves, and choke mechanisms.
Ensure that the main components–like the float bowl, needle valve, and air/fuel mixture screws–are free from debris. These elements play a direct role in the engine’s fuel efficiency and power output. Once you pinpoint the exact assembly, check for any clogging or wear that might obstruct fuel flow.
After cleaning, adjust the screws to match the manufacturer’s recommended settings. This will help restore smooth engine operation and prevent issues like flooding or hesitation during acceleration. Accurate calibration is key to maintaining fuel efficiency and engine longevity.
For optimal troubleshooting, always refer to specific technical schematics available for the engine model you’re working with. These diagrams provide a clear overview of how each part fits into the overall assembly and assist in identifying potential issues that might affect performance.
Understanding the Engine Fuel System Components
For accurate repairs, focus on the key elements like the fuel intake valve, choke, and air-fuel mixture control. Begin by identifying the flow paths of air and fuel within the engine’s intake system. Proper alignment of the intake valve and the choke is critical for ensuring the optimal air-to-fuel ratio during startup and operation.
Fuel flow adjustment: Start by inspecting the fuel shut-off valve to confirm it’s working smoothly. A clogged valve can restrict fuel delivery, causing starting issues or poor engine performance. Clean or replace the valve if necessary.
Mixture control and adjustment: The air-fuel mixture screw, typically found near the intake manifold, regulates the balance between fuel and air for idle and full-speed performance. Adjust it for smooth idling and consistent throttle response.
Choke operation: Check the choke linkage for proper operation. A malfunctioning choke can prevent the engine from receiving the right amount of air during cold starts, leading to stalling. Lubricate the linkage to ensure it opens and closes freely.
Inspect the float bowl for debris, as it can disrupt the fuel supply. Clean the bowl thoroughly and check the float needle for proper sealing to prevent leaks or flooding.
Understanding the Key Components of Small Engine Fuel Systems

Ensure optimal performance by recognizing the main elements that control fuel mixing and delivery in your engine. These components influence combustion efficiency and smooth operation.
- Fuel Bowl: Holds the fuel before it’s mixed with air. A properly functioning fuel bowl ensures consistent delivery and helps prevent leaks.
- Throttle Plate: Regulates the airflow into the engine by adjusting its position. A worn or misaligned throttle plate can cause inconsistent engine speed.
- Jet(s): Control the amount of fuel entering the air stream. If clogged, it can lead to fuel starvation or flooding. Regular cleaning is crucial.
- Choke: Adjusts the air/fuel mixture during startup by restricting air intake. Be mindful of choke settings, as improper use can lead to poor starting performance.
- Needle Valve: Controls the flow of fuel from the fuel tank into the fuel bowl. A malfunctioning needle valve can cause flooding or insufficient fuel delivery.
Examine these parts regularly and replace any worn or damaged components to maintain proper fuel flow and engine operation.
Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnosing Fuel System Problems
Step 1: Check the fuel quality. If the engine isn’t starting or is sputtering, old or contaminated fuel might be the issue. Drain the fuel tank and replace it with fresh fuel to eliminate any potential blockages caused by impurities or ethanol separation.
Step 2: Inspect the air intake. Blocked air filters are a common cause of poor performance. Remove the filter and clean it or replace it if it’s excessively dirty. A clean filter ensures proper airflow for optimal combustion.
Step 3: Examine the throttle linkage. Ensure the throttle is moving freely and is not stuck in a closed position. A malfunctioning throttle can cause the engine to stall or fail to accelerate properly.
Step 4: Test the fuel flow. Disconnect the fuel line and use a container to catch any fuel that flows from the tank. If fuel doesn’t flow freely, there might be a blockage in the line or a clogged fuel valve that needs to be cleaned or replaced.
Step 5: Inspect the choke mechanism. A faulty choke can prevent the engine from starting or cause rough running. Check if the choke is functioning smoothly and is fully opening and closing as needed.
Step 6: Clean the needle valve and seat. If the fuel mixture is too rich or too lean, the needle valve may be clogged. Clean it thoroughly with a suitable solvent to ensure proper fuel delivery.
Step 7: Check for air or fuel leaks. Small cracks in the fuel lines or gaskets can cause air or fuel to escape, leading to poor performance. Inspect the entire fuel system for any visible cracks or leaks and replace damaged parts.
Step 8: Test the ignition system. A weak spark can cause misfires or difficulty starting the engine. Check the spark plug for carbon buildup or wear, and replace it if necessary.
Step 9: Reset the settings. If adjustments were made to the fuel mixture or idle screws, reset them to factory settings as a baseline. Minor adjustments can be made later for fine-tuning.
Step 10: Reassemble and test. After completing the above checks and repairs, reassemble the components and test the engine. Make sure it runs smoothly and check for any irregularities that might indicate further issues.
How to Replace or Clean the Engine Carburetor

Ensure the engine is turned off and completely cool before starting any repair work. Disconnect the spark plug wire to prevent accidental starts while working on the engine.
For Cleaning: Remove the air filter cover and disconnect the fuel lines from the intake system. Take out any screws holding the assembly in place, and carefully detach the intake system from the engine. Use a carburetor cleaner to remove debris and fuel residue from all internal parts. Let it sit for a few minutes before using a soft brush or compressed air to clean the small passages. Reassemble the system once the components are dry.
For Replacement: Once you’ve removed the intake assembly, disconnect the choke and throttle linkages. Carefully unbolt the carburetor and remove it from the engine. Before installing a new part, ensure it matches the engine model specifications. Place the new carburetor in position, and secure it with the bolts. Reconnect the linkages, fuel lines, and air filter cover.
After Installation: Reattach the spark plug wire, add fresh fuel, and start the engine. Monitor its performance to ensure the new part is functioning correctly, and check for any fuel leaks. If necessary, fine-tune the throttle and choke settings for optimal engine operation.