If you’re troubleshooting electrical issues in your vehicle, begin by examining the distribution blocks and circuit mapping. Ensure you have the correct reference materials for pinpointing which connections control specific functions. It’s crucial to familiarize yourself with the layout to avoid unnecessary errors during repair.
Start by locating the primary system access points, as they often house the critical connectors for both the cabin and engine compartment. Detailed circuit illustrations will give you clarity on how each wire and terminal is positioned, helping you to prevent costly mistakes when addressing issues like power outages or malfunctioning components.
Key areas to check: Central relay clusters, backup power sources, and emergency shut-off systems should be among your first points of interest. These are typically where failures occur, especially when wiring suffers from wear or poor contact. Make sure to verify each section for proper current flow and continuity.
Having a complete visual of your system’s configuration is essential. Be sure to verify all connections against the relevant charts, and double-check the integrity of the grounding wires. Not all issues stem from the obvious failures–small faults can lead to larger problems if not addressed promptly.
Electrical Circuit Layout and Troubleshooting
If you’re troubleshooting the electrical system, start by checking the primary circuit location under the dashboard and near the engine compartment. These areas house essential relays and connection points for critical systems. To simplify diagnostics, follow these steps:
- Inspect the main relay box near the driver’s side, usually located close to the steering wheel.
- Check for any visible signs of wear, such as corrosion or burnt terminals, which could indicate issues with power distribution.
- Ensure all connections are secure, particularly those related to the ignition, lighting, and air conditioning systems.
For systems requiring specific attention, such as lighting or airbags, locate the secondary distribution unit in the engine bay. These locations often feature dedicated sections for high-demand components.
- Air conditioning units are typically found in the upper-left sections of the engine bay.
- Lighting controls and engine management often share a section near the front of the vehicle.
- Check for any missing or blown protection devices to prevent electrical surges from damaging vital components.
Always replace faulty components with the correct ratings, as undersized or mismatched parts may lead to further malfunctions. Consult specific component manuals for exact replacement specifications to ensure compatibility with your system’s requirements.
Understanding the Electrical System Layout and Components

When troubleshooting electrical issues in a large vehicle, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with the exact configuration of the central power distribution system. The layout typically includes multiple circuits, each responsible for powering various components such as lights, engine systems, and auxiliary features. Knowing which circuit controls what can save time and prevent unnecessary replacements.
Key Components:
- Main Power Supply: This section directs current to the primary vehicle systems, such as ignition and power steering.
- Auxiliary Circuits: These smaller, secondary circuits manage systems like air conditioning, dashboard electronics, and accessories.
- Relays: Often located near the center, relays act as switches that control high-current components from low-power sources.
- Breakers: These provide overcurrent protection to prevent electrical damage from surges.
Always verify the amperage rating for each circuit to avoid overloads. When identifying faults, use a multimeter to check continuity and inspect for any signs of corrosion or damage to connectors. If a certain component stops functioning, check its dedicated circuit first before assuming the problem is with the part itself.
Common Issues:
- Blown Fuses: Common when circuits are overloaded, easily replaceable but ensure the root cause is identified.
- Loose Connections: Corroded or disconnected wires can lead to intermittent power loss.
Consult your vehicle’s manual for a detailed layout of each section to understand its purpose better and maintain a functional electrical system.
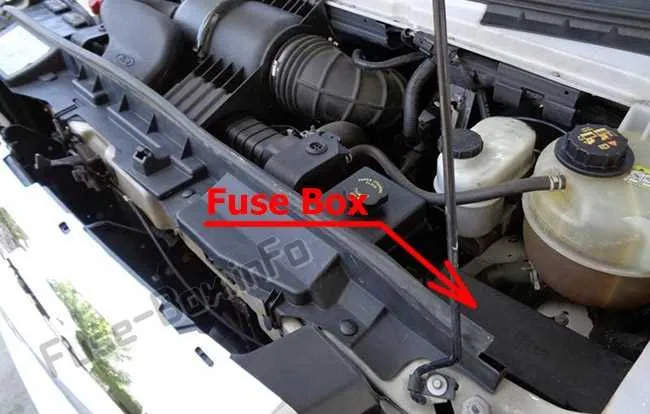
How to Locate and Identify Specific Fuses on the Ford e450
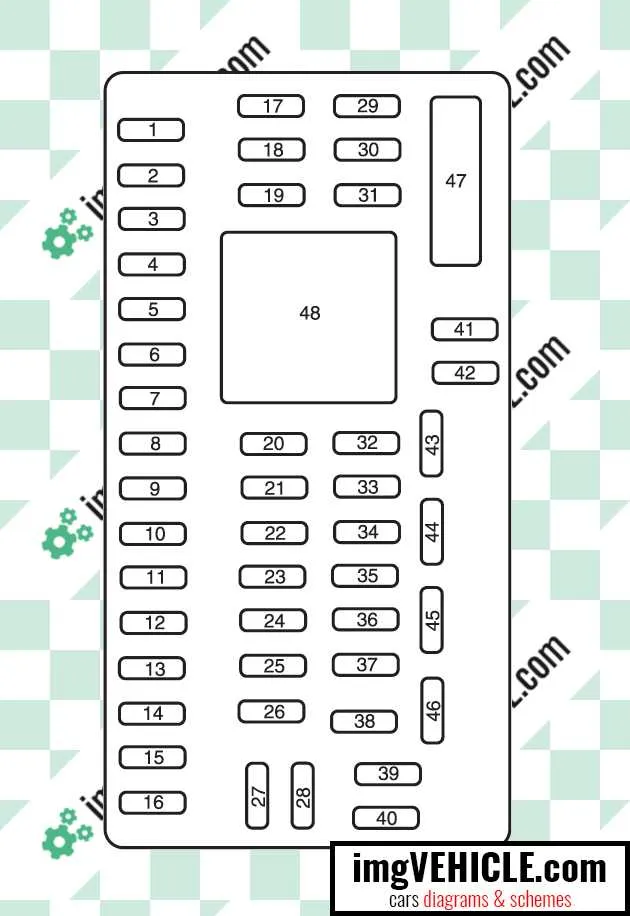
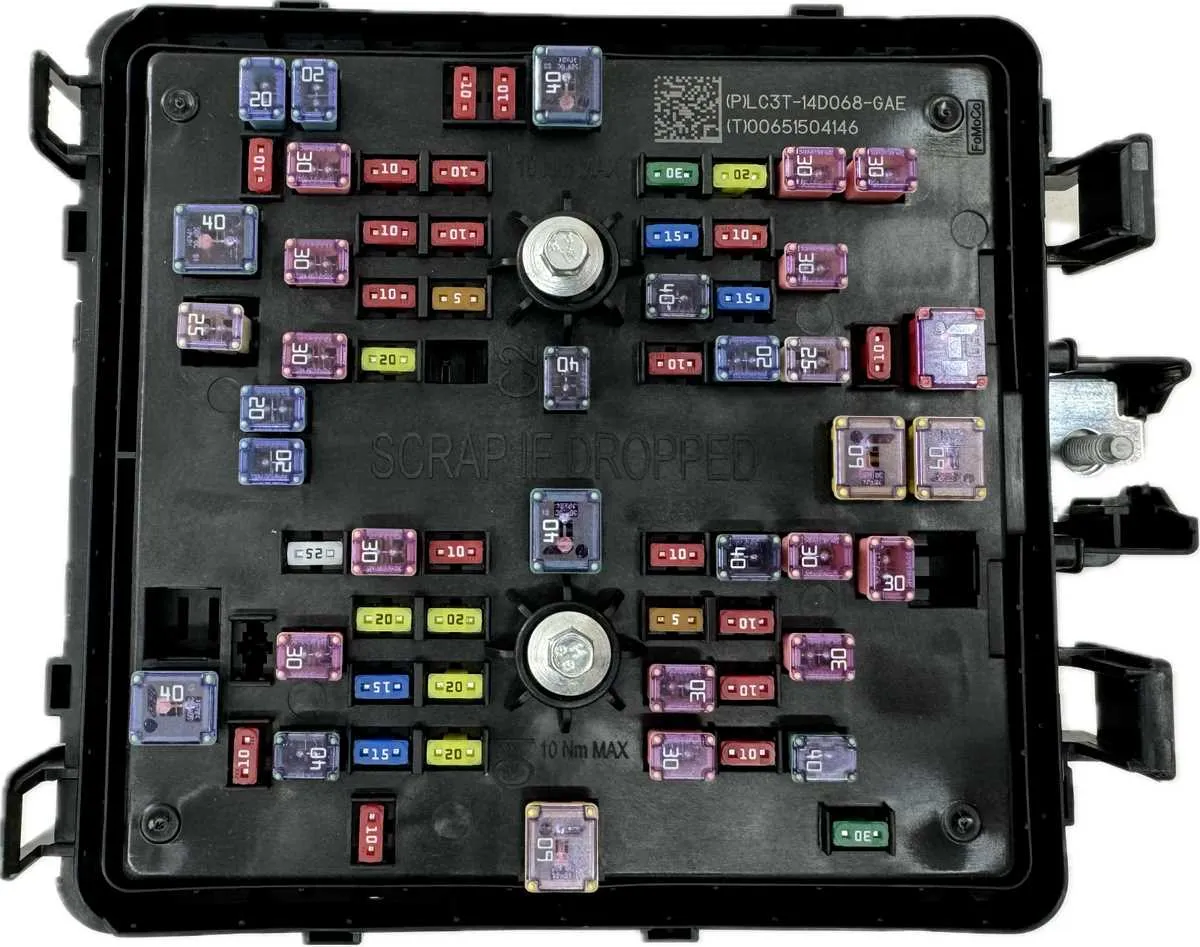
To identify a specific component in the electrical system, first refer to the vehicle’s manual, which includes the detailed circuit allocation for each part. Typically, the main unit can be found near the driver’s side or under the dashboard, but some models have secondary locations in the engine compartment.
Start by checking the cover for a printed map, indicating the layout and function of each component. If the guide is missing or unreadable, you can often find it by cross-referencing the vehicle model year and electrical system layout online. Knowing the approximate location of the component will help narrow down your search to the relevant area.
For a more precise identification, remove the cover and observe the numbers or labels near each connection. These will correspond to a particular function, often related to lighting, air conditioning, or ignition. In some instances, you might need to use a multimeter or continuity tester to verify which one is faulty.
If unsure, you can check the component’s continuity with a tester. If the electrical path is open, the unit is faulty. Always replace damaged units with the same amperage rating to avoid overloading the system.
Troubleshooting Common Electrical Issues in the Vehicle
Check the power distribution unit: If your vehicle experiences electrical problems, the first step is to inspect the power distribution unit. Look for any burnt or damaged connections that could indicate a malfunctioning circuit. Pay particular attention to the larger components, as they may overheat and cause issues.
Inspect the connections: Loose or corroded terminals can create intermittent electrical problems. Ensure that all wiring harnesses are securely connected, and use a multimeter to verify the voltage at each terminal. Corrosion can often be cleaned with a wire brush or a cleaning solution designed for electrical contacts.
Look for blown links: A key indicator of an electrical issue is a blown link, especially if specific systems stop functioning. Always replace a faulty link with one of the correct rating. Using a link that is not rated for the proper amperage can cause further damage to the system.
Verify ground connections: Poor ground connections are a common cause of erratic behavior in electrical systems. Ensure that all ground straps are intact and properly attached to the chassis. A poor ground can result in electrical components not receiving proper power.
Test the relay circuits: Relay malfunctions can also lead to power issues. Use a diagnostic tool to check if the relays are functioning properly. If a relay is suspected to be faulty, replace it and recheck the system’s operation.
Examine the wiring for short circuits: A short circuit can cause a system to fail entirely. Trace the wiring for any exposed or frayed cables that might be causing an unintended connection. If a short is identified, repair or replace the wiring as necessary.
Check for overloads: If too many components are drawing power simultaneously, it can overload certain circuits. Ensure that each system is drawing the appropriate amount of power. Consider upgrading the power distribution system if you consistently encounter overload issues.
Ensure proper fuse ratings: Always use fuses with the correct amperage rating for each circuit. A fuse that is too large can fail to protect the system, while one that is too small may blow prematurely. Consult the vehicle’s service manual for the correct fuse ratings for each circuit.