If you’re experiencing issues with electrical components in your vehicle, understanding the layout of the power distribution panel is crucial. This guide will help you identify the correct circuits and troubleshoot any problems efficiently.
Start by locating the primary panel, usually positioned beneath the dashboard or near the engine compartment. Ensure all connections are secure, and verify that no relays or terminals are damaged. Each fuse controls specific functions such as lighting, air conditioning, or power windows, so pinpointing the right one will save you time.
Important note: Always replace blown fuses with the same amperage rating to avoid causing further damage to the system. If the fuse continues to blow, it might indicate an underlying electrical fault that requires professional inspection.
Additionally, some models feature a secondary control unit in the engine bay, designed to handle high-demand systems like the alternator and ignition. Make sure to check both locations if you’re dealing with multiple issues.
Refer to your vehicle’s manual for an exact layout, but generally, these panels are marked clearly to assist you in making the right repairs. For detailed information on which fuse controls which system, consult a reliable schematic for your specific model.
Electrical Component Layout for F-250 Model
For efficient troubleshooting and repairs, refer to the electrical layout of the vehicle’s main control unit, located under the dashboard and engine compartment. Ensure the relays and circuit breakers are correctly mapped according to the specific location guide to prevent issues like blown circuits or faulty wiring. Keep a replacement list for fuses near the manual for quick reference during maintenance tasks.
Inside the cabin, the first compartment holds the central power distributor, while the second, often in the engine bay, manages more high-powered components. Check each location carefully for any damage to connections and replace components based on the specific amperage requirements listed in the manual. This ensures the longevity of the electrical system and reduces the likelihood of system failures.
Consult the vehicle’s service manual for precise pin assignments and wiring pathways if further diagnostics are needed. Always double-check connections to avoid unnecessary damage or overloads in the system. Additionally, consider keeping a few spare elements on hand in case of sudden electrical faults, especially during off-road or harsh environmental conditions.
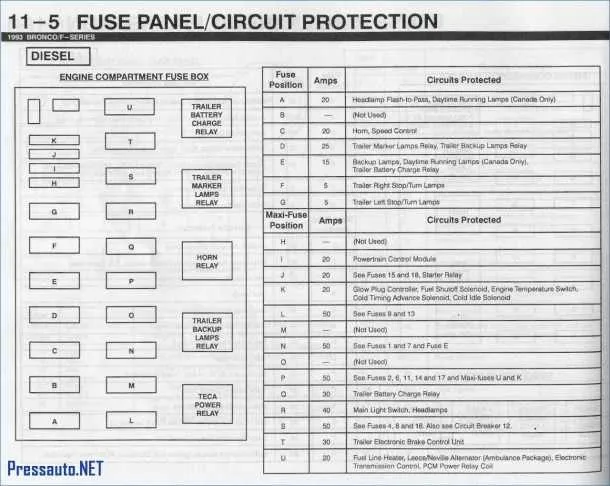
Identifying the Electrical Component Locations in the Vehicle’s Power Distribution Unit
To locate the necessary fuses for each system in your vehicle, begin by inspecting the main distribution panel under the dashboard on the driver’s side. This panel holds key electrical elements crucial for everyday vehicle functions.
- Interior lighting: Fuse #15
- Power windows: Fuse #20
- Air conditioning: Fuse #25
- Horn: Fuse #30
For external systems, such as headlights and wipers, check the rear compartment assembly. The exact fuse positions are marked directly on the panel cover or can be referenced through the vehicle’s manual.
- Headlights: Fuse #10
- Windshield wipers: Fuse #18
- Brake lights: Fuse #12
Ensure each fuse is securely seated in its socket and inspect the wire connections for any signs of wear or corrosion.
Understanding the Purpose of Each Fuse in the Fuse Box
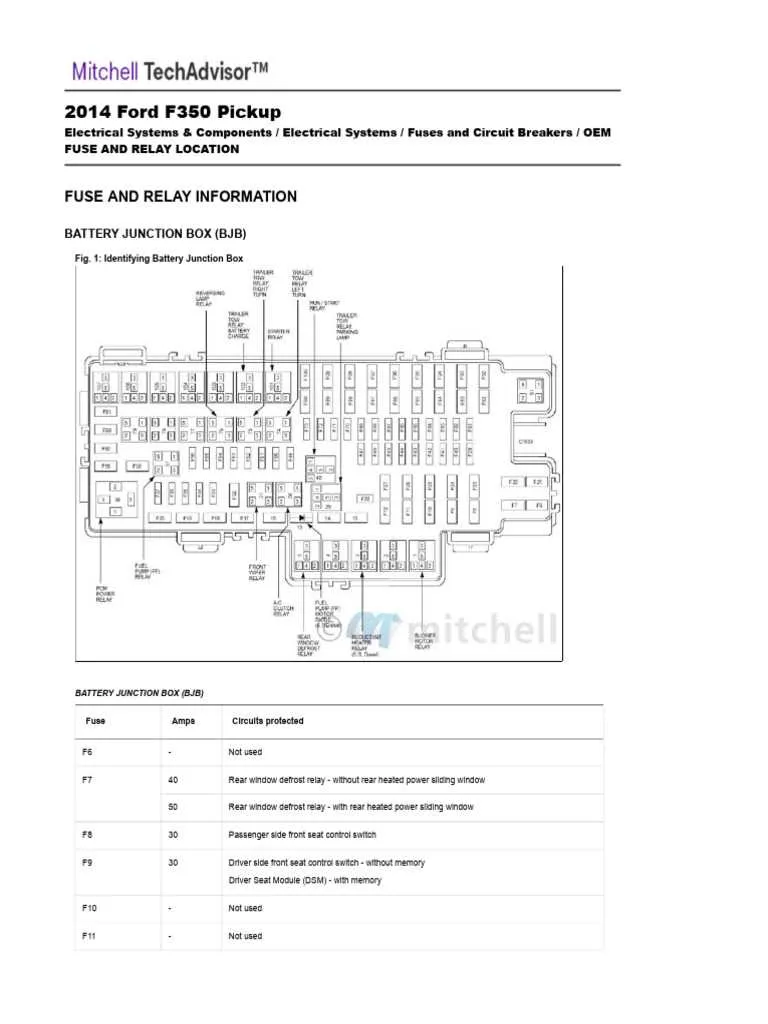
The electrical system in your vehicle relies on individual circuits to power various components. Each circuit is protected by a specific safety element that helps prevent damage due to overload or short circuits. Understanding which circuit each safety component protects is crucial for troubleshooting and repairs.
The safety components are typically assigned to specific vehicle systems like lighting, HVAC, infotainment, and critical engine parts. To locate a malfunctioning circuit, identify the corresponding safety element by its rating and position in the panel. A blown safety element often indicates an issue with the associated system, such as a malfunctioning relay or wiring problem.
For example, if the interior lights fail to work, check the corresponding safety element for that circuit. If it’s blown, replacing it should restore function. Similarly, components like windshield wipers, power windows, or the radio often have their own dedicated protection circuits. Each one can be checked and replaced independently to avoid unnecessary repairs to the entire system.
In case of repeated failures, consult the vehicle’s manual for a detailed list of each protection element and its purpose. Ensure that the replacement matches the original specifications to maintain optimal operation. Pay attention to the amperage rating to avoid electrical damage. Incorrect replacements can cause further damage to the system or even lead to fire hazards.
Regular inspection and testing of the protective components can help detect issues early, saving you time and money on repairs. Knowing exactly which component is being protected allows for more accurate diagnostics, leading to faster resolutions when issues arise.
How to Replace Fuses in the Vehicle’s Electrical System
To replace a blown fuse in the vehicle’s panel, start by locating the panel and opening it. Most of the time, this is located under the dashboard on the driver’s side or inside the engine compartment. The panel cover is often secured with clips or screws, so use a screwdriver or simply pull it open depending on the model.
Once you have access to the fuses, use a fuse puller tool, which is usually included in the vehicle’s toolkit, or a pair of needle-nose pliers. Grasp the defective fuse and gently pull it out of its slot. Be cautious not to damage the surrounding fuses or connectors while removing it.
Check the fuse’s condition before installing a new one. A blown fuse typically has a broken filament or is visibly discolored. Ensure you replace it with one of the correct amperage, which can usually be found in the vehicle’s manual or on the fuse panel cover itself.
Insert the new fuse carefully into the empty slot. Make sure it fits snugly and is aligned with the correct orientation. After replacement, check if the electrical system is working properly by testing the circuit that was previously malfunctioning.
If the new fuse blows immediately, it may indicate a deeper electrical issue, such as a short circuit. In such cases, it’s best to consult a professional technician for further diagnosis.