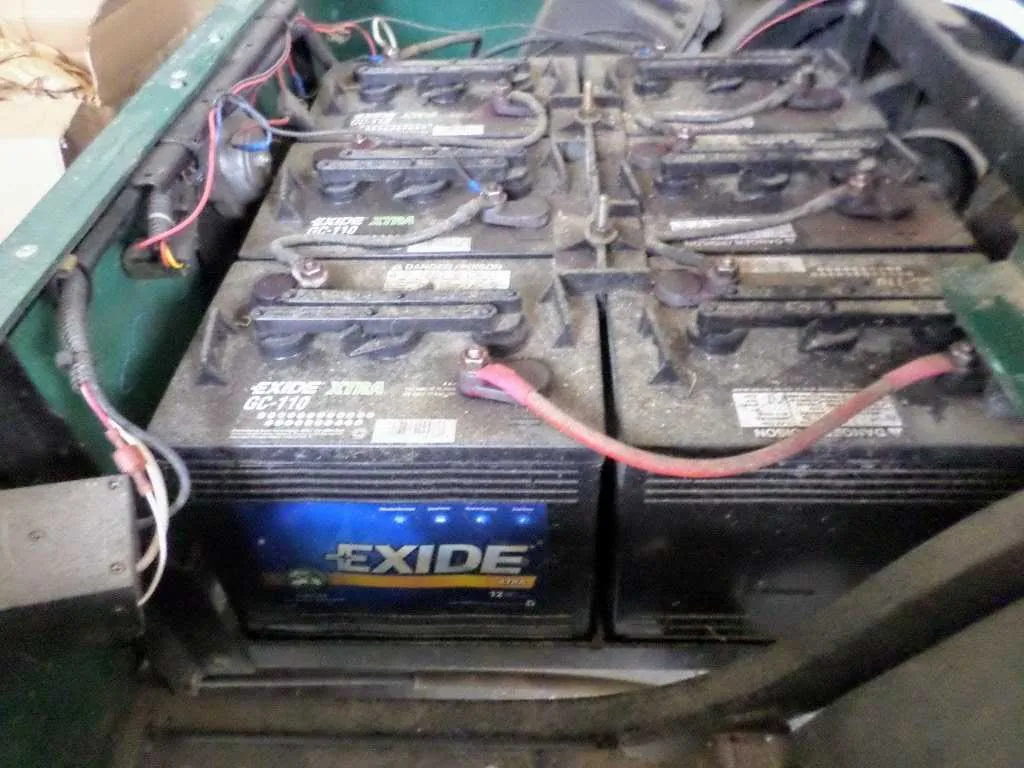

To ensure optimal performance of your vehicle’s electrical system, follow this precise wiring method. Start by identifying the positive and negative terminals on each energy source. The correct connection between these components ensures a seamless flow of current, preventing issues like power loss or short circuits.
Step 1: Begin by linking the positive terminal of the main power source to the first connector. This will serve as the primary input for the power flow. Once connected, verify that the link is secure and there are no visible signs of wear.
Step 2: The negative terminal should then be properly connected to the ground point. Ensure this connection is tight and well-insulated, as it serves as the return path for the electrical flow, minimizing the risk of electrical interference.
Step 3: Double-check all connections before activating the system. Poor connections or loose wires can lead to inefficient operation or even system failure. Test the vehicle’s power levels after setup to confirm all components are working properly.
Wiring Setup for Electric Vehicle Power System
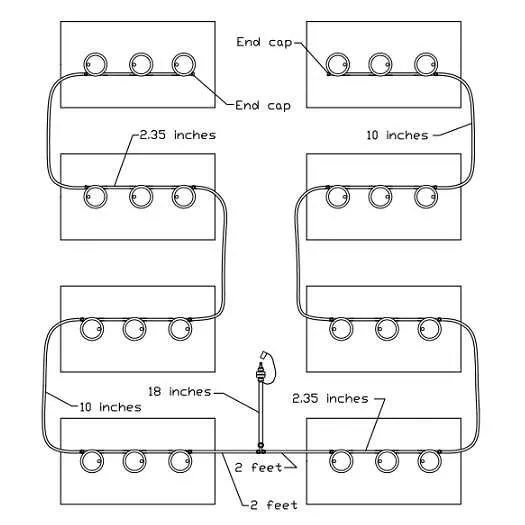
For an efficient and safe power distribution in your electric vehicle, follow these steps to ensure the correct configuration of your power cells:
- Start by connecting the positive terminal of the first cell to the corresponding terminal of the second one using a thick cable. This ensures proper current flow between the units.
- Next, link the negative terminal of the last unit in the series to the main frame ground or the dedicated negative connector.
- The main connection to the power distribution system should come from the positive terminal of the final unit, ensuring that the energy supply is stable and reliable.
- Ensure that all connections are secure, free from corrosion, and are tightly fitted to prevent energy loss or potential hazards.
After completing these steps, always verify the entire power setup with a multimeter to check for any inconsistencies or short circuits. Safety checks are crucial before powering up the system.
Understanding Terminal Connections and Setup
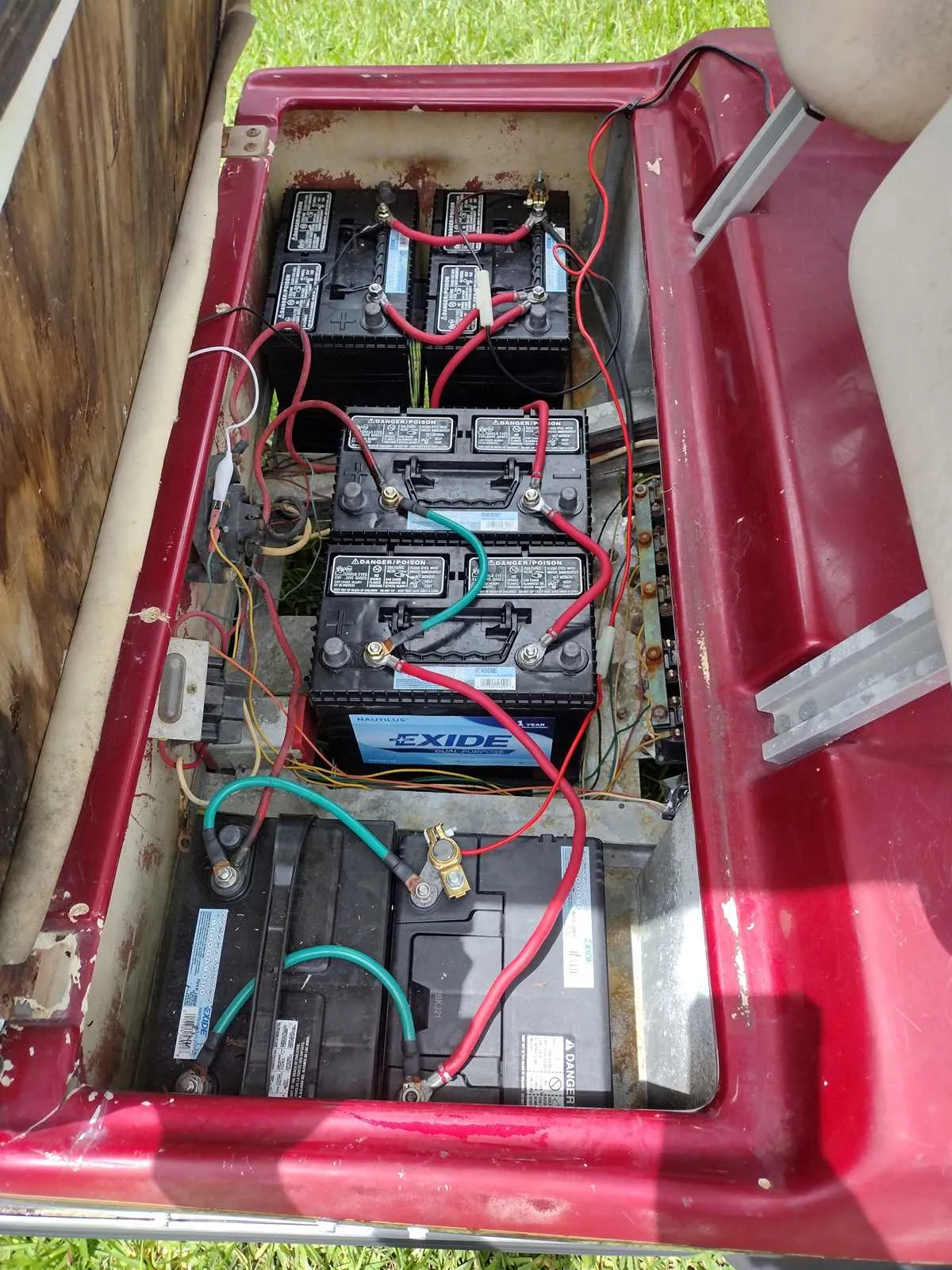

Start by identifying the positive and negative terminals. The positive terminal is typically marked with a “+” sign and often features a red cable. The negative terminal is marked with a “-” sign, usually paired with a black cable. Always connect the positive terminal first to avoid accidental short circuits.
Proper Sequence: Always connect the positive terminal before the negative one. This minimizes the risk of sparks or electrical mishaps. When disconnecting, reverse the order–negative first, followed by positive. This ensures safety and prevents damage to the system.
Connection Quality: Ensure that all connections are tight and free from corrosion. Loose or corroded terminals can cause inefficient power flow, leading to reduced performance and potential overheating. Regularly check for any signs of wear on cables and connectors.
Key Tip: Use anti-corrosion paste on terminals to reduce oxidation and enhance the longevity of the connections. This simple step improves the efficiency and reliability of the entire power system.
Step-by-Step Guide to Wiring the Power Sources
1. Prepare the Tools and Materials: Ensure you have all necessary items: connectors, cables, terminal lugs, wrenches, and insulated gloves for safety. Check if the power sources are properly discharged before beginning the installation.
2. Connect Positive Terminals First: Start by attaching the positive leads to each unit. Use the proper size cables and securely tighten each connection with a wrench. The positive terminals are usually marked with a “+” sign or red color.
3. Secure the Negative Terminals: After connecting the positive terminals, move on to the negative ones. Be sure that the negative terminals are connected to the frame or the designated common point in the power setup. This ensures proper grounding.
4. Link Units in Series: For units connected in series, ensure that the negative terminal of one unit is linked to the positive terminal of the next. This forms a continuous electrical circuit and increases the overall voltage.
5. Double-Check All Connections: Once all connections are made, verify each one. Ensure that the cables are securely tightened, and there is no loose wiring that could cause a short circuit.
6. Insulate Exposed Contacts: Use appropriate insulating materials to cover any exposed metal on terminals or connectors to prevent accidental short-circuits.
7. Test the System: After completing the wiring, power up the system and check for functionality. Monitor the voltage and ensure each component is operating correctly. If there is an issue, inspect the connections once again.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips
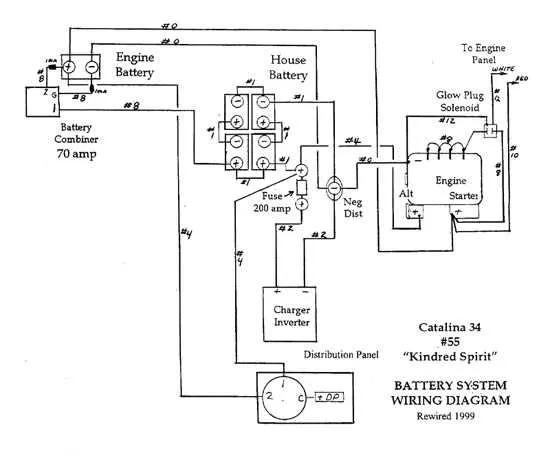
Check the voltage regularly. If the power unit is not turning on, verify if all connections are secure and corrosion-free. Loose or dirty terminals are a common cause of poor power delivery.
If your ride is sluggish or not maintaining charge, ensure that each cell in the power pack is providing the right output. A single underperforming cell can affect the entire system.
For persistent issues, measure the voltage with a multimeter to identify weak or dead cells. If any cell falls below the required voltage, it should be replaced to prevent further damage to the system.
If the system is not holding a charge, ensure that the charger is functioning properly. A faulty charger may cause the unit to not reach full charge, leading to performance issues.
Inspect the wiring for wear, fraying, or signs of overheating. Damaged wires can cause intermittent power issues or failure to start.
Check the connections for signs of rust or corrosion, especially in high-humidity environments. Clean the terminals using a wire brush and a mixture of baking soda and water to remove any build-up.
When the unit does not accelerate or responds slowly, verify that the motor and speed controller are in good condition. Issues with the controller or motor can result in delayed or unresponsive movement.
Ensure the fuse is intact. A blown fuse can prevent the system from starting, and replacing it can restore normal function.