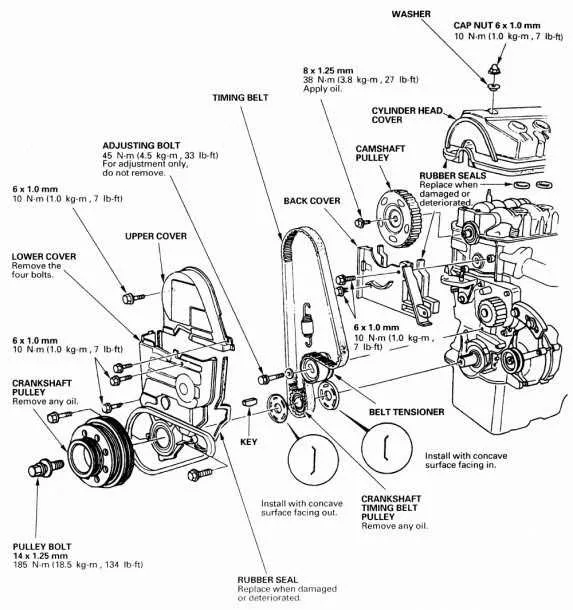
For anyone working on a mid-size sedan, understanding the layout of internal mechanical elements is crucial for efficient maintenance and repair. Knowing the specific location and function of each major component ensures you can diagnose issues quickly and accurately. For best results, refer to a comprehensive visual reference that clearly marks each segment of the mechanical system. These references are invaluable for both professional mechanics and DIY enthusiasts.
Timing mechanisms, pistons, and the fuel system all play essential roles in the proper functioning of a vehicle’s drivetrain. Recognizing their interconnections and being able to locate each one swiftly can save you significant time. Start by identifying the key features: the main block, the camshaft setup, and the accessory belt. These elements must be in alignment to guarantee smooth operation and prevent future malfunctions.
Every part has a designated role that is vital to the vehicle’s overall performance. Pay particular attention to the cooling and lubrication systems, as they keep the components from overheating and reduce wear over time. Regular maintenance of these parts is often overlooked, yet it is one of the most cost-effective ways to extend the vehicle’s life.
Key Components of a Vehicle’s Powertrain
For optimal performance, regularly inspect the timing belt and the crankshaft for wear. Ensure the camshaft is aligned properly to avoid misfiring. Replace the cylinder head gaskets if you notice any leakage or loss of compression, as this can drastically affect engine efficiency.
The fuel injection system must be free from clogs, so clean or replace the fuel injectors as needed. It’s critical to check the pistons for any signs of cracking or scoring, as this can lead to significant damage and loss of power.
Monitor the cooling system, focusing on the radiator and water pump. Overheating often stems from a failing water pump or a clogged radiator. Inspect the exhaust manifold for cracks or signs of excessive heat, as these can lead to poor fuel economy and engine stress.
Ensure the spark plugs are firing correctly and replace them at the manufacturer’s recommended intervals. A faulty ignition coil can lead to misfires, affecting overall performance and fuel consumption.
Lastly, regularly change the oil filter and ensure the oil is clean. This will prevent sludge build-up, which can clog vital channels and hinder the flow of lubricants to moving parts. Keep the crankcase ventilation system in check to avoid pressure buildup, which can affect the engine’s ability to function smoothly.
Understanding the Layout of Engine Components
When examining the layout of key components under the hood, focus on the main assemblies and their interconnections. The power unit consists of several crucial elements that work together seamlessly to ensure optimal performance.
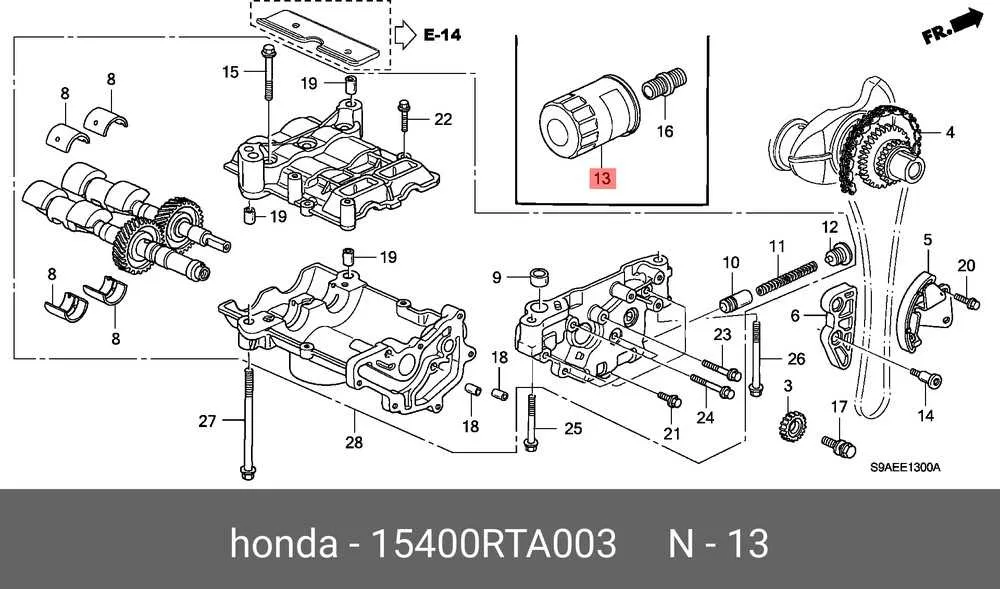
Start with the block which houses the cylinders. This is the core where combustion takes place. Located centrally, it forms the foundation of the entire setup. Surrounding it are the valve train elements, including the camshaft and the rocker arms. These parts control the intake and exhaust valves, ensuring proper airflow at each phase of operation.
Timing belts or chains are connected to the camshaft, playing a pivotal role in synchronizing the opening and closing of the valves with the piston movement. This timing mechanism is essential for efficiency and avoiding interference between moving parts.
The crankshaft is mounted at the base, converting the linear force from the pistons into rotational energy. Alongside, the connecting rods link the pistons to the crankshaft, transferring the combustion energy. These rods are designed to withstand immense stress, and their durability is vital for long-term functionality.
One critical part of the system is the cooling system, including the radiator and thermostat. These components ensure the entire setup maintains a safe operating temperature by circulating coolant fluid. The proper operation of the thermostat, in particular, ensures that the engine reaches the ideal temperature quickly and stays there during use.
Finally, the intake manifold and the exhaust system are strategically placed to regulate airflow into and out of the cylinders. Properly calibrated, these systems maximize fuel efficiency and minimize emissions.
Key Components in the Powertrain and Their Functions
The crankshaft plays a critical role in converting the linear motion of pistons into rotational force. Positioned at the base of the motor, it transfers power to the transmission system, enabling vehicle movement. Regular inspection for wear and tear is crucial to prevent costly failures.
The camshaft controls the timing of valve openings and closings. It ensures that the air-fuel mixture enters the combustion chamber at the right moment. A malfunctioning camshaft can lead to poor engine performance, increased fuel consumption, and emissions. Regular valve lash adjustments are necessary to maintain optimal engine timing.
The timing belt synchronizes the camshaft and crankshaft, ensuring proper valve movement relative to the piston cycle. A broken timing belt can result in severe engine damage, especially if the valves collide with the pistons. Routine inspection and replacement according to manufacturer intervals are essential for longevity.
The intake manifold directs the flow of air into the combustion chamber. It ensures even distribution, allowing each cylinder to receive an adequate air-fuel mix. Over time, buildup of carbon deposits can restrict airflow, reducing efficiency and power. Regular cleaning is advised to maintain performance.
The fuel injectors spray a precise amount of fuel into the combustion chamber, contributing to a stable air-fuel ratio. Clogged or malfunctioning injectors can lead to misfires, reduced power, and poor fuel economy. It’s recommended to use fuel additives periodically and replace injectors when necessary to avoid such issues.
The ignition system, including spark plugs and coils, ignites the air-fuel mixture within the cylinders. Worn or faulty components can result in incomplete combustion, affecting acceleration and increasing emissions. Inspecting and replacing spark plugs at recommended intervals ensures efficient ignition and optimal engine function.
The oil pump circulates lubricating oil throughout the motor, reducing friction and cooling moving components. A failing pump can lead to overheating and rapid component wear. Routine oil changes and using the correct viscosity oil are essential to maintain proper circulation and prevent engine damage.
The exhaust system directs harmful gases away from the motor and reduces emissions. The catalytic converter plays a key role in this by converting toxic substances into less harmful compounds. A clogged or damaged exhaust system can decrease engine efficiency and increase emissions. Regular inspection is crucial for maintaining optimal function.
Common Issues with Engine Components and How to Identify Them
Frequent issues with key components can lead to decreased performance and efficiency. Here are some of the most common problems and tips for identifying them:
- Excessive Oil Consumption: Often caused by worn-out piston rings or faulty valve seals. Look for signs like blue smoke from the exhaust or frequent oil top-ups.
- Overheating: A faulty cooling system, including issues with the radiator or thermostat, can result in overheating. Check for high temperature readings on the dashboard or coolant leaks under the vehicle.
- Misfires: This could indicate faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, or fuel injectors. You may notice rough idling, engine stuttering, or poor acceleration.
- Loss of Power: A clogged air filter or damaged fuel pump can restrict airflow or fuel delivery. Symptoms include sluggish acceleration or poor performance during highway driving.
- Oil Leaks: Seals or gaskets may degrade over time, causing oil leaks. Check for visible oil spots under the vehicle or dark oil residue around the engine bay.
For accurate diagnosis, perform a visual inspection and use a diagnostic scanner if necessary. Regular maintenance and addressing issues early can prevent major repairs and extend the lifespan of the vehicle.