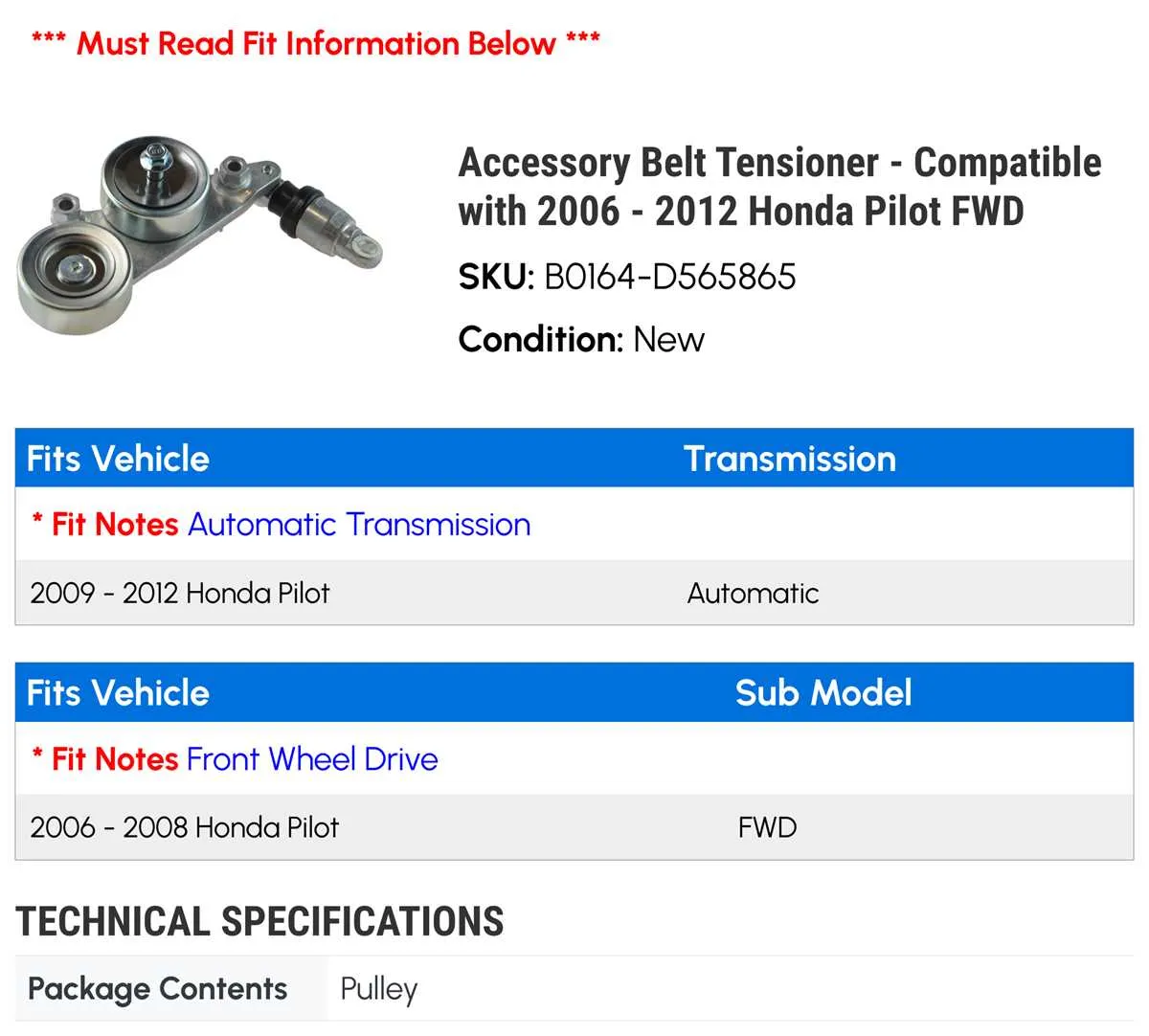
When troubleshooting or replacing components in the engine of your vehicle, it’s crucial to have a clear understanding of the accessory drive system. A visual reference for the pulley and tensioner setup can help streamline the repair process. Identifying the correct routing pattern for the main drive component is essential for proper function, avoiding damage to engine parts, and ensuring that all accessories receive adequate power.
Always double-check the part numbers on the individual components before attempting any reinstallation. Each engine variant may feature slight differences in accessory configurations, including pulley sizes and mounting points. This ensures that the new parts fit correctly and operate smoothly within the system.
Ensure the tensioning device is properly adjusted, as incorrect tension can lead to premature wear or slippage. Over time, the tensioner spring may lose its effectiveness, leading to reduced performance and noise. If you notice unusual sounds or poor accessory operation, it could indicate that the spring needs replacement or re-tensioning.
After verifying the proper component alignment, check that the routing matches the diagram closely. Even a minor misalignment could cause unnecessary wear on the system and lead to costly repairs down the line.
A Complete Guide to the Serpentine System Layout
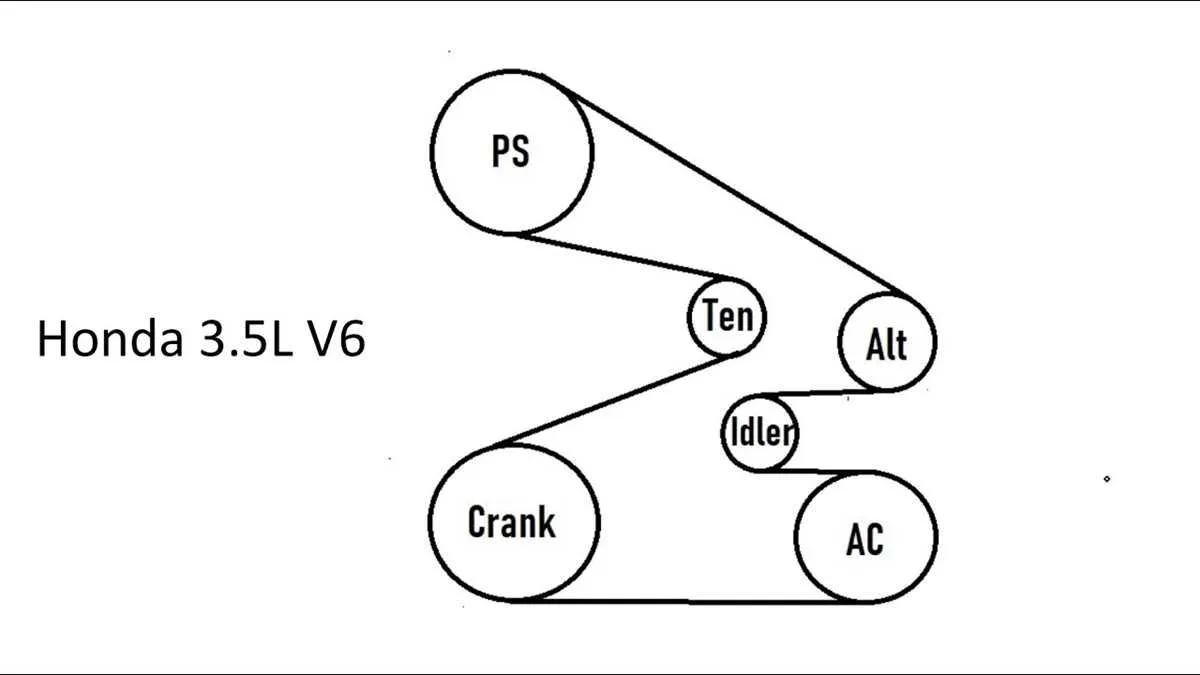
Ensure that you have the correct routing and tensioning details for the accessory drive components. This will help prevent malfunction or premature wear. The layout for the serpentine system must be followed precisely for proper operation.
The configuration involves several key pulleys, including the alternator, power steering pump, air conditioning compressor, and other auxiliary units. Each part must be properly aligned to reduce strain and increase the lifespan of the components.
| Component | Location | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Alternator | Top, near engine front | Charges the battery |
| Power Steering Pump | Side, near the bottom | Facilitates steering fluid movement |
| AC Compressor | Front, near engine block | Cools the air inside the cabin |
| Water Pump | Lower center | Circulates coolant throughout the engine |
Each part should be properly secured with no slippage or improper tension. Be sure to follow the prescribed specifications for installation and maintenance. Incorrect routing can lead to overheating or unnecessary wear.
It’s important to inspect the system periodically for signs of damage or wear, including checking for cracks or fraying. A well-maintained configuration ensures reliable performance and prevents potential breakdowns.
Step-by-Step Serpentine Route Installation

Start by loosening the tensioner pulley. Use a ratchet and socket to rotate it counterclockwise, relieving tension on the loop. Once the pressure is off, remove the existing loop if applicable.
Next, carefully route the new loop following the proper sequence. Begin at the crankshaft pulley, passing it around the alternator, and then around the water pump. Ensure that the loop fits snugly into each groove.
As you move along, bring it over the power steering pump and under the idler pulley. Pay close attention to the correct direction of the tensioner, which must engage the loop appropriately.
Once the new component is in place, recheck its alignment, ensuring it runs smoothly over all pulleys without being twisted or misaligned. Rotate the tensioner again to increase the pressure, securing the component in place.
Final Check: Turn the engine by hand to verify that the loop moves freely and makes no unusual noises. If everything looks good, start the engine and listen for any irregularities. If the tension feels off, repeat the steps, adjusting accordingly.
How to Identify and Replace the Timing Belt in Your Vehicle
If your engine starts making unusual noises or you’ve reached the recommended replacement interval, it’s time to inspect the timing chain. Check for signs of wear such as fraying or cracks. If the timing mechanism appears worn or damaged, it must be replaced promptly to prevent engine failure.
Start by locating the timing mechanism, which is usually found at the front of the engine. You’ll need to remove the engine cover and possibly other components to access it. Once exposed, inspect the timing gear for any signs of slack or misalignment.
When replacing the timing component, make sure to align the gears correctly. Use a tool to lock the camshaft and crankshaft in place before removing the worn part. Ensure the new part is properly tensioned, as both over-tightening and under-tightening can cause malfunction.
Important tip: Always replace the tensioner and pulleys along with the mechanism to ensure proper functionality and prevent future issues.
Once installed, rotate the crankshaft by hand to ensure there’s no resistance and the gears are properly meshed. If the engine cranks smoothly, you’re good to go. Reassemble the components in reverse order, double-checking for proper alignment.
After the replacement, monitor for any unusual sounds or performance issues. If you’re not confident in the process, seeking professional assistance is recommended.
Common Issues with the Drive System and How to Fix Them
When the drive components of your vehicle show signs of wear, immediate action is required to avoid further damage. Here are the most common issues related to the system and how to address them:
- Excessive Wear on Tensioners: The tensioner pulley can wear out over time due to stress, leading to poor function. To fix this, inspect the pulley for cracks or damage. Replace it with a new one if necessary.
- Squealing or Grinding Noise: A high-pitched squeal usually indicates a misaligned component or a pulley issue. Check for debris or damage in the pulleys, and ensure all are properly aligned. Lubrication may solve minor noise issues, but replacement is necessary if misalignment is severe.
- Loose Components: A slack system can result from worn-out components. Check for any parts that may have come loose over time, such as pulleys or mounts. Tighten any loose bolts and replace any worn-out components.
- Snapping: A snapping noise typically indicates a broken part within the drive assembly. Inspect the main drive components for damage or corrosion. Replace any damaged elements immediately to avoid engine damage.
- Overheating: If overheating is happening within the system, it may be due to worn-out friction components. Ensure that the cooling system is working properly, and check the condition of all components. Replace any worn friction materials to prevent overheating.
Regular inspections and timely replacements of worn parts will ensure long-term functionality and prevent severe damage to the engine. Always follow manufacturer recommendations for maintenance schedules and use high-quality replacement parts for repairs.