
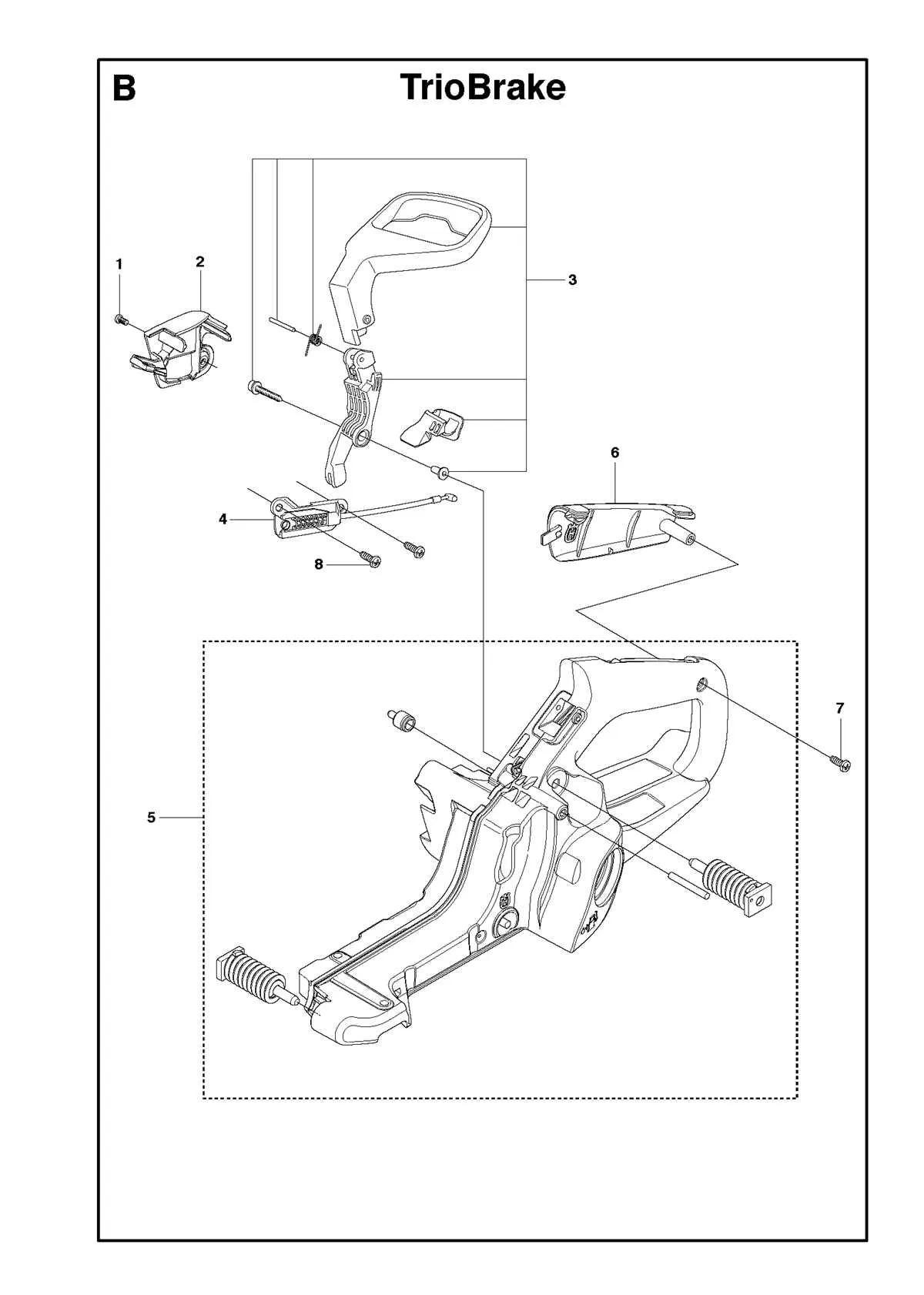
If you are looking to maintain or repair your outdoor power equipment, a clear understanding of the internal layout is essential. Start by consulting a comprehensive visual map that shows the arrangement and connection of key elements in the tool. This will help you to identify each section with precision, ensuring you focus on the right components during repairs or upgrades.
The layout typically includes detailed views of the engine housing, air filter assembly, and fuel system. Pay close attention to the fuel lines and the carburetor, as these parts often require cleaning or adjustment to maintain proper performance. Also, don’t overlook the lubrication system, which is crucial for smooth operation and longevity.
To avoid unnecessary disassembly, make sure you have a clear overview of the fastening mechanisms, including screws and bolts. These can be tricky to manage if not identified correctly. Use a diagram that highlights the exact placement of each part and label each component for easy identification when working on the tool.
Key recommendations: Regularly inspect the spark plug and ignition system to prevent starting issues. If the power tool has experienced significant wear, focus on the piston and cylinder, as these are often the most affected parts. Make sure to consult a reliable guide for the exact specifications of your model for optimal maintenance.
Understanding the Component Layout for Your Saw
To maintain optimal performance, it’s crucial to familiarize yourself with the internal structure of your saw. Here’s a breakdown of the main elements and their arrangement, which will guide you in troubleshooting or assembling the unit correctly:
| Component | Location | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Engine | Center | Powers the tool |
| Air Filter | Near the engine | Prevents dirt from entering the engine |
| Bar | Front | Holds the chain, guides it during use |
| Chain | Attached to the bar | Performs the cutting function |
| Clutch | Near the engine | Engages or disengages the chain |
| Oil Pump | Side of the engine | Lubricates the chain during operation |
| Throttle | Handle | Controls engine speed |
| Ignition System | Near the engine | Ignites the fuel mixture |
| Fuel Tank | Back | Stores fuel for the engine |
| Handle | Front and back | Provides control and maneuverability |
When assembling or servicing your tool, ensure that each part is securely positioned according to this layout for smooth operation. Improper assembly can lead to malfunction or excessive wear.
How to Identify and Locate the Key Components in the Diagram
Start by examining the engine housing, which is typically shown in the center of the visual. It’s the base for most internal mechanisms, including the ignition system and carburetor. The housing will often be marked with distinct lines to indicate where various components attach.
Next, focus on the drive mechanism. Look for the clutch drum and drive sprocket, which are usually located near the rear section of the assembly. These parts are connected directly to the engine and play a crucial role in power transmission to the cutting equipment.
Pay attention to the fuel system, typically placed in the lower section. This includes the fuel tank, fuel lines, and primer bulb. These elements are vital for fuel delivery and engine operation.
The air filtration system is another key area, generally located near the engine. Look for the air filter cover and surrounding components, which are crucial for maintaining engine performance by keeping debris out of the intake system.
For proper maintenance, locate the spark plug, often marked by a small symbol near the top of the engine. It’s essential for ignition and should be easily accessible for inspection and replacement.
Finally, check the bar and chain assembly. Look for the bar nuts, chain brake, and adjuster mechanism, which will typically be located on the side of the unit for quick adjustments and safety checks.
Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing Common Components in the Saw
Start by ensuring the tool is completely powered off and the spark plug is disconnected to avoid accidental starts. Wear protective gloves to handle sharp components safely.
Replacing the Air Filter: Remove the cover using a screwdriver, then take out the old filter. Inspect the air intake area for debris. Insert the new filter, ensuring it fits securely, and replace the cover. Ensure the filter sits properly to avoid any air flow restrictions.
Replacing the Fuel Line: First, disconnect the fuel tank from the engine. Use pliers to remove the old fuel line from the fuel filter and carburetor. Install the new line by pushing it onto the filter and carburetor fittings, ensuring it is tight and free of kinks.
Replacing the Spark Plug: Use a spark plug wrench to remove the old plug. Check the gap on the new plug using a spark plug gauge. Install the new plug by hand tightening it and then securing it with the wrench, making sure it is not over-tightened.
Replacing the Bar and Chain: Remove the side cover, chain brake, and old bar. Clean the area of any debris before installing the new bar and chain. Fit the new chain on the sprocket, ensuring the teeth face the correct direction. Reattach the side cover and tighten the chain for proper tension.
Replacing the Carburetor: Disconnect the fuel lines and the throttle linkage from the carburetor. Remove the screws holding the carburetor in place. Position the new carburetor carefully and reattach the fuel lines and throttle linkage. Tighten the screws to secure it, ensuring no fuel leaks.
After replacing any component, inspect all connections and perform a test run to ensure everything is functioning properly. Always check for proper tension and alignment before using the saw again.
Troubleshooting: Understanding the Role of Each Component in the Saw’s Function
Start by checking the spark plug. A faulty plug can prevent ignition or cause misfires. Ensure it is clean and free from carbon buildup.
- Fuel System: If the engine hesitates or stalls, the fuel filter might be clogged. Inspect and replace if necessary.
- Air Filter: A dirty air filter can restrict airflow, leading to poor performance. Clean or replace the filter to maintain optimal engine power.
- Carburetor: Adjust the carburetor if the engine runs rich or lean. Misadjustment can cause inconsistent idling or difficulty starting.
Inspect the drive mechanism. If there’s difficulty in moving the chain, check for tension issues or damage to the chain brake assembly.
- Chain Tension: Ensure the chain is neither too tight nor too loose. A properly tensioned chain ensures smooth operation and prevents unnecessary wear.
- Clutch: If the engine revs but the chain does not rotate, inspect the clutch. A malfunctioning clutch may not engage properly with the drive sprocket.
Examine the ignition system. A faulty coil can lead to weak or inconsistent sparks, causing poor engine performance. Test the ignition coil for proper operation.
If none of these solutions resolve the issue, consider checking the compression. Low compression indicates potential internal engine damage, requiring professional inspection.