
To safely revive a 24-volt electrical system, ensure you have a suitable power source and appropriate tools. Connect two compatible batteries in parallel, matching positive to positive and negative to negative terminals. Always verify the integrity of the cables and connectors before attempting any procedure.
Step 1: Begin by ensuring the auxiliary power source is fully charged and able to supply the necessary voltage. Incorrect or low voltage can lead to system failure or even damage to sensitive components. Use heavy-duty cables for optimal current flow.
Step 2: Position both power sources close together to avoid unnecessary cable length, which can lead to voltage drop. Securely attach one cable to the positive terminal of the dormant system and the other to the corresponding terminal of the auxiliary power source. Repeat the process for the negative terminals.
Step 3: Once the connections are secure, allow the system to draw power for a short period, checking the voltage with a multimeter to ensure proper levels are reached. After this brief interval, test the functionality of the electrical system to confirm it’s fully operational.
Important: Never leave connections unattended, and ensure you disconnect the power source only after the system is fully functional to avoid potential damage to both systems.
Boosting Power for 24-volt Systems
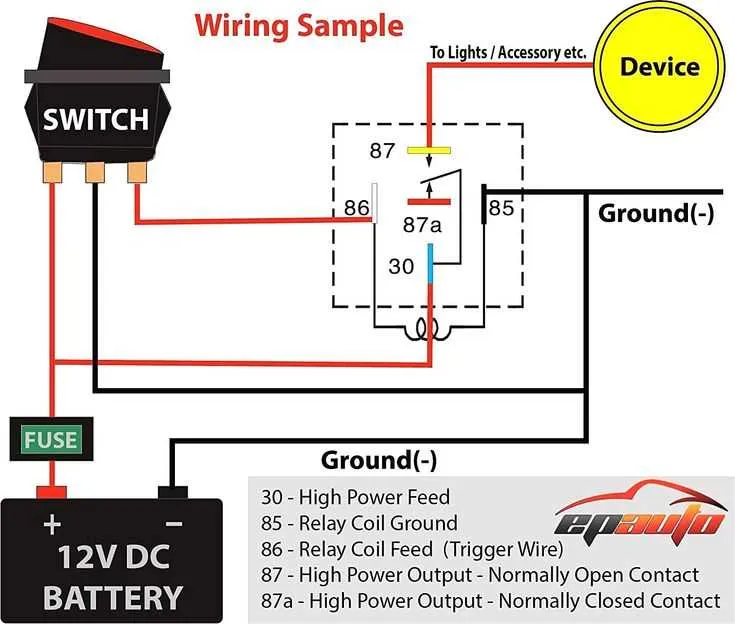
For restoring power in a 24-volt system, connect the positive terminal of the auxiliary power source to the positive terminal of the dead battery. Then, connect the negative terminal of the auxiliary power source to a metal part of the engine or frame of the vehicle that needs assistance. This will provide a secure ground connection, minimizing the risk of sparks near the battery.
Key Points:
- Ensure the cables are in good condition, with no visible wear or damage.
- Double-check that both systems share the same voltage to avoid electrical damage.
- Always attach the negative cable to a metal surface rather than directly to the negative terminal to reduce the risk of explosion.
Once everything is connected, wait a moment for the charge to transfer. After that, attempt to power up the dead system. If it doesn’t respond, give it a bit more time or check the cable connections for any loose contacts.
Important: Do not attempt to jump multiple systems at once, as this may overload the auxiliary power source. Always follow proper procedures to ensure a safe and effective restoration of power.
How to Properly Connect Jumper Cables for 24-Volt Systems
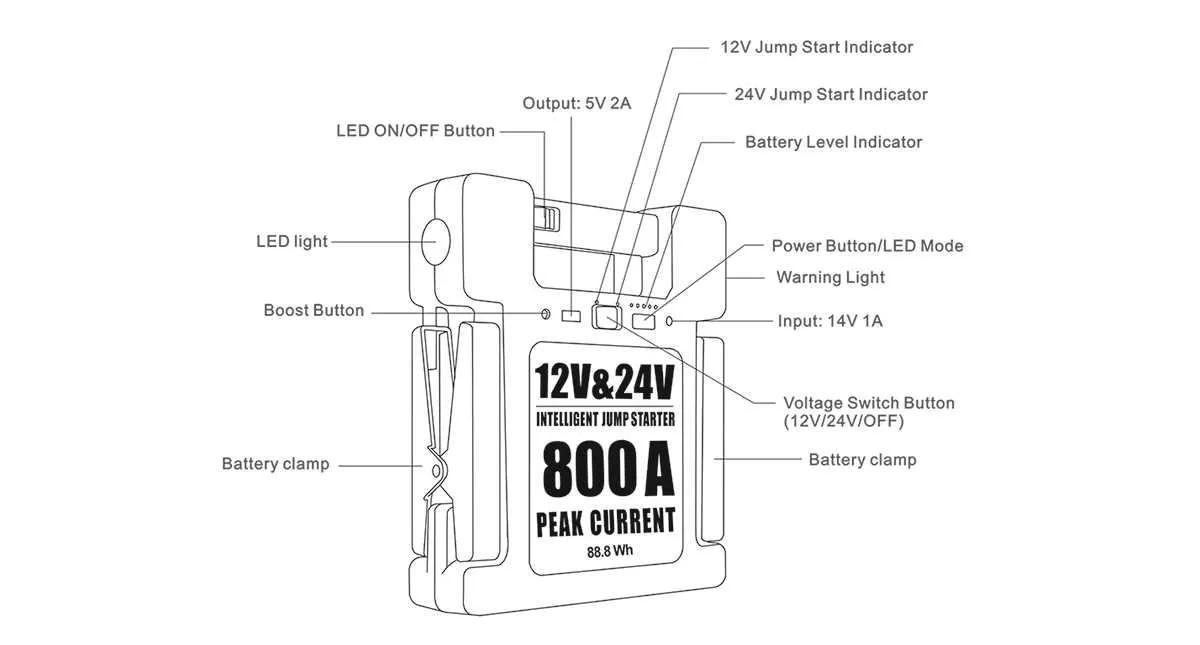
Ensure both batteries have matching voltage before connecting cables. Attach one cable’s positive end to the positive terminal of the dead unit and the other end to the positive terminal of the charged unit.
Next, connect the negative cable to the negative terminal of the working battery. Secure the remaining negative clamp to a grounded metal surface on the disabled vehicle–preferably away from the battery and fuel components.
Before powering on, double-check all connections are secure. Once ready, start the functional engine first, followed by the one requiring assistance. Let the active engine run for a few minutes before attempting to engage the second vehicle.
After successful operation, carefully remove the cables in reverse order. Always disconnect the negative clamp from the grounded point first, followed by the other negative terminal, and lastly, the positive connections.
Key Safety Precautions When Charging a 24-Volt Battery
Ensure correct polarity before connecting cables to avoid sparks or damage. Always connect the positive terminal of the good power source first, then the negative terminal of the dead battery. Reverse the order when disconnecting.
- Use only cables rated for the required voltage to prevent overheating or insulation failure.
- Wear rubber gloves and safety goggles to protect against battery acid and sparks.
- Ensure the batteries are located in a well-ventilated area to avoid the buildup of harmful gases.
- Do not allow cable clamps to touch any metallic parts of the vehicle to prevent short circuits.
- Inspect both batteries for leaks or cracks before proceeding.
Never attempt to charge a battery that shows visible signs of swelling or leakage as it poses a significant risk of explosion.
- Confirm the charge on the power source is sufficient to assist in the process.
- Allow the systems to stabilize for a few minutes before proceeding with any other actions.
- Avoid direct contact between the clamps after placement to prevent unintended arcs or damage.
Always follow manufacturer instructions for both the vehicle and charging equipment to ensure safe operation and maximum efficiency.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Powering Up a 24-Volt System
Ensure both batteries are of the same type and voltage to avoid damage. Using different voltages or types can cause overheating and permanent failure of the system.
Never connect cables to the wrong terminals. The positive lead must go to the positive terminal and negative to negative. Incorrect connections can lead to short circuits and damage the electronics.
Do not attempt to power up a system if there is visible damage to cables or terminals. Damaged components can result in sparks or fires when energized.
Avoid using cables that are too thin for the required current. Using cables that aren’t rated for the load will cause excessive heat buildup and can melt insulation, leading to hazardous conditions.
Wait until the system has fully discharged before attempting to connect power. Connecting before all systems are powered off can cause damage to sensitive components.
Check for proper grounding before making any connections. A poor ground can lead to erratic behavior, system failure, or even electrical shock hazards.
Don’t attempt to power up if the battery is already showing signs of excessive wear or failure. This can prevent the system from operating correctly and potentially cause further damage to the components.