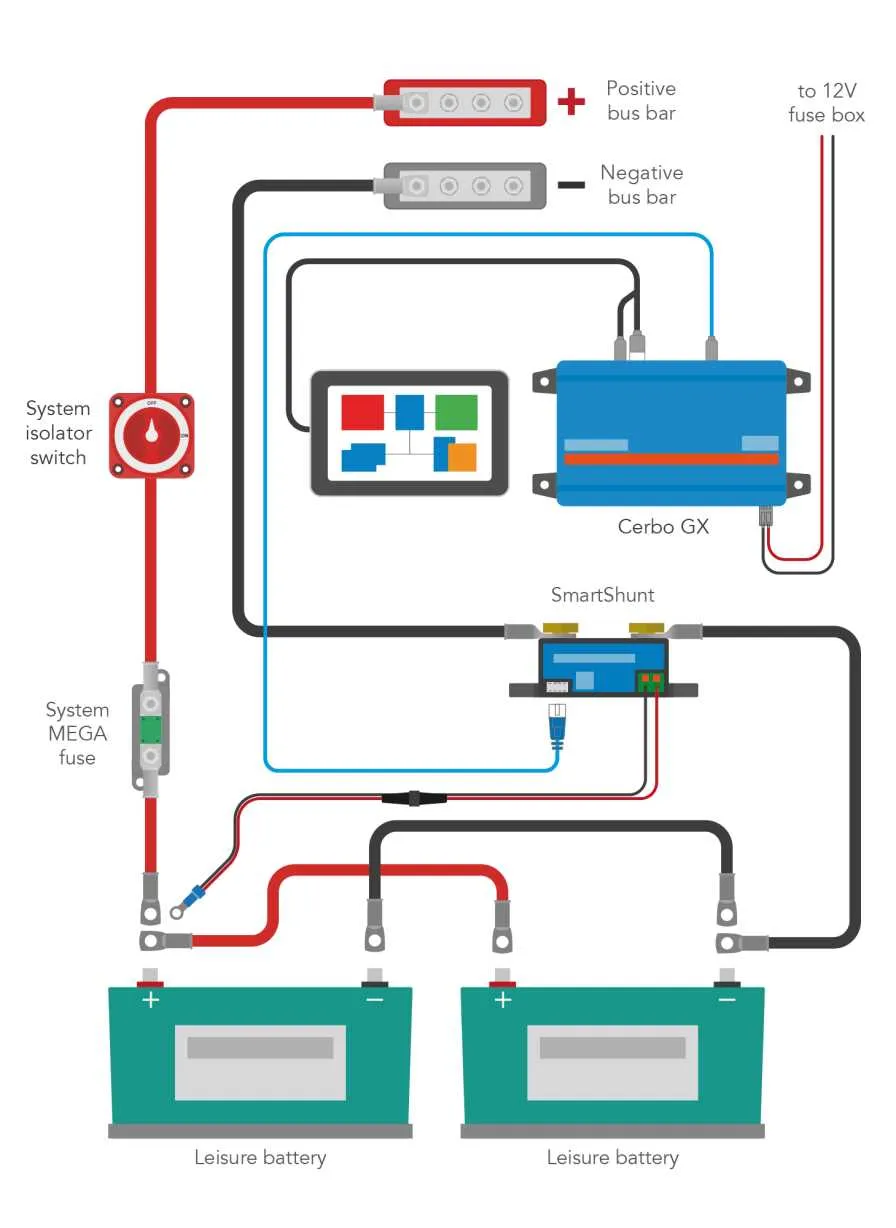
To ensure optimal performance and reliability in your recreational vehicle, integrating two power units into your system is essential for extended off-grid capability. The first step is connecting the two units in parallel for efficient load balancing. This configuration allows for an increased energy reserve without compromising the stability of your system.
Choosing the right components is crucial. Select cables with the proper gauge for your system’s power requirements. The shorter the cables, the less resistance there will be, which helps to maintain the longevity of the system. Aim for a size that can handle the maximum output to avoid any power loss or overheating.
Next, use a high-quality isolator to control the flow of energy between the units. This component ensures that the primary unit is charged first, while the second remains in standby mode until needed. The isolator also prevents backfeeding, which could damage your electrical system.
When connecting the units to your RV’s distribution panel, install a fuse or circuit breaker at each power unit’s input. This will provide protection against short circuits and overloads, preventing potential damage to the entire electrical system. Proper placement of these safety components is key to reducing risk.
Optimizing Your RV Power System with Two-Unit Setup
To enhance your vehicle’s power capacity, connect two energy storage units in parallel to maintain a reliable supply. Start by using thick gauge cables (at least 6 AWG) for the positive and negative connections between the two units. Ensure both power cells are of the same type, size, and charge level to balance the load effectively.
For optimal performance, choose a high-quality fuse between each energy cell and the main distribution panel, rated slightly higher than your maximum expected current to prevent overloading. Additionally, ensure that both units are securely mounted and properly ventilated to avoid overheating during use.
If you’re incorporating a charging system, such as solar or an alternator, connect both units to a dedicated controller to manage the charge flow. This setup ensures both cells receive an even charge, preventing one from draining faster than the other. Use an isolator or a smart relay to avoid reverse current flow, protecting your system from potential damage.
Finally, ensure proper maintenance by checking voltage levels regularly, especially when parked for extended periods, to avoid deep discharge that can shorten the lifespan of your system. By following these steps, you will maximize the energy efficiency and longevity of your vehicle’s electrical setup.
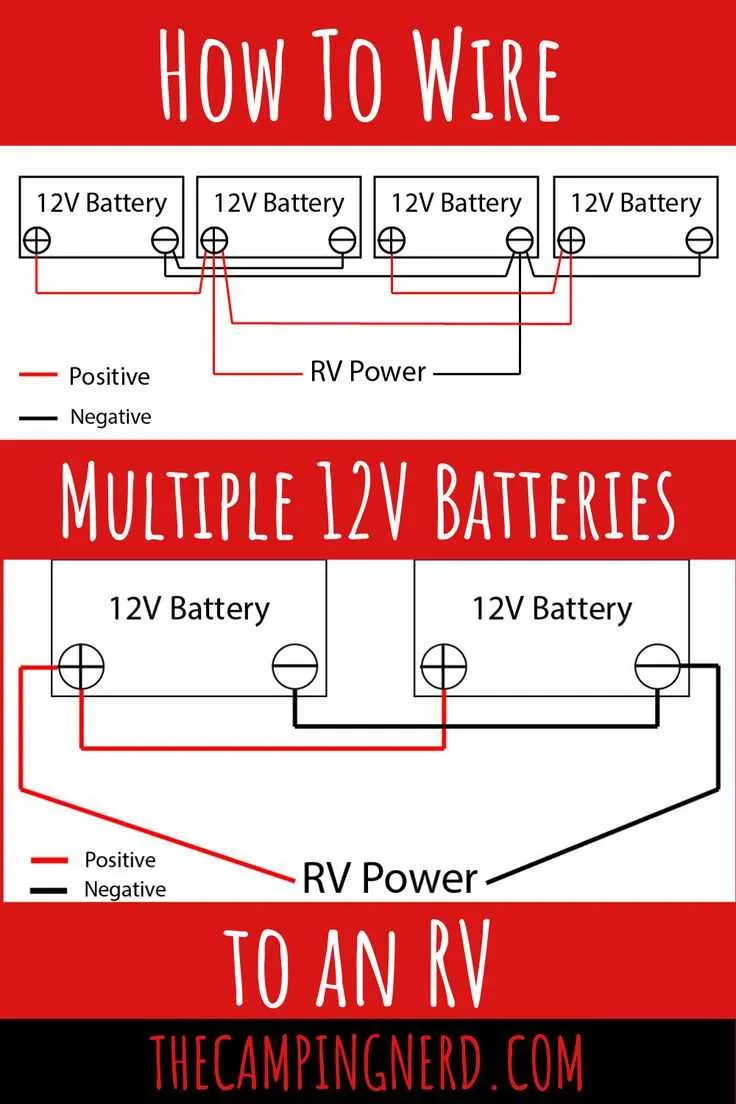
How to Connect Two Power Sources in Parallel for Increased Capacity
To expand your energy storage, connecting two power units in parallel can double the total available capacity while maintaining the same voltage level. Follow these specific steps for an efficient setup:
- Choose Compatible Units: Ensure both power sources have the same voltage rating. Mixing different voltages will result in uneven charging and may damage the system.
- Use Appropriate Cables: Select cables with a thick enough gauge to handle the combined current load. Typically, 4 AWG or 6 AWG cables are sufficient for most systems.
- Connect the Positives: Attach one cable from the positive terminal of the first unit to the positive terminal of the second unit. This will link both sources in parallel.
- Connect the Negatives: Similarly, run a cable from the negative terminal of the first unit to the negative terminal of the second unit. This completes the parallel circuit.
- Verify Connections: Double-check that all connections are tight and secure to prevent power loss or short circuits.
- Monitor Voltage: After the setup, use a multimeter to ensure that both units are at the same voltage level. If the voltage difference is too large, one unit might drain faster than the other.
By following these steps, you’ll increase your power storage capacity while ensuring both sources charge and discharge evenly. Proper maintenance and monitoring are key to maximizing the lifespan and efficiency of your setup.
Understanding the Correct Setup for Two-Power Source Systems with Isolators
When setting up a system with two separate energy sources and an isolator, ensure both power units are connected in parallel to maximize charging efficiency. The isolator should be installed between the two sources, allowing each to charge independently while preventing one from discharging the other. This ensures that the primary source stays charged for starting purposes, while the secondary unit provides additional power without risk of draining the first unit.
Use thick cables for the connections to minimize voltage drop. Typically, 6 AWG to 4 AWG cables are recommended depending on the system’s power demand. Fuse each line going to both power units to protect the system from overload or short circuits. For isolators, choose a high-quality smart model, which ensures the secondary unit is only connected when the main power source is sufficiently charged.
It’s crucial to connect the isolator to the vehicle’s charging system properly, making sure the unit can detect when the engine is running. This will allow the secondary power source to charge only when the alternator is actively supplying power, preventing unnecessary drain on the main unit.
For the best results, always test the system under load conditions before finalizing the installation. Check voltage levels across both sources to verify that the isolator is functioning correctly and that both units are receiving the proper charge when the engine is running.
Common Mistakes in RV Power Setup and How to Avoid Them
Ensure proper connection polarity when linking multiple power sources. Reversing the positive and negative terminals can cause severe damage to your system and connected devices. Always double-check polarity before securing wires.
Avoid using undersized cables. Using thin or low-quality wires leads to inefficient power flow and potential overheating. Opt for cables with the correct gauge, considering the distance and expected current load.
Never neglect fuse protection. Fuses or circuit breakers act as vital safety mechanisms. Always place them close to the power source to prevent any damage from electrical surges or shorts.
Don’t skip the grounding process. Proper grounding of your setup is critical to prevent electrical faults and ensure safe operation. Make sure that all components are grounded to a common point.
Check for proper venting in enclosures. When storing energy units, insufficient airflow can lead to heat build-up, causing damage or reducing efficiency. Make sure your system is housed in a well-ventilated area.
Ensure that connections are tight and secure. Loose or corroded contacts can lead to power loss or even fires. Regularly inspect connectors and replace any parts that show signs of wear or corrosion.
Don’t mix different types of power cells. Using mismatched units with varying capacities or ages can lead to imbalance and failure. Always pair units of the same type, age, and voltage rating for optimal performance.