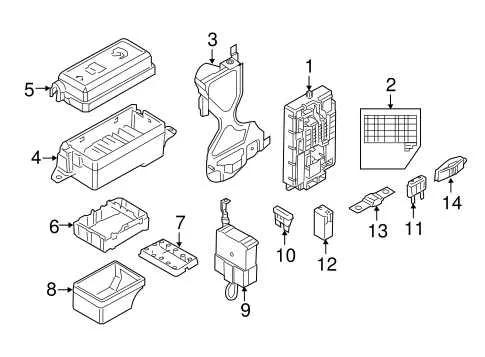
For efficient troubleshooting and maintenance of your vehicle’s electrical components, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with the layout of the electrical panel. Each circuit in your car is connected to specific relays and protection devices, which help manage power distribution throughout the system. Identifying these connections can save valuable time when diagnosing faults or replacing a malfunctioning part.
The first step is to locate the central control unit where the primary connections are housed. These units are typically located in the engine compartment or under the dashboard, with multiple sections dedicated to different parts of the vehicle, such as lights, sensors, and climate control systems. Each section is clearly marked to assist with quick identification of circuits and connectors.
When inspecting the system, always pay attention to the amperage ratings and wire configurations. Properly matching components ensures that the electrical load is managed safely, preventing overloads. For example, ensure that high-power devices, such as the air conditioning unit, are connected to appropriately rated connections, while lower-power components like interior lights can be routed through smaller circuits.
Lastly, it’s crucial to check for any signs of corrosion or wear that may impact connectivity. Over time, metal connectors can degrade, leading to potential power loss or short circuits. Replacing damaged connectors and ensuring all parts are tightly secured can extend the lifespan of the electrical system and prevent costly repairs.
Electrical Component Layout
The primary electrical distribution system is located in the engine compartment and cabin, with separate modules for each area. In the engine bay, you’ll find the main relay panel, which handles critical functions like engine management, lighting, and air conditioning. Inside the cabin, there is a second unit that controls interior electronics such as infotainment, airbags, and window mechanisms.
Start by checking the schematic for each unit based on the function you need to diagnose. For engine-related issues, focus on the primary module. If you’re troubleshooting interior functions, the cabin unit is your reference point. Be sure to refer to the specific position of each relay and connection in the schematic for accurate replacements or maintenance.
Common issues include blown circuits related to the power steering or central locking, which are often traced back to specific relays. The location and function of each fuse are indicated clearly in the electrical layout, and if a particular component is not working, inspecting the associated relay or switch could provide a quick resolution.
Understanding the Layout of the Electrical Distribution Units
For effective troubleshooting and maintenance, it’s crucial to familiarize yourself with the specific locations of electrical components and their respective fuses in your vehicle. Below is a detailed breakdown of the key elements to focus on:
- Primary Unit Placement: Located near the driver’s side dashboard, usually within the cabin. This unit controls critical interior functions like lighting, HVAC, and infotainment systems.
- Secondary Unit Positioning: Found in the engine compartment, it powers external components such as headlights, horn, and wipers. It’s typically situated close to the battery for easy access to high-current circuits.
- Numbering System: Each slot within the unit has a unique number that corresponds to a specific component. Ensure to check the vehicle’s manual for exact references.
- Identification of Failed Components: A blown connection is often identifiable by a visible break or discoloration in the metal element. Test with a multimeter to confirm functionality before replacement.
Be sure to consult the reference sheet within your vehicle for exact details on the layout, as the arrangement may vary slightly depending on the year and model. Proper identification and management of these units are essential for avoiding electrical issues down the road.
Identifying Electrical Component Locations and Functions
Locate the main power distribution panel under the dashboard near the driver’s side. This panel houses critical relays for essential systems like the lighting and ignition circuits. Ensure to check the individual slots for identification labels, which specify each relay’s role.
For rear lighting, inspect the compartment near the trunk, where additional relays handle rear brake lights and reverse functions. Always refer to the markings next to each slot for clarity on which system each relay powers.
If you’re troubleshooting non-functioning climate control or fan systems, check the dedicated section near the passenger footwell. Here, relays controlling the cabin temperature and air circulation are often grouped together.
Pay close attention to the fuel pump control relay, which can typically be found in the engine bay. It’s essential to confirm its proper operation, especially if you’re experiencing power issues related to fuel delivery.
In case of electrical issues affecting interior functions like power windows or seats, check the interior panel. These relays are often grouped in specific locations depending on whether the issue lies with the power window motor or seat adjustment mechanism.
How to Replace and Troubleshoot Electrical Circuit Components
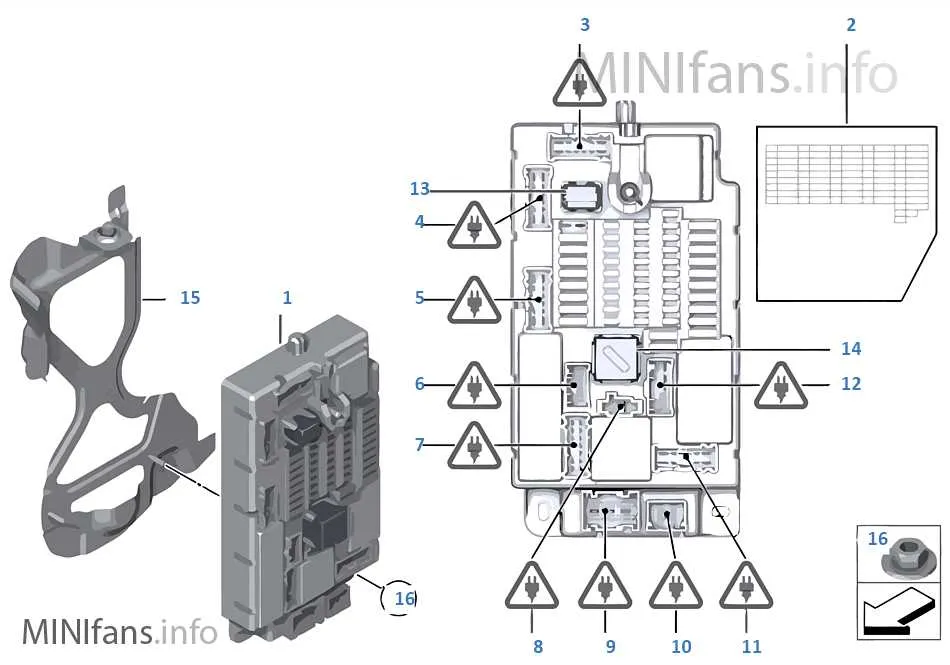
First, locate the electrical component panel. The cover is typically secured with clips or screws. Open it carefully to expose the wiring and connections. Before starting, always disconnect the battery to avoid any accidental short circuits.
If you suspect a blown component, use a multimeter to check continuity. Set the device to the resistance (Ω) setting and touch the probes to both ends of the element. A lack of continuity indicates a failure. If there is continuity, the issue might be elsewhere in the circuit.
When replacing a failed element, ensure you use the correct amperage rating. Installing an incorrect component can cause damage to other parts of the electrical system. Gently remove the damaged part and install the replacement, making sure it fits securely into the connection points.
For troubleshooting persistent issues, inspect the wiring for signs of wear, corrosion, or loose connections. Corrosion can interfere with electrical flow, so clean any affected terminals with a wire brush and ensure they are tightly secured.
If the problem persists, examine the relay system. A malfunctioning relay can prevent power from reaching certain circuits. Check for any burnt contacts or internal damage, and replace the faulty relay if necessary.
After replacing the faulty part, reconnect the battery and test the circuit to verify the fix. If the issue reoccurs, consider consulting the vehicle’s wiring schematic to track down potential problems deeper in the electrical network.