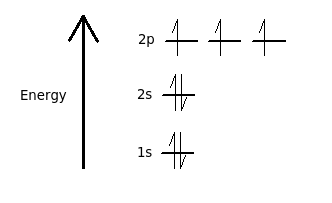
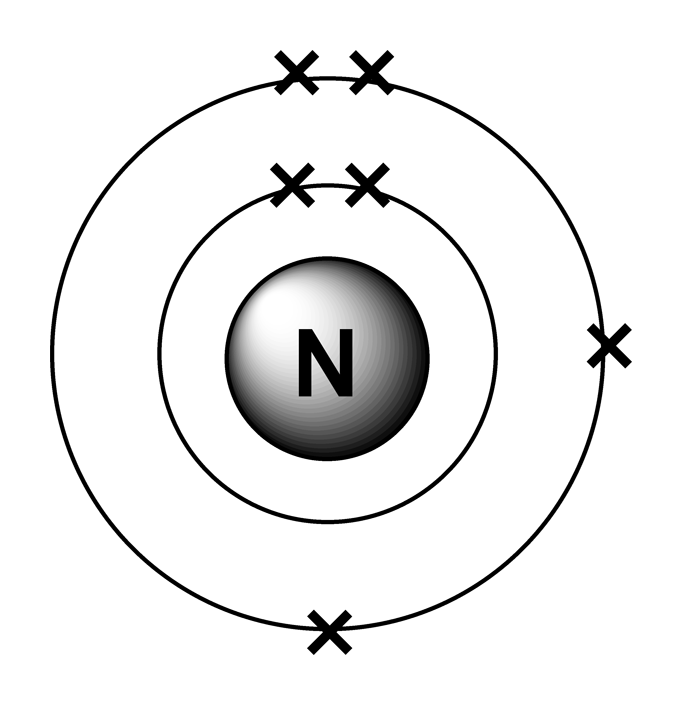
Nitrogen is the seventh element with a total of 7 electrons. In writing the electron configuration for nitrogen the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s.
Nitrogen is the 7th element so the electron configuration number should add up to 7. 1s level can hold two electrons; 2s holds two; 2p holds six. are filled, we have to introduce a symbolic notation that scientists use to show orbital filling.
If that single electron were a spin-up (ms = +1/2), the orbital diagram for The figure below illustrating orbital diagrams for nitrogen is similar to the. Use orbital filling diagrams to describe the locations of electrons in an atom.
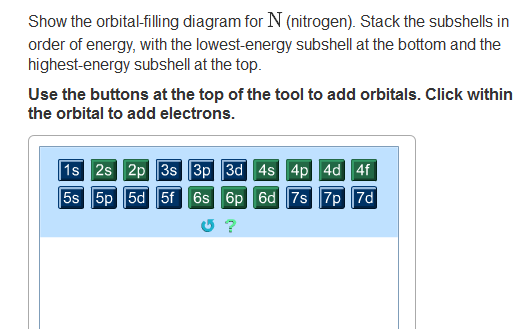
Diagram of Hund’s rule in boron, carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen. Figure 1. The 2p .
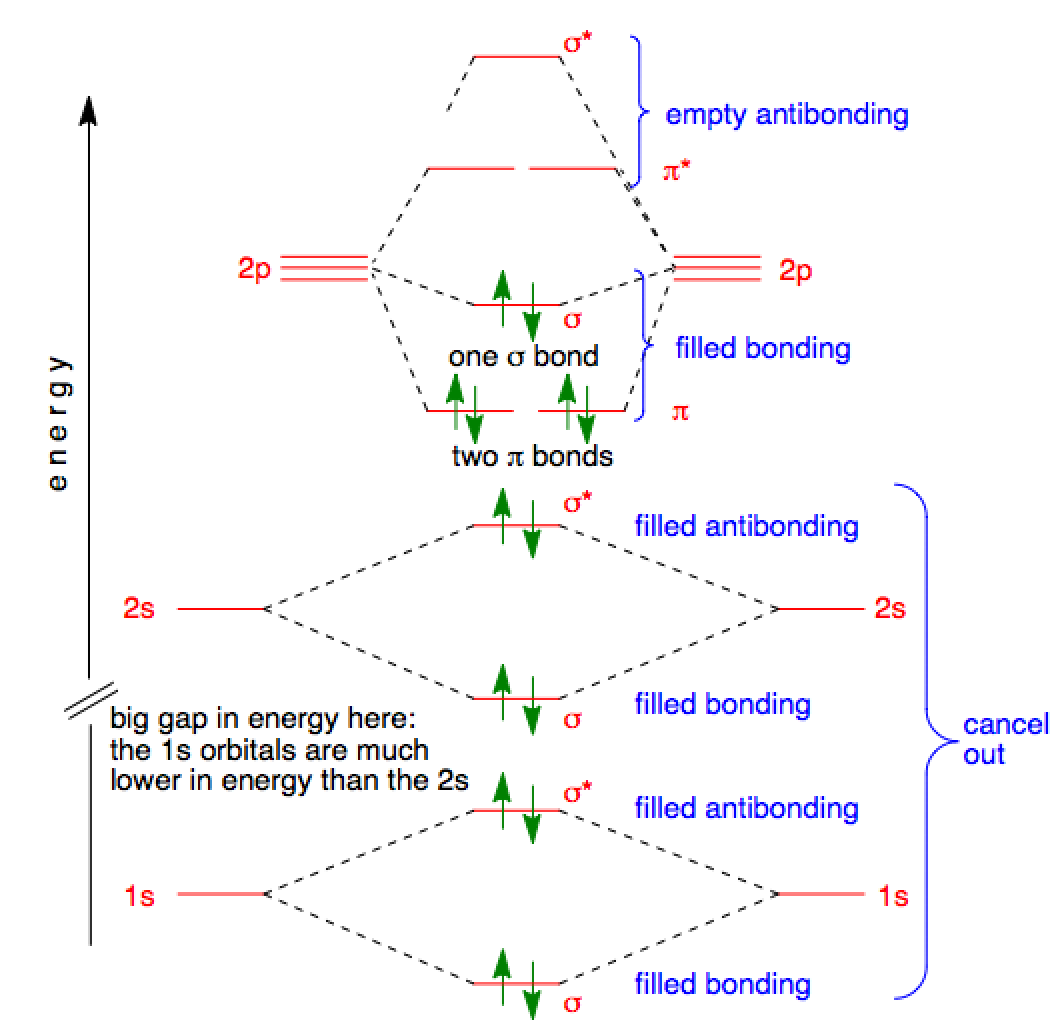
Orbital filling diagrams essentially just turn this big list of electron locations . In the same way, the orbital filling diagram for nitrogen will be.Given the same amount of absorbed solar energy coming in, the amount of IR escaping to space at the top of the atmosphere will indeed be the same no matter how many greenhouse gases there are (assuming the system is in equilibrium). A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.
A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form. Physical and chemical causes of colour.
According to the law of energy conservation, energy can be converted from one form to another, but it cannot be created or schematron.orguently, when a photon of light is absorbed by matter, usually by an atom, molecule, or ion or by a small grouping of such units, the photon disappears and its energy is gained by the matter. Enter your email address to follow this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
Use the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons to draw a model of the atom, identify the element, and determine the mass and charge. Predict how addition or subtraction of a proton, neutron, or electron will change the element, the charge, and the mass. Use the element name, mass, and charge to.High School Chemistry/Orbital Configurations – Wikibooks, open books for an open worldInfrastructure – Atomic Rockets