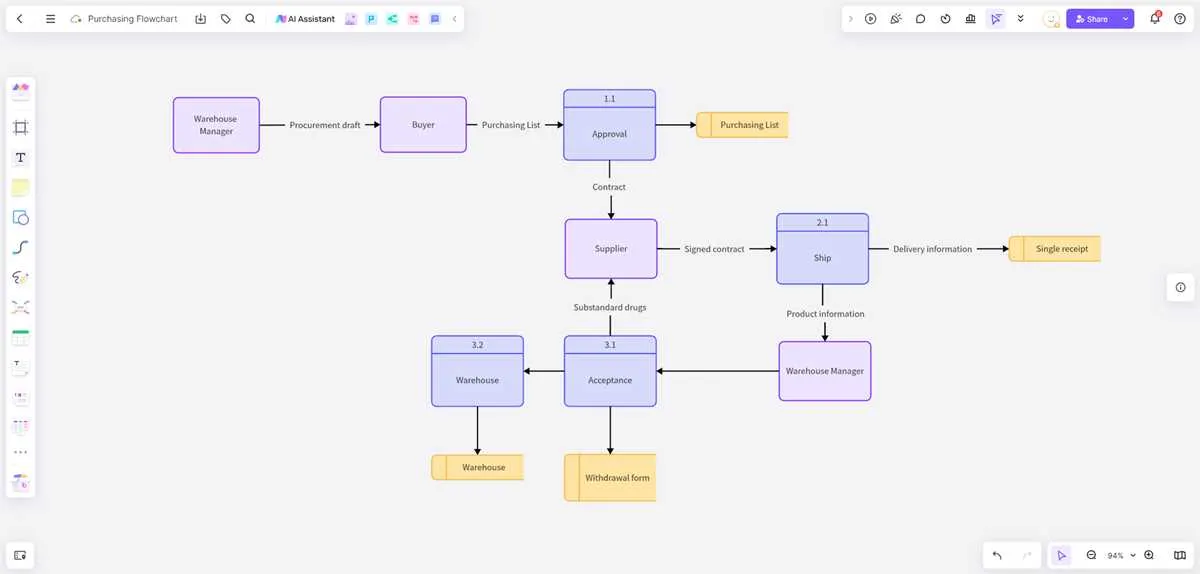
To ensure efficiency in obtaining goods or services, it’s critical to outline the sequence of key steps involved. Begin by clearly defining your requirements and assessing your needs, as this will serve as the foundation for the entire operation. At this stage, setting specific, measurable goals can prevent ambiguity and help in aligning all future actions toward a well-defined outcome.
Identifying potential suppliers is the next vital step. Researching and evaluating options based on their track record, pricing, and delivery capabilities helps in narrowing down the best candidates. After selecting suitable vendors, issue a request for quotations (RFQ) to invite offers and compare them on relevant criteria.
Once an offer is selected, it’s time to formalize agreements and negotiate terms. Contract management is essential here, ensuring that all deliverables, payment schedules, and deadlines are clearly outlined. Maintaining transparent communication throughout the entire procedure ensures both parties are aligned on expectations.
Finally, regular monitoring and follow-up are necessary to track the delivery of goods or services against established benchmarks. Proper documentation and review at this stage guarantee that any discrepancies are swiftly addressed, allowing for future improvements in subsequent acquisitions.
Steps to Streamline Purchasing Workflow
To enhance the efficiency of purchasing operations, it’s crucial to follow a systematic approach that ensures transparency, reduces delays, and optimizes resource allocation. Here are the essential steps for a well-structured acquisition system:
- Needs Identification: Begin by clearly identifying the requirement. Gather input from relevant departments to ensure that all essential specifications are captured accurately.
- Vendor Selection: Research potential suppliers based on reliability, quality, and cost-effectiveness. Create a shortlist of vendors that meet the organization’s needs.
- Request for Quotes (RFQ): Send out RFQs to selected vendors. Ensure the requests are detailed to avoid ambiguity and get accurate bids.
- Bid Evaluation: Compare the received proposals. Assess vendors on factors like price, delivery timelines, after-sales support, and overall value proposition.
- Approval: Obtain necessary internal approvals based on the evaluation criteria. This step often requires the participation of senior management or the finance team.
- Purchase Order Issuance: After approval, issue a formal order detailing the terms and conditions. Ensure the document is comprehensive and legally binding.
- Goods Receipt and Inspection: Upon delivery, verify the received goods against the purchase order. Inspect quality, quantity, and compliance with specifications.
- Invoice Verification and Payment: Cross-check the supplier invoice against the order and delivery receipt. Process payment once the goods and terms are confirmed.
- Record Keeping: Document all relevant transactions for auditing purposes. Maintain a system for tracking past acquisitions to inform future decisions.
Each of these stages ensures that the organization adheres to standard operating procedures, maintains control over expenditures, and secures the necessary items or services efficiently.
Steps to Design a Procurement Workflow Model
1. Identify key stages: Start by outlining the major phases of the acquisition cycle, from identifying needs to receiving goods or services. These stages should represent the critical milestones for tracking and decision-making.
2. Define roles and responsibilities: Clearly assign tasks to specific individuals or departments involved in each stage. Ensure that each step in the workflow is linked to the person responsible for it to avoid confusion.
3. Map decision points: Mark the points where decisions need to be made, such as approvals or evaluations. Specify who makes the decision and what criteria they use, ensuring these points are clearly visualized.
4. Establish communication channels: Outline how different teams or departments will interact at each stage. Indicate whether communication is direct or routed through a central system and specify information exchange methods.
5. Include timelines: Set estimated timelines for each stage to ensure that the entire cycle remains on track. Timelines also help identify potential bottlenecks in the overall flow.
6. Simplify visual representation: Avoid clutter in the model by limiting the number of steps shown. Focus on high-level actions, leaving out overly detailed information that may confuse rather than clarify the process.
7. Identify dependencies: Clearly define how each step depends on the completion of previous ones. This ensures a seamless transition between stages and highlights potential delays if dependencies are not met.
8. Review and optimize: After designing the model, review the entire process to identify inefficiencies or redundancies. Test the workflow for clarity and ensure all users can easily follow the steps.
9. Automate where possible: Incorporate technology to streamline repetitive tasks or approvals. Consider software tools that integrate with your existing systems to reduce manual intervention and speed up the process.
10. Continually update: Regularly revisit the workflow to adapt to changes in business requirements, market conditions, or technology. An outdated workflow can lead to confusion and inefficiency.
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Operations and How to Avoid Them
Ensure clear communication with suppliers from the start. Misunderstandings regarding terms, delivery schedules, and payment conditions often lead to delays and disputes. Define expectations in contracts and agreements, leaving no room for ambiguity.
Minimize reliance on a single vendor. Sole supplier relationships can be risky if unforeseen circumstances affect the supplier’s ability to deliver. Diversifying your sources ensures that if one supplier faces challenges, others can step in without disrupting your entire system.
Stay vigilant about compliance with legal and regulatory standards. Missing key requirements can result in fines, reputational damage, or delays. Regularly review applicable laws and guidelines in all regions where you operate.
Automate tracking and documentation as much as possible. Manual handling of orders and contracts increases the chances of human error. A digital system that tracks everything from purchase orders to invoices reduces mistakes and streamlines the overall system.
Integrate teams involved in the supply chain. Fragmentation between procurement, finance, and operations often results in bottlenecks. Create regular cross-department meetings to ensure alignment and quicker decision-making.
Monitor supplier performance consistently. Not checking on your vendor’s capacity or delivery reliability may lead to poor service or quality. Implement performance evaluations that focus on key metrics like on-time delivery and product quality.
Anticipate and mitigate risks. External factors such as geopolitical events or raw material shortages can disrupt your supply chain. Develop contingency plans that outline alternative suppliers, materials, and delivery methods in case of an emergency.
How to Integrate Technology into Your Procurement Flow Diagram
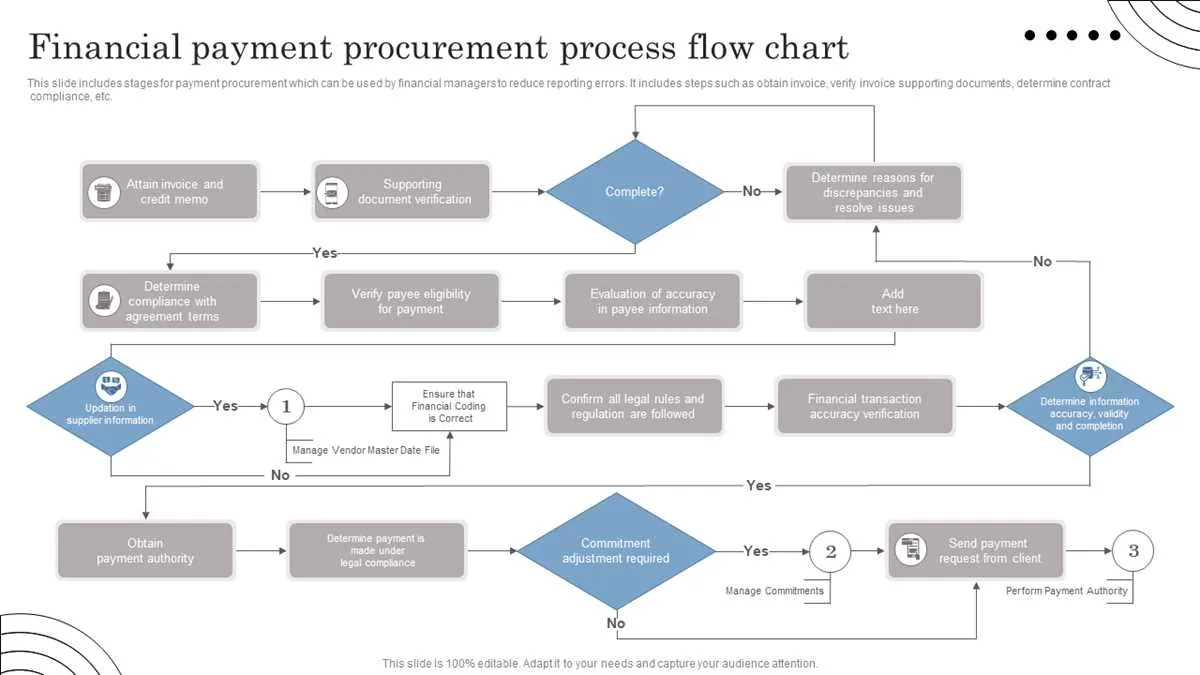
To enhance operational efficiency, incorporate automation tools at every stage, from supplier selection to contract management. Use specialized software for supplier evaluation to streamline data collection and minimize human errors. Integrate machine learning algorithms to predict supplier performance based on historical data, ensuring more accurate decision-making.
Cloud-based platforms allow real-time collaboration among teams, making document management and approval workflows faster and more transparent. Using e-signatures instead of manual approvals speeds up contract execution and reduces the likelihood of delays.
Leverage AI-driven analytics to assess trends and optimize purchasing decisions. Automated systems can notify teams about inventory levels, pricing fluctuations, and vendor performance, allowing proactive decision-making and preventing stockouts or over-purchasing.
Incorporating blockchain technology can ensure the integrity of your agreements, providing an immutable record of transactions that is accessible at any time, minimizing disputes and enhancing accountability with suppliers.
Invest in integration tools to connect your procurement activities with finance, logistics, and other departments. This seamless connection enables automatic updates in accounting systems and provides a comprehensive view of costs, helping to maintain control over budgets.