Ensure proper placement of the water extraction system to achieve efficient performance and minimal wear. Proper positioning is critical to maintain constant water flow and prevent operational failures. It is essential to select the correct depth and location based on geological conditions and the water table.
Consider the type of motor and its specifications when choosing the right pumping unit for the task. Match the motor power with the system’s required capacity to avoid overloading or underperformance. A reliable power source is crucial to sustain long-term operation.
Check for proper seal and casing installation to prevent contamination and loss of pressure. A secure casing ensures the integrity of the water flow and reduces the likelihood of system failure. Regular maintenance and inspection of seals can extend the lifespan of the setup.
Plan the pipe layout carefully to minimize friction losses. Use high-quality piping materials that can handle the pressure and environmental conditions. A well-planned piping system will ensure that water is delivered to the household efficiently and without significant energy loss.
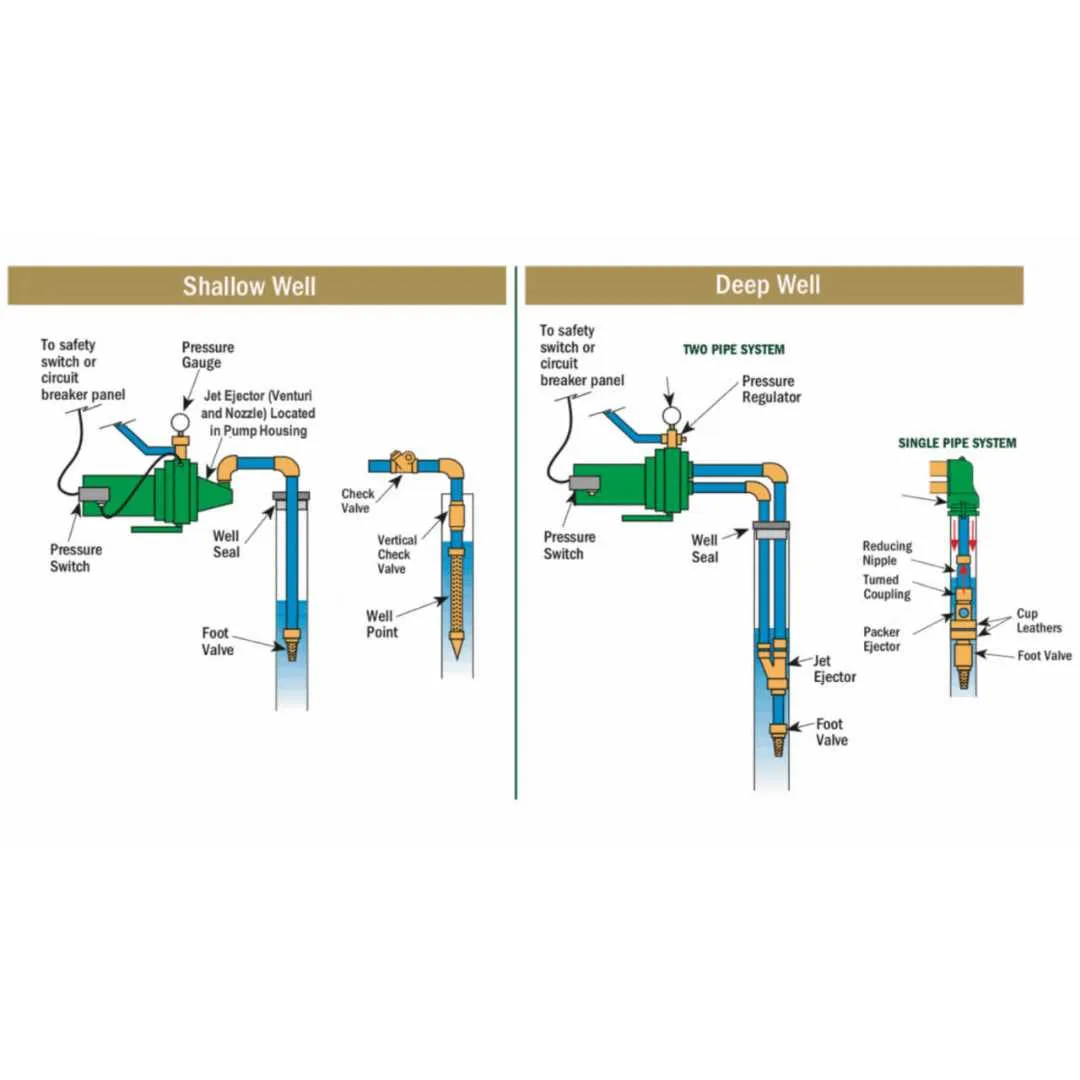
Water Supply System Configuration
For optimal water extraction, ensure correct installation and maintenance of the components responsible for lifting groundwater. Here are the key elements to consider:
- Submersible Unit: Choose a submersible pump suited for your depth and flow rate requirements. Check the horsepower to match the capacity needed for your household.
- Intake Screen: A filter or intake screen should be placed at the water entry point, preventing debris and particles from entering the system.
- Drop Pipe: Use corrosion-resistant materials for the drop pipe, and ensure proper alignment to prevent disconnection during operation.
- Power Supply: Ensure the power supply is reliable and correctly rated to prevent fluctuations or damage to the motor.
Proper sizing and positioning of each part are critical for longevity and efficient operation. Regularly monitor the system for wear, leaks, or blockages to maintain performance.
Consider these points when installing a lifting mechanism for groundwater to maximize efficiency and reduce future maintenance needs.
Understanding the Key Components of a Household Water System
Ensure the water extraction unit is properly installed to avoid water contamination. A reliable intake mechanism at the deepest point of the underground source ensures consistent water supply. Always verify that the sealing mechanism around the access pipe is intact to prevent external pollutants from entering the system.
The motorized unit should be positioned above ground level to maintain efficiency. When selecting this component, opt for models that are rated for your household’s needs, factoring in the depth of the extraction point and the volume of water required. Regular maintenance checks are critical to prevent malfunction due to wear and tear.
Incorporating a filtration unit within the pipeline helps in maintaining water quality by trapping unwanted particles before reaching the storage tank. Make sure filters are replaced or cleaned periodically, especially during seasons with high water turbidity.
Include a pressure switch to regulate the water flow and maintain consistent pressure levels. These switches are programmed to activate the motor when the pressure drops below a set threshold. It’s crucial to adjust this threshold based on the water demand of the household to avoid unnecessary energy consumption.
A protective casing around the motor is essential for safeguarding it from environmental conditions. Use materials that are resistant to rust and corrosion, as exposure to water and air can degrade components over time.
How to Properly Install a Water Lift System
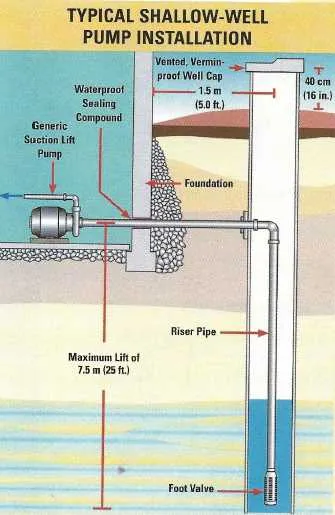
Begin by selecting a suitable location for the system, ensuring it’s easily accessible for maintenance. Measure the depth of the water source and determine the type of unit required–submersible or jet-style. This choice depends on the depth of the source and the flow rate needed for your household.
1. Positioning the Unit: Ensure the equipment is placed at the proper level in the shaft. For submersible units, this typically means positioning it at least 10 feet below the surface to avoid air suction and ensure smooth operation. For jet systems, the lift height should align with manufacturer guidelines.
2. Secure the Mounting Brackets: If using a jet unit, secure the brackets tightly to the casing to prevent any movement or misalignment over time. Use corrosion-resistant fasteners to guarantee durability in the environment.
3. Connect the Discharge Pipe: The discharge pipe should be securely attached to the system, with a watertight seal to prevent leaks. Check the material specifications to ensure compatibility with the pipe size and pressure requirements.
4. Electrical Connections: Before connecting the electrical supply, ensure the system is grounded properly to avoid electrical hazards. Verify the power requirements and use a dedicated circuit with appropriate breakers to handle the system’s energy consumption.
5. Test the System: Once the unit is in place and connected, conduct a test to ensure proper flow and pressure. Monitor for unusual noises or vibrations, which could indicate issues with alignment or blockages. Confirm that the system runs smoothly under full load.
6. Regular Maintenance: Establish a routine maintenance schedule to inspect and clean the system, checking for debris buildup or corrosion. Clean the intake filter regularly to maintain optimal efficiency and avoid pump burnout.
Troubleshooting Common Pumping Issues
Ensure power supply stability: If the system fails to operate, first verify that there is a consistent flow of electricity to the motor. A blown fuse or tripped breaker is often the cause of a lack of function. Reset the breaker or replace the fuse as necessary.
Check the pressure switch: A malfunctioning pressure switch can prevent proper water flow. Ensure the switch is set correctly and free from debris. If the switch is stuck or shows signs of wear, replace it to restore function.
Inspect the pressure tank: If there is irregular water flow or fluctuations in pressure, check the air charge in the pressure tank. An undercharged tank can result in inadequate water delivery. Adjust the air pressure to match the manufacturer’s specifications.
Examine the intake line: Obstructions in the intake line can lead to weak water output. Inspect for any blockages or kinks along the intake pipe. Remove any debris or replace the pipe if it is damaged.
Test the motor: If the system is running but there is little to no water flow, the motor might be failing. Test the motor for proper function by listening for abnormal sounds. If the motor makes strange noises or fails to turn on, it may need to be replaced.
Inspect for leaks: Water loss due to leaks in the piping system can reduce efficiency. Look for damp areas around pipes, fittings, and seals. Tighten or replace any faulty connections to prevent further water loss.
Examine the impeller: If the motor is running, but there is no water being moved, check the impeller. A broken or clogged impeller will prevent proper water movement. Clean or replace the impeller if necessary to restore full functionality.