To ensure optimal temperature control and prevent scalding, it’s crucial to familiarize yourself with the water distribution system that regulates hot and cold water flow. Understanding how these components work together is essential for safe installation and effective operation.
In the installation process, focus on the key components: the temperature regulator and the pressure balancing mechanism. The temperature regulator ensures that the water temperature stays within a safe range, while the pressure balance system prevents sudden fluctuations in water flow, which could cause discomfort or accidents.
Make sure that the setup incorporates a reliable mechanism to prevent cross-flow between hot and cold water sources. This is especially important in systems where consistent water temperature is necessary, such as in homes with varying water pressure or in high-demand areas.
When troubleshooting, check for: blockages in the inlet pipes, malfunctioning temperature controls, or worn-out seals that may cause leakage. Regular maintenance of these components will prolong the system’s lifespan and maintain its efficiency.
By addressing these aspects, you can improve the comfort and safety of your water system while ensuring long-term performance.
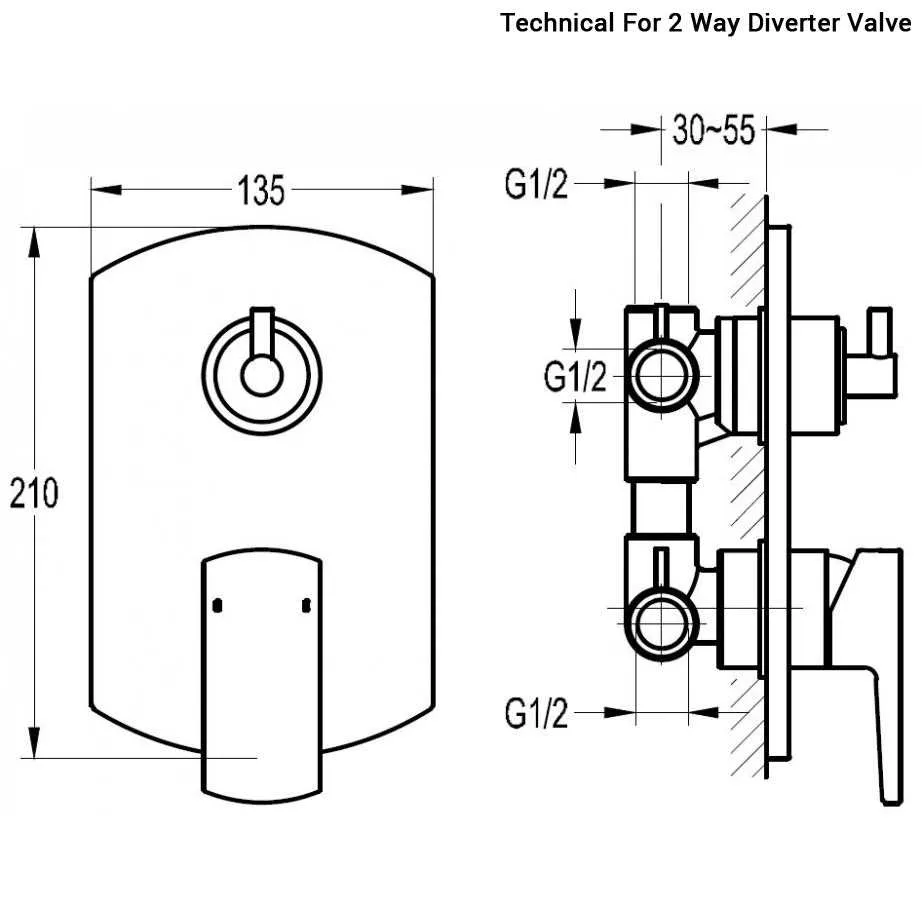
Installation Guide for Water Temperature Control Mechanism
Ensure the system’s cold and hot water pipes are correctly connected to the inlets. Proper sealing of connections prevents leaks and ensures reliable performance. Use a Teflon tape for threaded connections to enhance leak resistance.
When positioning the unit, make sure it is installed at an accessible height, typically around 4-6 feet from the ground, to facilitate easy adjustments. Maintain a 1-2 inch clearance from surrounding walls to allow for any expansion or contraction caused by temperature changes.
Ensure the hot water inlet is positioned correctly, often marked with a red or other clear indicator. This helps avoid errors during setup and ensures the mechanism operates effectively. Adjust the temperature control component to accommodate the expected temperature range based on user preference and safety standards.
If the unit features a temperature limiter, set it to prevent water from exceeding 120°F (49°C) for safety. Additionally, verify that the temperature control device is calibrated, ensuring consistent regulation of water flow and temperature.
Test the system after installation by running both cold and hot water through the unit, checking for any unusual sounds or leaks. If any issues arise, recheck the connections and calibration settings. Make sure the flow rate is balanced to ensure proper mixing of the two water sources.
Understanding the Components of a Shower Mixing Valve
The core components of a water control system for showers include the temperature control mechanism, diverter, and pressure balance regulator. Each part plays a critical role in maintaining optimal water flow and temperature consistency.
Temperature regulators allow precise adjustments between hot and cold water, ensuring a steady mix. These components are typically designed with internal thermostats to prevent sudden temperature fluctuations, providing safety against burns or cold shock.
The diverter directs the water flow either to the head or a handheld attachment. This part is crucial for user flexibility, allowing easy switching between different water outlets based on preference.
Pressure regulators ensure water flow remains steady, preventing issues like water hammer or inconsistent pressure changes when other taps are used elsewhere in the plumbing system. The regulator works by balancing the pressure from both hot and cold sources, maintaining a smooth experience.
Understanding these components ensures proper installation and maintenance of the system. Regular inspection of seals and gaskets is essential for preventing leaks and preserving long-term functionality.
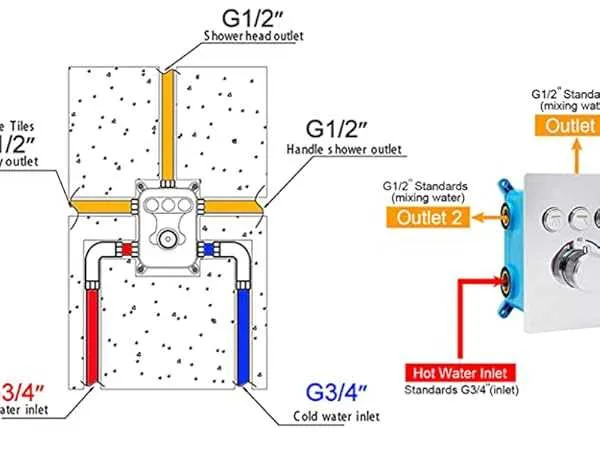
Understanding the Components of a Water Control System Layout
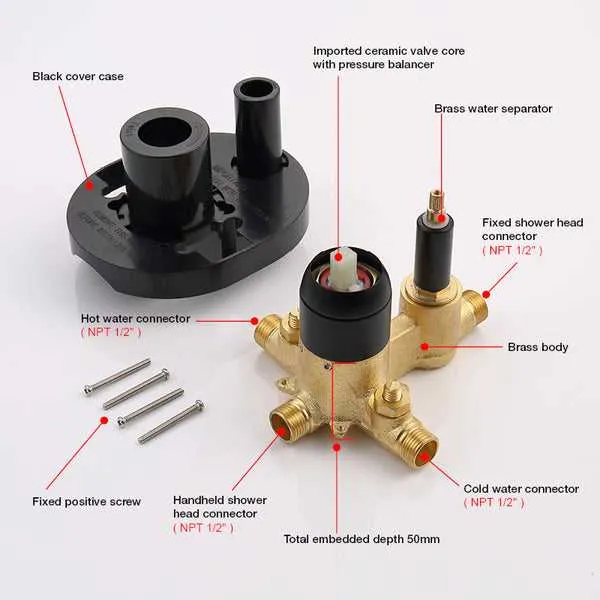

To properly interpret a water control system layout, follow these steps:
- Identify the Inlet Pipes: Locate the cold and hot water supply lines. These are typically represented by straight lines with labels for each source.
- Locate the Flow Adjustment Points: These are often marked with arrows or dials indicating the flow direction. Understanding these will help you regulate temperature and water flow.
- Recognize the Connection Points: Look for intersections where different elements join. These points are crucial for ensuring proper installation.
- Understand the Control Mechanism: This part will indicate how the temperature and pressure are adjusted. It may include a lever, knob, or digital interface.
- Check for Water Flow Paths: Tracing the flow paths will help you understand how water moves through the system. Some layouts use dashed lines or shaded areas to indicate the flow’s direction and pressure zones.
- Review the Sealing and Locking Mechanisms: Pay attention to any seals or locking devices shown, as they ensure a leak-free and stable setup.
By following these steps, you can easily decipher a water control system layout and ensure proper installation and maintenance.
Common Issues in Temperature Control Systems
If you encounter inconsistent water temperature, check the pressure balance. A drop in water pressure can disrupt the system’s ability to regulate heat effectively. To fix this, inspect the inlet filters for clogs and clean or replace them as needed.
Another frequent problem is erratic water flow. This can often be traced back to wear and tear of internal components. Replacing faulty cartridges or seals will restore proper performance. Ensure you have the right parts compatible with your system model.
In cases of water temperature fluctuations, the root cause may lie in the control mechanism. A malfunctioning temperature control lever can fail to maintain a steady setting. Test the lever for smooth operation and replace it if necessary.
Mineral buildup from hard water is a common culprit for reduced flow and efficiency. Regular maintenance, such as descaling the components, will extend the lifespan of the unit and improve functionality.
If you hear unusual noises during operation, this might indicate air trapped in the system or loose connections. Bleed the system and check all connections to ensure a tight seal and proper alignment of parts.