For efficient maintenance or replacement of the front engine pulley system, follow the exact path layout to ensure proper tension and alignment of the multi-ribbed loop. Incorrect installation may cause premature wear or failure of critical components such as the alternator, water pump, and power steering pump.
The routing follows a specific sequence: starting at the crankshaft pulley, the belt travels over the tensioner, idler pulleys, and accessory pulleys in a precise order. Familiarize yourself with the exact pulley arrangement before removing the worn loop to avoid misrouting during reassembly.
Always refer to the factory-recommended configuration and check for correct tension using a gauge or the automatic tensioner mechanism. Using the correct belt with proper width and rib count matching the vehicle’s engine setup guarantees optimal performance and longevity of the drive system.
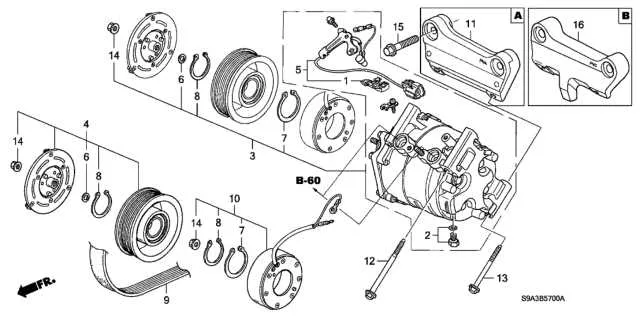
Drive Belt Routing for the 03 CR-V
For proper installation of the accessory drive loop on the 03 CR-V, ensure the routing follows the factory pattern precisely to maintain tension and prevent premature wear. The path begins at the crankshaft pulley, wrapping around the alternator, then the air conditioning compressor, followed by the power steering pump, and finally around the tensioner pulley before returning to the crankshaft.
Use a belt tension gauge to verify the correct tension after fitting. The tensioner is spring-loaded and should be positioned so the belt maintains optimal tightness without excessive slack. Misalignment or incorrect routing can lead to noise, slipping, or damage to the components.
When replacing the loop, inspect all pulleys for wear or damage and replace the tensioner if the spring mechanism feels weak. This layout supports efficient operation of all engine-driven accessories and extends the lifespan of the drive system.
Locating and Identifying Drive Belt Components on CR-V Models from 2003
Start by opening the hood and facing the engine from the front of the vehicle. The continuous loop used for powering multiple accessories is positioned on the passenger side of the motor. Identify the tensioner pulley first; it is spring-loaded and maintains proper tension on the loop, typically found near the alternator. Adjacent to it, locate the idler pulleys which guide the routing without transmitting power. The crankshaft pulley, the largest wheel at the bottom center of the engine, drives the entire system. Above or near it, find the water pump pulley and the air conditioning compressor pulley, both critical for coolant circulation and cabin cooling, respectively.
Use the factory stamped markings or labels on the engine cover for precise positioning if available. The path of the power transmission loop weaves around these pulleys in a specific order: starting from the crankshaft, moving to the alternator, then the tensioner, compressor, idlers, and finally the water pump. Confirm each component’s function by cross-referencing with the accessory it drives, ensuring proper recognition before any maintenance or replacement.
Step-by-Step Guide to Reading the CR-V Drive Pulley Routing
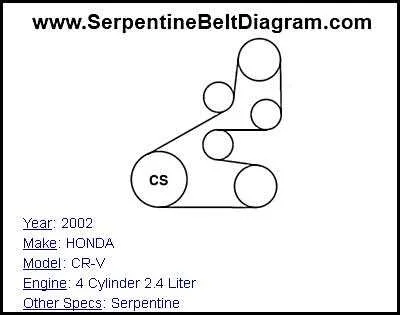
Start by locating the main engine pulley near the front of the motor compartment. Identify the tensioner pulley, which maintains proper tension on the drive loop. Trace the path from the crankshaft pulley, noting how the loop wraps around each accessory: alternator, power steering pump, air conditioning compressor, and water pump.
Observe the direction of the loop as it moves over and under each wheel. Confirm the loop’s correct positioning by comparing the routing pattern to the layout printed on the under-hood sticker or the factory service manual. Make sure no part of the loop is twisted or misaligned with any grooves on the pulleys.
Check the tensioner’s position; it should apply firm pressure to the loop, preventing slack but not causing excessive tightness. If the tensioner is fully compressed or extended, the routing may be incorrect or the loop may need replacement. Use a flashlight to ensure the loop fits perfectly within the pulley channels, avoiding any signs of wear or glazing.
Finally, after verifying the path, rotate the crankshaft pulley manually to confirm smooth movement of the entire system without slipping or misrouting. This visual inspection ensures all accessories are properly driven and reduces the risk of premature wear or failure.
Common Routing Patterns and Troubleshooting for CR-V Accessory Drive
Follow the correct loop configuration to ensure optimal tension and prevent premature wear. The typical layout includes the crankshaft pulley driving the alternator, power steering pump, air conditioning compressor, and tensioner pulley in a specific sequence.
- The drive loop usually starts at the crankshaft, moving to the alternator, then the A/C compressor, followed by the tensioner, and lastly the power steering pump before returning to the crankshaft.
- Tensioners are spring-loaded and must maintain firm pressure; a loose path causes slipping and noise.
- Inspect pulleys for misalignment or damage as this can cause uneven wear or squealing sounds.
- Replace the loop if cracks, glazing, or fraying appear to avoid sudden failure.
Troubleshooting steps:
- Verify the loop follows the proper path according to manufacturer specifications–incorrect routing leads to malfunction or accessory damage.
- Check tensioner operation by applying pressure; if it doesn’t resist or moves freely, it requires replacement.
- Listen for chirping noises at startup; this often indicates slipping due to insufficient tension or worn material.
- Use a pry bar carefully to test tensioner spring strength–excessive play means loss of proper tension.
Proper installation and routine inspection extend component lifespan and prevent breakdowns related to accessory drive failures.