Start by turning off the main power supply to prevent electrical hazards. Use a voltage tester to confirm that the circuit is de-energized before proceeding with any work. Ensure all connections are made with the correct gauge wires, as specified in your unit’s manual, to avoid overheating or short-circuiting.
Next, properly secure the connections to the terminals on the unit. Attach the live wire to the designated terminal and the neutral wire to the corresponding port. Make sure the ground wire is connected to the metal frame of the appliance to ensure safety. Double-check that all screws are tightly secured to avoid loose connections.
When placing the unit, confirm that it is level and positioned according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Proper alignment will ensure optimal performance and safety. Additionally, ensure the wiring is not pinched or strained when mounting the appliance.
Important note: Always verify local codes and regulations, as they may require additional safety measures, such as using specific circuit breakers or grounding techniques.
Electrical Setup of a Floor-Mounted Heating Unit
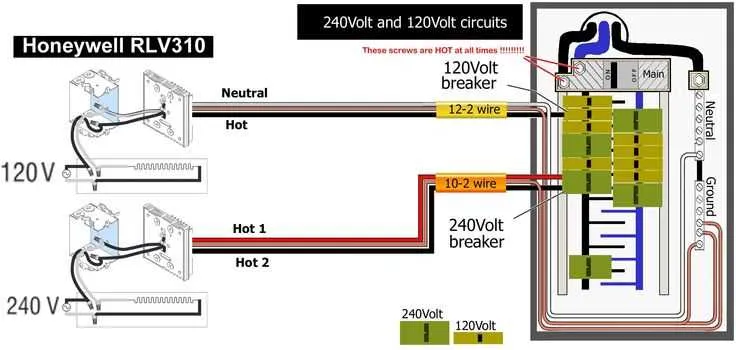
Start by connecting the heating element directly to a dedicated 240V circuit, ensuring it is protected by a 20-30 amp breaker. Use a three-wire cable, with two hot wires (black and red), a ground wire (green or bare), and a neutral wire (white) if required by local codes.
The following points are essential:
- Ensure that the device is located at least 6 inches from any wall or obstruction to ensure proper airflow.
- For units controlled by a thermostat, wire the thermostat to control the power sent to the heating unit, following manufacturer instructions.
- Always confirm the unit’s power rating before wiring to avoid overloading the circuit.
- Double-check connections, ensuring all are tight and secure to prevent shorts or overheating.
Below is a table showing common components and their connections:
| Component | Connection Description |
|---|---|
| Hot Wires (Black/Red) | Connect to the terminals marked “L1” and “L2” on the unit or thermostat |
| Neutral Wire (White) | If applicable, connect to the neutral terminal |
| Ground Wire (Green or Bare) | Connect to the ground terminal of the device and junction box |
| Breaker | Install a 20-30 amp double-pole breaker in the panel box for protection |
Choosing the Correct Gauge Wire
Use 12-gauge wire for circuits with up to 20 amps. For systems requiring higher current, such as those with 240V and more power, opt for 10-gauge wire. Ensure the wire is rated for the correct amperage based on the appliance’s power demand and the circuit breaker size.
Avoid using lower gauge wires, like 14-gauge, for appliances requiring 20 amps or more, as they may overheat and lead to safety risks. Always refer to local electrical codes to confirm the appropriate wire size for your specific application.
If you’re working with 240V systems, choose copper over aluminum wire for better conductivity and durability. Copper has lower resistance, which improves performance and reduces heat buildup.
Step-by-Step Guide to Connecting the Thermostat to an Electric Heating Unit
Start by turning off the power at the circuit breaker to prevent any electrical accidents. Use a voltage tester to ensure the lines are de-energized.
Remove the cover of the thermostat to expose the internal connections. Locate the terminal blocks where the wires from the electrical panel will connect. Typically, these include a common wire (neutral), a live wire (hot), and a load wire going to the heating element.
Connect the neutral wire to the neutral terminal. Ensure this wire is securely attached to avoid loose connections that could lead to electrical hazards.
Next, connect the hot wire to the live terminal. Tighten the screws carefully to avoid any risk of fire or short circuits.
The load wire will connect to the terminal marked for heating control. This wire regulates the power sent to the heating unit. Ensure it is firmly secured.
Once all connections are made, double-check that the wires are placed correctly and there are no exposed copper strands that could cause short circuits.
After securing the wiring, replace the thermostat cover and turn the power back on at the breaker. Test the unit by adjusting the temperature and confirming the heating element activates.
Always follow manufacturer guidelines and, if unsure, consult a licensed electrician to ensure compliance with local electrical codes.
Safety Precautions and Code Compliance When Installing a Heating Unit
Ensure compliance with local electrical codes to prevent safety hazards during installation.
- Disconnect power before starting the installation process to avoid electrical shock.
- Verify that the electrical circuit is adequate for the unit’s requirements; check amperage and voltage ratings.
- Install a dedicated circuit breaker to prevent overloading. The unit should not share a circuit with other appliances.
- Place the unit at least 12 inches away from combustible materials, such as curtains or furniture, to reduce fire risks.
- Use proper gauge wire as specified by the manufacturer to prevent overheating.
- Ensure that all connections are secure, and that no exposed wires are left unattended.
Adhere to the National Electrical Code (NEC) guidelines and any local amendments, especially concerning clearances and grounding. Failure to comply with these standards could lead to malfunction or fire hazards.
- Confirm that the installation location allows for proper air circulation and avoids blocking vents or airflow.
- Use a non-corrosive grounding system to prevent electrical faults and ensure safety.
- Check that all devices, including thermostats, are installed in locations where they won’t be affected by external heat sources.
After installation, perform a functional test to verify that the unit operates correctly, and inspect for any unusual sounds or odors. Routine maintenance should be scheduled annually to ensure long-term safety and efficiency.