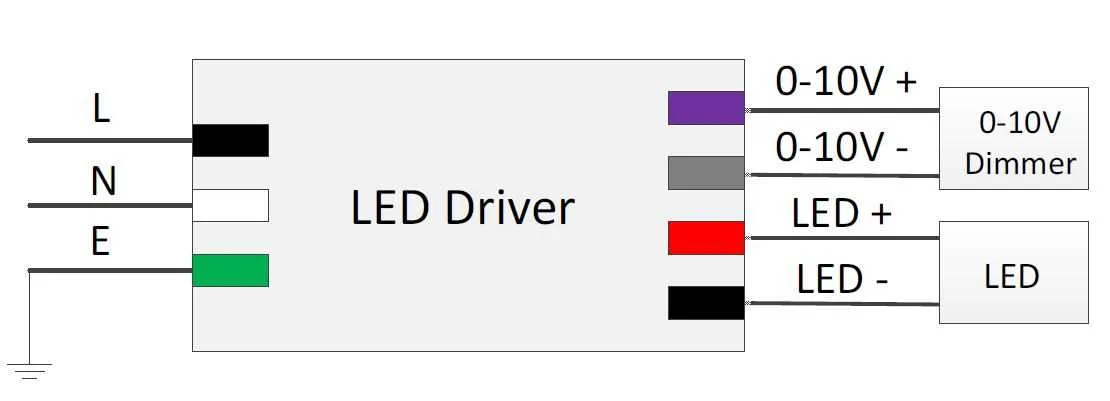
To properly configure a lighting system with adjustable brightness control, ensure that the components are connected to the correct terminals. First, identify the control input and output terminals on both the power source and the light fixture. It is crucial to match the voltage specifications of each component to avoid damage or malfunction.
Make sure to use a compatible control signal, typically ranging from 0 to 10 volts, to regulate the intensity of the lights. The control signal should be wired directly to the appropriate input terminal of the fixture. Ensure the wiring is secure and insulated to prevent short circuits.
For smoother operation and to avoid flickering, keep the distance between the control source and the light fixture as short as possible. Additionally, using a shielded cable helps minimize electrical interference and enhances the overall stability of the system.
Tip: Always verify the specifications of each component before installation to confirm they support the desired range of voltage input and output. This ensures that the system operates efficiently and without issues over time.
Finally, after connecting the control mechanism, test the system by gradually adjusting the voltage and observing the light’s response. Make fine adjustments to the control if necessary, ensuring consistent and reliable performance.
0-10V Control Circuit Setup
Connect the control input (positive) to the voltage control line, typically marked as “DIM” or “Control.” The negative side should go to the common or ground terminal of the power supply or driver. Ensure that the power source for the light fixture is correctly isolated from the control lines to prevent interference.
The voltage range for this control system generally spans from 0 to 10 volts, where 0V represents the minimum brightness and 10V corresponds to full intensity. For optimal results, it is essential to use cables designed for low-voltage communication to avoid signal loss.
To implement a smooth response, make sure the control driver supports a range from 0V to 10V, as some systems may require precise calibration to adjust the response curve between brightness levels. Proper termination of unused control wires is also important to avoid voltage spikes that could damage sensitive electronics.
If you’re using a multi-channel controller, each channel should correspond to its own set of control leads. Cross-talk between channels could reduce system performance. Use shields or twisted-pair cables to minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI), especially in environments with significant electrical noise.
Check manufacturer specifications for any necessary resistors or capacitors that should be included in the circuit. These components are often required to stabilize the signal and prevent fluctuation, ensuring consistent performance across the entire range of voltage levels.
Understanding the Components of a 0-10V Control Circuit
When designing a system that adjusts lighting intensity via a low-voltage control signal, several key elements must be properly integrated. The most critical component is the power supply, which delivers the required voltage and current to operate the system. The control signal is typically transmitted through two wires, one for the signal itself and another for the common ground. The device receiving the control input, such as a compatible ballast or driver, adjusts the brightness based on the signal received.
The signal generator is often a wall switch or a dedicated dimming controller, capable of varying the output within a specific range to achieve the desired light level. The control circuit should also include a resistor or a voltage regulator to prevent signal overloads, ensuring proper functioning across the full range of adjustment.
In addition to the control elements, the compatibility of all components must be verified. Not all devices can interact with each other without special interfaces, so ensure that both the control unit and the load (driver or ballast) support the same voltage levels and communication protocols. Proper grounding of the system is essential to avoid electrical interference that could affect signal accuracy.
Proper installation and maintenance of the circuit will ensure long-term reliability and optimal performance. Regular checks for wiring integrity and secure connections are recommended to prevent signal disruptions.
How to Connect 0-10V Dimming Wires to a Compatible Fixture
To connect a 0-10V control system to a light fixture, ensure the fixture supports the low-voltage control input. First, identify the control wires: typically, a positive (V+) wire and a negative (V-) wire. The V+ wire is usually the blue one, while the V- is black.
Connect the V+ (blue) wire from the control system to the corresponding terminal on the fixture. Similarly, connect the V- (black) wire to the negative terminal. For a proper connection, make sure to securely fasten the wires using wire nuts or terminal screws, depending on the fixture design.
If using a power supply with multiple control channels, verify that each channel is linked to the correct fixture terminal. Pay attention to the fixture’s voltage ratings to avoid overloading. Once all connections are made, power on the system and test the light adjustment functionality.
Always double-check wiring polarity to ensure proper operation, as incorrect wiring can cause malfunction or damage. Follow manufacturer instructions for specific wiring methods and safety guidelines to achieve optimal results.
Troubleshooting Common 0-10V Lighting Control Issues
If you’re experiencing issues with your lighting system’s brightness control, follow these steps to identify and resolve common problems:
- Check the Voltage Range: Ensure the voltage at the control wires falls within the specified range for the system to operate correctly. Typically, this should be between 0-10V. If it’s out of range, you may need a new power supply or resistor.
- Verify Connections: Inspect all connections for secure contacts. Loose or corroded terminals can cause flickering or non-responsive adjustments. Ensure each wire is properly seated and tightened.
- Inspect the Control Signal: If adjustments are not responding as expected, use a multimeter to measure the control signal at the input terminals. A weak or fluctuating signal may indicate a problem with the control unit or the wiring.
- Check for Interference: Interference from other electrical systems can affect signal quality. Ensure that control wires are kept away from power lines or high-voltage sources. Use shielded cables if necessary to minimize noise.
- Test with a Known Working Device: To rule out potential issues with the controller or load device, temporarily swap the components with a known working unit. This can help pinpoint whether the issue is with the controller or the connected lighting fixture.
- Ensure Proper Grounding: A poor ground connection can lead to erratic performance or complete failure of the control signal. Double-check grounding points to ensure they are secure and properly connected.
By following these steps, most common control issues can be identified and resolved quickly. If problems persist, consider contacting the manufacturer or an experienced electrician for further assistance.