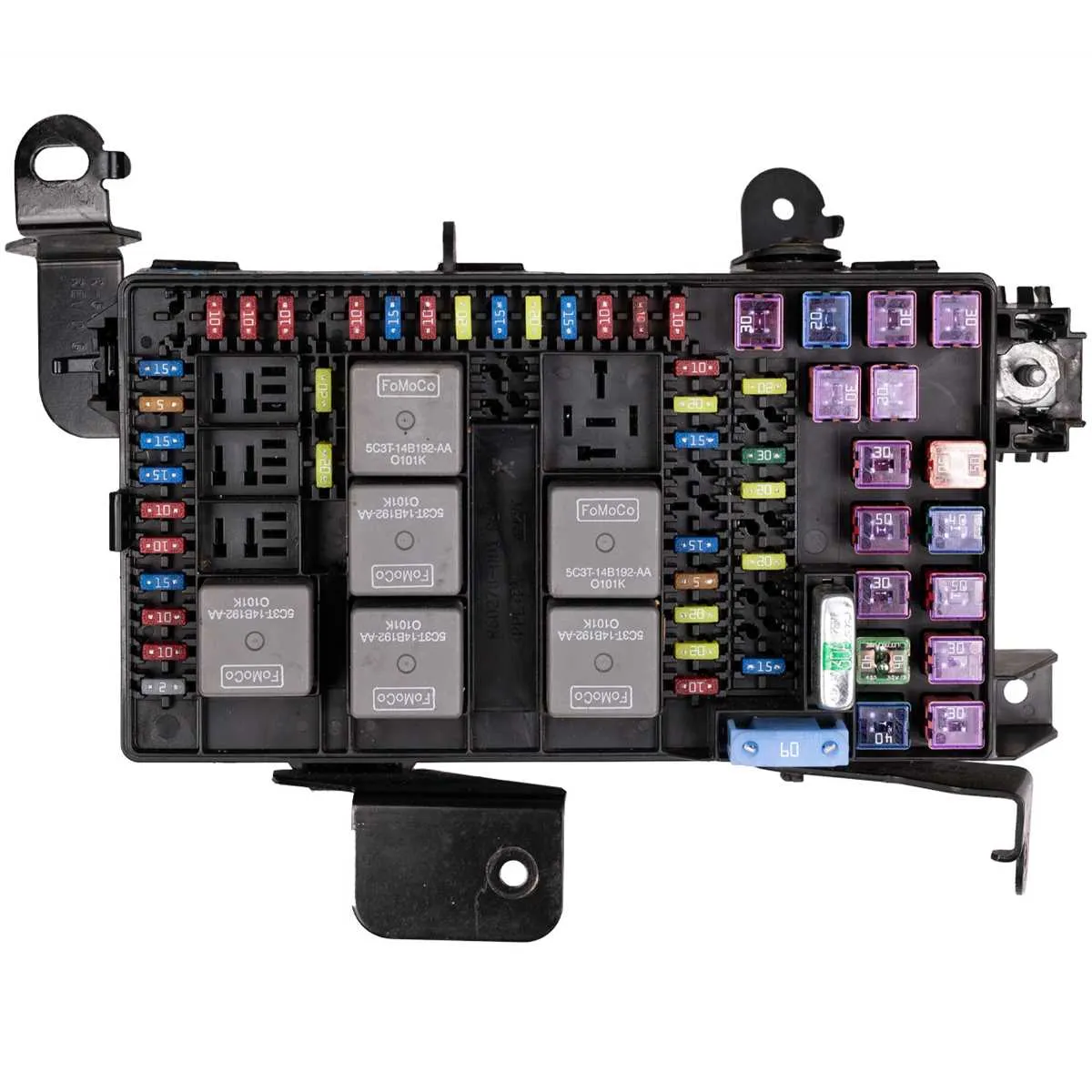

Locate the primary power distribution center under the dashboard on the driver’s side to access all key circuit protectors for your 2006 mid-size sport utility vehicle. Each relay and protective device is precisely labeled to assist with rapid identification and troubleshooting of electrical faults.
Essential tip: Reference the internal cover label to verify amperage ratings and specific assignments for each protective component. This ensures correct replacement and prevents overloads that may cause system failures.
For auxiliary systems such as lighting, HVAC, and engine management, the secondary relay block is positioned within the engine compartment near the battery. Its layout distinctly separates high-current circuits from lower-power controls for safety and efficiency.
Maintenance advice: When inspecting or replacing any electrical safety devices, disconnect the negative battery terminal to avoid short circuits and potential damage to electronic modules.
06 Model Electrical Panel Layout
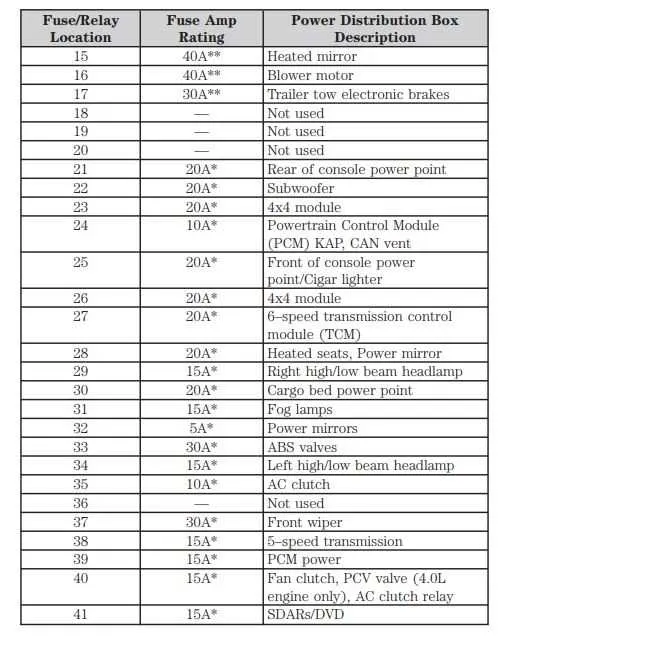
Locate the primary power distribution panel under the dashboard on the driver’s side for easy access. This panel contains all the critical circuit protectors responsible for interior and exterior electrical components.
Each slot is clearly numbered and labeled for systems like headlights, ignition, HVAC, and audio equipment. For the 2006 version, position #12 controls the rear defroster, while position #7 safeguards the fuel pump relay.
Refer to the identification chart printed on the underside of the cover to identify amperage ratings–commonly 10A, 15A, or 20A–and ensure replacement units match original specifications.
For under-hood panels, the secondary array near the battery contains high-current protectors for the cooling fans and ABS module. Slots #3 and #5 are frequently associated with these functions and should be checked first when troubleshooting.
Always disconnect the battery before servicing any circuit protectors to avoid electrical shorts or damage. Use a tester to verify continuity if a particular electrical function is failing.
Locating and Identifying Each Fuse in the 2006 SUV Power Panel
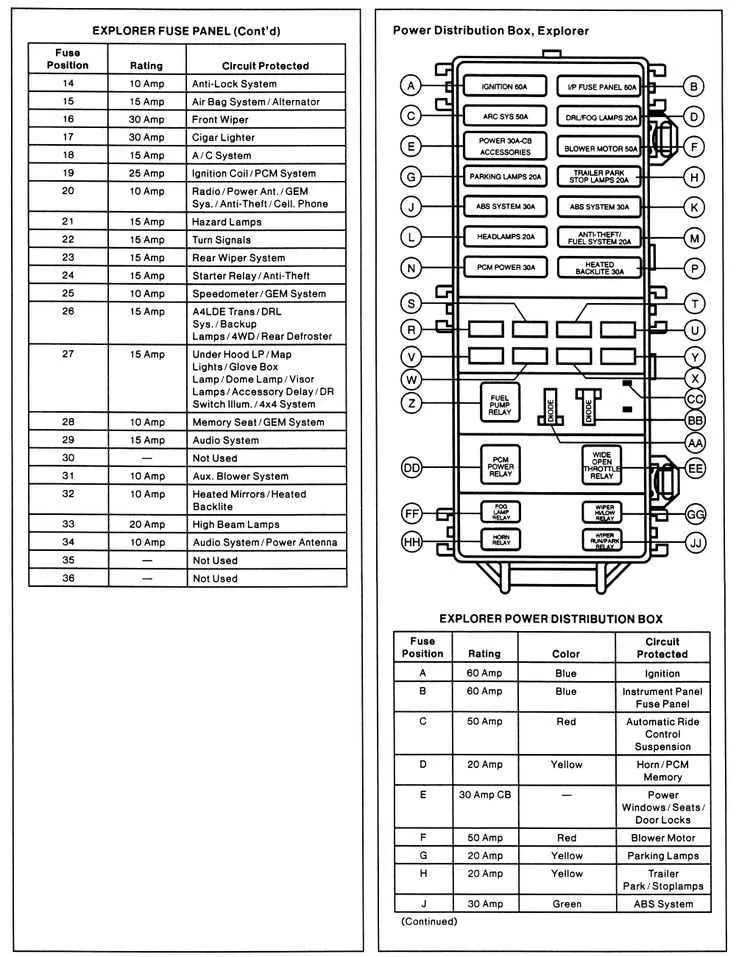
Access the main electrical panel beneath the dashboard on the driver’s side to find all circuit protectors. Each slot is numbered and corresponds to a specific system, such as headlights, fuel pump, or air conditioning. Use the panel cover’s label to match numbers with functions quickly.
The secondary unit is located in the engine compartment near the battery. It contains high-amperage protectors for critical components like the ignition system and cooling fans. Identify each by comparing the assigned amperage rating printed on the protective element with the reference chart inside the lid.
For the interior panel, position 10 protects the power windows, while slot 14 manages the radio and interior lights. In the under-hood section, a 40-amp protector at position 5 controls the radiator fan, and a 30-amp element at position 9 is dedicated to the ABS system.
Always verify amperage values and physical condition before replacing any circuit protector to avoid damage. Refer to the numeric coding and legends printed on both panels for precise identification without guesswork.
Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing a Blown Fuse in the 06 Vehicle
Start by turning off the ignition and removing the key to ensure safety. Then, locate the electrical panel inside the cabin or under the hood. You will need a working replacement component of the same amperage as the original one.
- Identify the exact location of the malfunctioning part by consulting the vehicle’s electrical layout.
- Use a fuse puller or needle-nose pliers to carefully remove the damaged part from its slot. Avoid using excessive force to prevent damage to the surrounding components.
- Inspect the old component to confirm it’s blown–typically, the metal strip inside will be visibly broken.
- Insert the new piece into the same slot, ensuring it fits securely and is aligned properly.
- Once in place, test the related system to confirm functionality.
- If the issue persists, repeat the process and check for any potential wiring problems that may be causing repeated failures.
Ensure that you use the right amperage for the replacement, as using a higher or lower rating can cause electrical malfunctions or even fire hazards. If unsure, refer to the user manual for specific amperage details.
Troubleshooting Common Electrical Issues Using the Wiring Layout
Start by checking the main power distribution panel. Identify if any connectors are loose or disconnected. This can often cause issues with the car’s electrical functions, including lights, radio, or windows.
If specific components aren’t functioning, consult the corresponding section in the wiring layout. For example, the headlights or tail lights might be powered by a particular relay or circuit that can be traced easily. Look for any signs of blown connectors or corrosion, especially around the contact points.
Test the current in suspect areas using a multimeter. Cross-reference the results with the values listed in the layout guide to confirm if there’s a short or open circuit affecting power flow.
Check the continuity of the relays by examining whether they are receiving the right amount of current. A relay that doesn’t activate correctly could result in non-functioning parts such as the horn or the air conditioning. Replace faulty ones promptly to restore normal operation.
Ensure that all power routes are intact. If you notice consistent issues, the grounding system might be compromised. The wiring map will guide you to the primary grounding points, which should be free of dirt or rust that could obstruct the circuit.
For intermittent issues, inspect the connectors for any signs of wear or loose connections. Over time, vibrations from driving can cause electrical components to shift, leading to fluctuating power. Tightening or replacing faulty terminals can often resolve these irregularities.
Lastly, keep track of any changes to electrical performance after repairs. If the same issues arise repeatedly, there could be a deeper wiring fault that requires more advanced diagnostics.