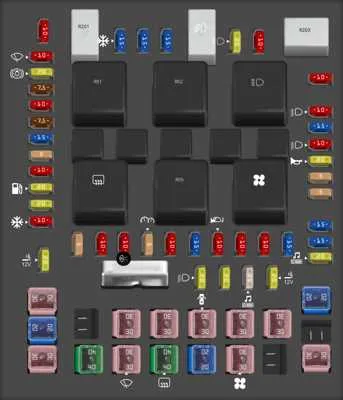
To easily identify and address issues with your vehicle’s electrical components, refer to the layout of the main circuitry panel under the hood. This resource will provide you with all the necessary details about the positioning of individual relays and connectors, ensuring you can quickly troubleshoot and replace malfunctioning parts without unnecessary hassle.
Knowing the exact location of each electrical element within your car is crucial for any repair or upgrade. The connections you’ll find here control various functions, from lighting to advanced mechanical systems. Understanding the role of each component, including which ones serve as primary fuses or power relays, allows for precise action when dealing with electrical failures.
For anyone unfamiliar with the setup, the detailed guide on component positioning is an invaluable tool. Once you pinpoint the section responsible for a particular feature, you can easily diagnose issues, such as a blown circuit or malfunctioning relay. If you’re in doubt, always consult the manufacturer’s specifications before making any adjustments or replacements.
Pay attention to the marked configurations on the electrical board, as they often contain information about power ratings and control functions. Each part is typically marked with a number or a symbol, which simplifies identifying the right component quickly and effectively.
14 F150 Electrical Layout Guide
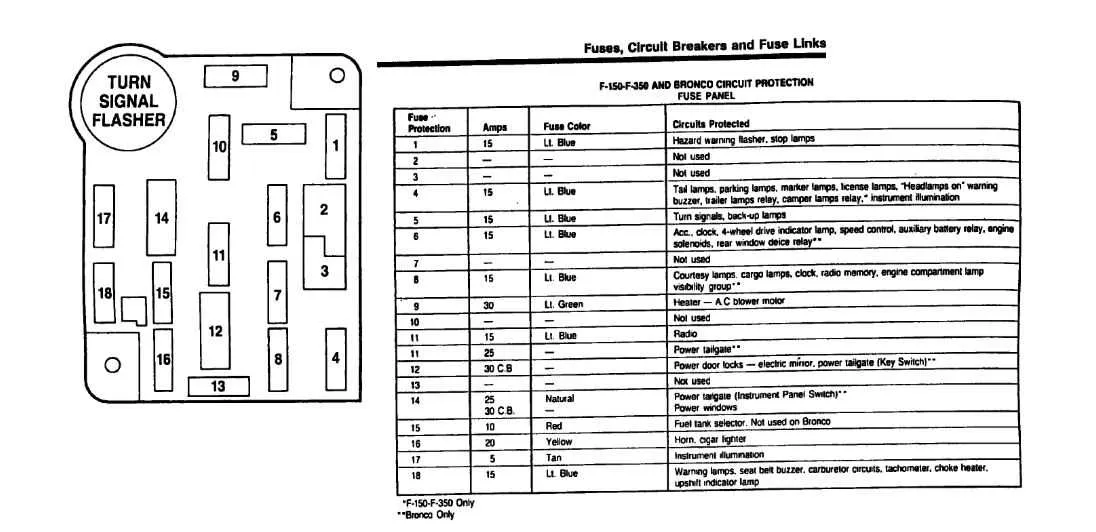
If you need to locate specific relays or components in your vehicle’s electrical setup, refer to the centralized distribution panel. It’s located in the engine compartment for easy access. Components like the alternator, air conditioning, and lighting circuits are all connected here.
Ensure you know the function of each individual connection to troubleshoot effectively. For example, the connector for the headlamps is typically found in the section closest to the battery. The accessory connections are usually labeled on the back cover, helping you identify them with ease.
In case of a malfunction, begin by checking the high-current distribution area, where heavy-duty circuits like the ignition and power steering relays are located. These parts are crucial and can cause major issues if they become compromised.
The under-dash arrangement is more compact and houses the interior-related systems, including the infotainment unit and airbag control. Follow the color-coding or markings to ensure accuracy when repairing or replacing any components.
Always refer to the owner’s manual for a detailed list of each section’s roles and specific amperage ratings. This will help you replace damaged elements with parts that match the original specifications.
Understanding the 14 F150 Fuse Box Layout and Component Locations
Start by locating the primary electrical panel under the hood on the driver’s side, near the battery. It houses the critical relays and circuits for engine management, lighting, and the alternator. If your vehicle has an auxiliary relay, you’ll find it in a separate compartment. For components linked to the cabin, check the secondary panel beneath the dashboard on the left side. This unit supports interior electronics like the climate control system, audio equipment, and cabin lighting.
Ensure that you identify each circuit’s amperage rating, as these determine the safety parameters for your vehicle’s electrical components. Use a multimeter to confirm the integrity of each connection. If there is a malfunction, start with checking the main power relay, which distributes current across the system. Be cautious when handling connections to prevent damage to sensitive parts.
For convenience, list the locations of key components such as the ignition relay, powertrain control module (PCM) relay, and fan motors. Note that the smaller fuses within the main panel are dedicated to specific systems, including the fuel injectors, air conditioning, and the anti-theft alarm. When replacing any part, always ensure that the replacement meets the manufacturer’s specifications for optimal performance.
How to Identify and Replace a Blown Fuse in a 14 F150
To replace a faulty component in your truck’s electrical system, first, locate the relevant section in the engine compartment or cabin where the protective units are housed. Open the panel carefully, ensuring it’s cool and dry.
Next, visually inspect each element to spot any that are visibly damaged. If the component is transparent, look for a broken metal strip inside. Use a multimeter set to continuity mode to double-check whether the element is indeed non-functional. For further certainty, compare with a known working unit from another circuit.
Once identified, remove the damaged unit by pulling it straight out. Be sure to note the amperage rating, usually written on the side. Purchase a replacement part with the same specifications. Ensure the new unit fits snugly into place and secures properly within the socket.
Before reassembling, test the circuit by turning the ignition on and checking if the affected system operates as expected. If problems persist, recheck connections or look for issues elsewhere in the wiring.
Common Electrical Issues in the 2014 Ford Pickup and Troubleshooting Tips
If you’re experiencing electrical malfunctions in your 2014 Ford truck, there are a few common problems to keep an eye on. Many of these issues can be traced back to specific connections or components in the vehicle’s power distribution system. Here are some key troubleshooting tips to resolve these problems quickly and efficiently:
- Blown Circuits: Often caused by power surges, a blown circuit can lead to various components losing power. Check the associated relay or terminal and replace any damaged parts.
- Loose Connections: Wiring that is loosely connected can cause intermittent power loss. Inspect all connectors thoroughly, especially the ones under the dashboard and near the engine compartment.
- Corroded Terminals: Corrosion at electrical terminals can prevent proper conductivity. Clean the affected terminals with a wire brush and apply dielectric grease to prevent further buildup.
- Overloaded Systems: Overloading specific circuits can lead to overheating and failure. Ensure you’re not running too many accessories or high-power devices off the same circuit.
- Faulty Relays: A malfunctioning relay may cause a device to stop working altogether. Use a multimeter to test the relay’s operation and replace if necessary.
To minimize electrical issues, follow these general guidelines:
- Always replace damaged wires with high-quality replacements designed for automotive use.
- Check and clean all connectors during routine maintenance to avoid corrosion buildup.
- Double-check power demands on individual systems to prevent overloading.
Regular inspection and immediate attention to any electrical irregularities can save you time and money in the long run.