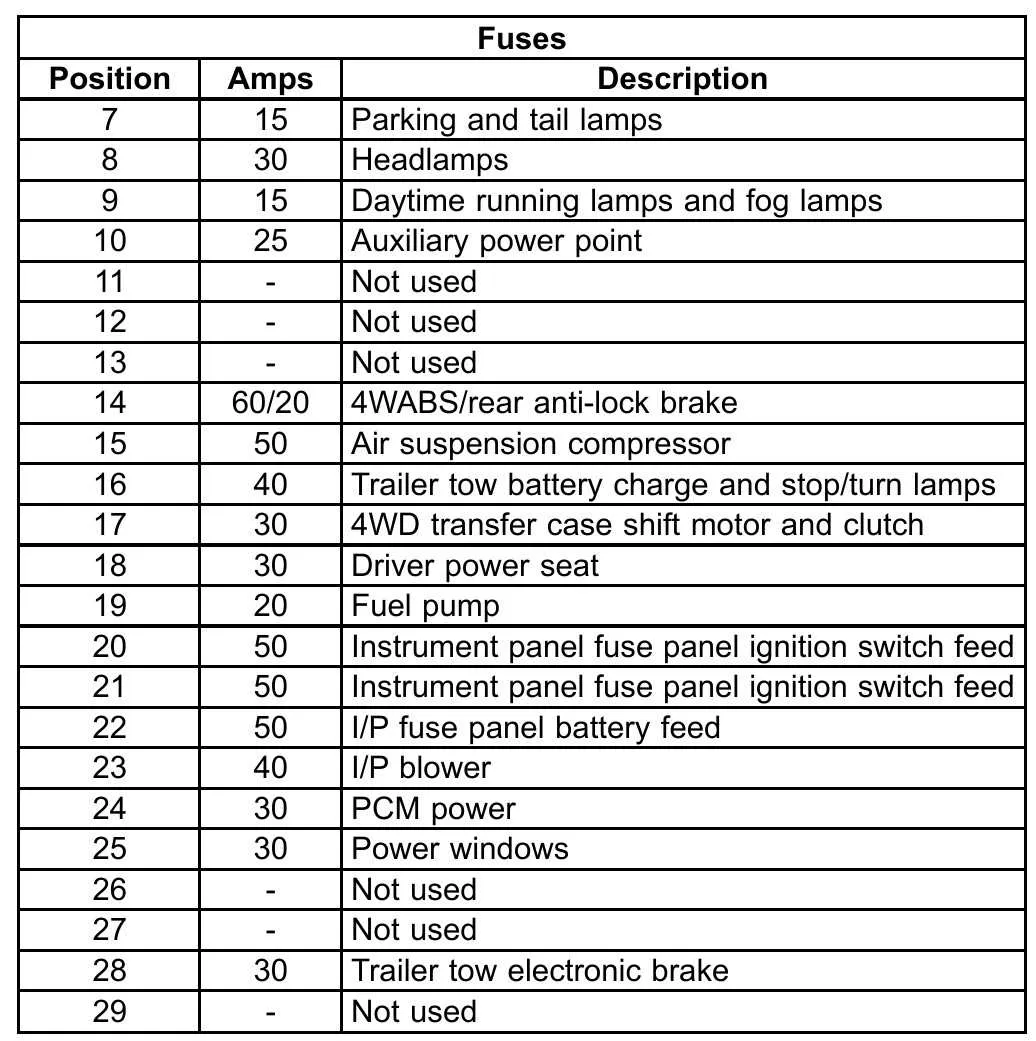
When troubleshooting electrical issues in your vehicle, it’s crucial to understand the location and structure of the central power control. A well-organized fuse panel ensures proper functioning of various components, from lights to engine systems. If you’re facing problems with electrical connections, the first step is to check the control unit near the engine area for the proper allocation of power.
Refer to the official map for the specific placement of relays, switches, and protection elements. Typically, these units are located close to the engine, and you can find detailed labels for each circuit. Make sure to verify the correct amperage ratings for each circuit to avoid short circuits or damage to sensitive components.
Key components to check: Start by identifying the main power relays and checking for any blown protection elements. Also, ensure the connections are tightly secured, as loose wires can cause intermittent faults. If you’re uncertain about the specific function of each part, it’s helpful to consult a manual or use an online resource for a detailed layout.
Before replacing any faulty parts, double-check the electrical connections and ensure you’re using the correct part numbers and ratings to maintain safety and proper operation.
Electrical Component Layout for Engine Compartment

For proper functionality and quick troubleshooting, refer to the following guide that outlines the layout of the electrical system located in the engine area. Each section is clearly defined, with specific details on the allocation of various relays and connectors. This will help in diagnosing issues or replacing malfunctioning parts.
| Position | Component | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Relay for Fuel Pump | Controls the fuel pump relay for engine operation. |
| 2 | Starter Relay | Responsible for initiating the engine’s starting process. |
| 3 | Headlight Circuit Breaker | Regulates power flow to the headlight system. |
| 4 | Ignition Coil Relay | Provides electrical power to the ignition system. |
| 5 | Cooling Fan Relay | Controls the operation of the cooling fan for temperature regulation. |
| 6 | Horn Relay | Manages the electrical flow to the horn. |
| 7 | Windshield Wiper Relay | Operates the windshield wipers for visibility in adverse weather. |
| 8 | AC Compressor Relay | Regulates the operation of the air conditioning compressor. |
| 9 | ABS System Relay | Ensures power is supplied to the anti-lock braking system. |
When inspecting or replacing any part, ensure all connections are secure to prevent electrical malfunctions. A multimeter can help test the continuity and voltage output at each component for verification. Additionally, always consult the specific model’s technical manual for additional details or changes to this layout over time.
How to Identify Electrical Component Locations in the Engine Compartment
To locate the various electrical parts in the engine compartment, follow these clear steps:
- Open the vehicle’s front cover and secure it in place.
- Locate the central panel, typically positioned near the battery or along one of the vehicle’s sides.
- Check the top of the panel for labeling, which should identify the individual elements inside.
- If no labels are visible, refer to the detailed instruction sheet, usually available inside the driver’s side door frame or glove compartment.
- Ensure the power is switched off before working with any connections to avoid damage or injury.
The engine compartment electrical panel houses components responsible for powering various vehicle functions, such as lights and air conditioning. For identification:
- The largest sections of the panel typically handle major components like cooling fans and engine management systems.
- Smaller sections often manage less demanding elements, such as the windshield wipers and lights.
If the labeling is unclear or missing, use a multimeter to test individual connections for continuity, making sure to reference the wiring scheme in the manual.
Common Electrical Problems and Solutions in the Vehicle’s Fuse Area
Start by inspecting the connections for any visible corrosion or damage. Ensure all wires are tightly secured to their respective terminals. Loose or corroded connections can lead to electrical failure or intermittent power loss.
If you notice that certain components stop working suddenly, check the relay switches and fuses for wear. A malfunctioning relay can prevent power from reaching critical systems. Replace any blown relays with the exact replacement to avoid circuit issues.
For recurring electrical issues, consider using a multimeter to test the continuity of circuits. If no continuity is detected in a particular path, there may be a break in the wiring that needs repair.
Some users report frequent problems with the power windows, lighting systems, or ignition. In these cases, inspecting the main power circuits for any voltage drop is crucial. A significant drop may indicate a failing connection or poor grounding.
If you suspect a faulty component, like the alternator or ignition switch, disconnecting the battery before performing any tests or replacements is essential to avoid further electrical damage.
When troubleshooting persistent electrical faults, examine the area for signs of overheating, which can cause plastic components to melt and short-circuit. This may require replacing damaged wiring or insulating materials.
Always refer to the vehicle’s manual for exact specifications when replacing parts to ensure compatibility and safe installation.
Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing Fuses in the Vehicle’s Engine Compartment
Start by locating the power distribution center, usually found near the engine bay. This component houses multiple electrical circuits that are protected by individual units. Open the cover carefully to access the internal components.
Identify the faulty unit by checking the circuit description on the inside of the cover or referring to the vehicle’s manual. Use a multimeter or a fuse tester to confirm whether the unit is blown. A blown one will have a visible break in the metal strip inside it.
Once identified, use a fuse puller or a pair of needle-nose pliers to remove the defective item. Be cautious not to damage the surrounding elements while extracting it.
Select the appropriate replacement from the set of spares provided with the vehicle, ensuring it matches the specifications in terms of amperage. Inserting the new unit should be done with care to ensure a snug fit, aligning it correctly within the slot.
After replacement, check the electrical functionality to ensure the issue is resolved. If the new unit blows quickly, check for underlying wiring problems that could be causing excessive current draw.
Finally, secure the cover back onto the distribution center and ensure everything is in its place. Regularly check the electrical systems to avoid future issues.