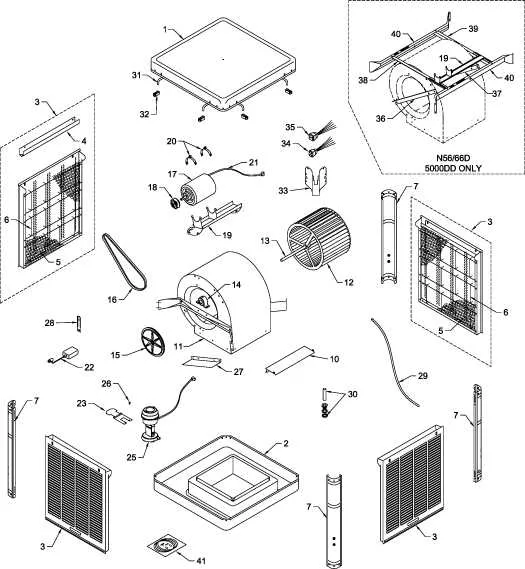
Always begin with inspecting the air delivery assembly: the rotary blade mechanism should spin freely without resistance. If motion is restricted, check for worn bushings or obstructions around the spindle shaft. Align the pulley and motor mount precisely to prevent belt misalignment and premature wear.
Next, examine the water distribution structure. Ensure the tubing network supplies each cellulose panel uniformly. Cracks or mineral deposits inside the conduit often cause uneven saturation. Replace compromised lines with flexible vinyl hoses of at least 1/4″ internal diameter for consistent flow.
Look into the reservoir system beneath the unit. The float valve should maintain water levels within half an inch from the designated mark. An imprecise float arm may result in overflow or pump starvation. Use an adjustable brass float for reliable regulation over time.
Assess the pump’s output capacity, usually labeled in gallons per hour (GPH). For units covering 1,000 square feet, a minimum of 500 GPH ensures adequate circulation. If the discharge pipe appears clogged, clean the intake screen thoroughly or replace the entire submersible component.
Finally, verify the electrical components. The switchgear and thermostat connections must be corrosion-free and properly insulated. Loose terminal screws can lead to intermittent startup or fan malfunction. Use dielectric grease on contact points to reduce oxidation and extend service life.
Essential Components Overview
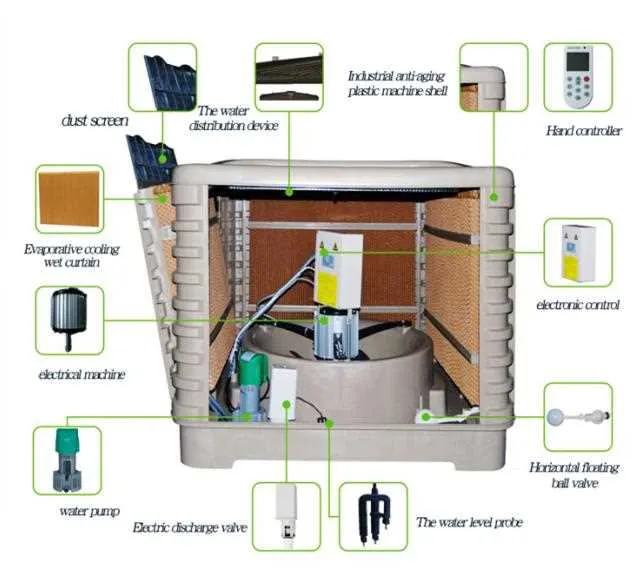
When assembling or repairing an evaporative air cooling unit, focus on understanding key elements such as the water distribution system, fan assembly, and air ducts. The fan, typically located in the center, drives the airflow across wet media, which helps to lower the temperature. A well-maintained water distribution system ensures consistent moisture delivery to the cooling pads, preventing dry spots and optimizing performance.
Pay special attention to the pump that circulates water to the pads. This pump must be regularly checked for clogs or damage, as it directly impacts the efficiency of the cooling process. Additionally, inspect the evaporative media for wear and tear, as clogged or deteriorated pads can drastically reduce cooling efficiency.
The motor housing, often located at the top, should be cleaned to avoid dust buildup, which can lead to overheating and failure. Ensure that all connections are secure, especially the electrical ones, to avoid short circuits or power disruptions.
Regular maintenance includes replacing filters, checking the integrity of water lines, and ensuring proper air exhaust flow. When replacing any components, ensure compatibility with the unit’s specific design and size for optimal airflow and efficiency.
Identifying Key Components of a Swamp Cooler
Start by locating the water reservoir, which supplies the moisture required for the cooling process. Ensure it’s properly filled and check for any blockages in the inlet valve that might restrict the water flow.
The next crucial element is the evaporative pad. Inspect its condition regularly, as it plays a vital role in the heat exchange. If the pad appears worn or clogged, replace it immediately to maintain optimal performance.
Locate the fan assembly, which is responsible for drawing air through the wet pad and circulating it into the living space. Listen for any unusual noises, as these can indicate misalignment or wear. Lubricate the fan motor to prevent overheating.
Pay attention to the exhaust vents. These allow the warm air to escape, ensuring the system functions efficiently. Ensure the vents are unobstructed and free from debris, as this can drastically reduce airflow.
Examine the control panel or thermostat, which regulates the system’s operation. Ensure that the settings match the desired indoor temperature and that the system turns on/off appropriately. If the settings seem off, consider recalibrating or replacing faulty components.
How to Troubleshoot and Replace Common Components
Begin by inspecting the motor for any signs of wear or overheating. If the fan isn’t turning or operates erratically, it could be a sign that the motor has burned out. Test the motor with a multimeter to check for continuity. If faulty, replace it with an identical model. Be sure to disconnect the power supply before performing any repairs.
If airflow is weak, check the fan blades for blockages or damage. Clean any debris obstructing the blades. If the blades are cracked or bent, replace them promptly to ensure optimal airflow. A worn-out fan belt can also reduce performance; examine it for cracks or fraying and swap it out if necessary.
Examine the pump and water distribution system for proper operation. If water isn’t flowing as expected, the pump may be clogged or faulty. Clean the pump’s intake and replace it if needed. Ensure the water lines are clear and free of blockages, as this can impact performance.
For an inefficient cooling system, check the pads for dryness, cracking, or buildup. If they appear damaged or clogged, replace them to improve moisture distribution and air cooling efficiency. Make sure the pads are properly aligned to avoid uneven cooling.
Don’t overlook the electrical components. Inspect the wiring for corrosion, fraying, or loose connections, especially around the motor and pump. Replace any damaged wiring and ensure secure connections to avoid electrical failures.
Test the system’s thermostat to ensure it’s accurately regulating temperature. If the temperature doesn’t match the setting, replace the thermostat to maintain the system’s efficiency.
Lastly, check the float valve in the water tank. If the water level isn’t maintained properly, it could lead to pump failure. Clean the float valve and replace it if malfunctioning.
Understanding the Role of Each Component in the Cooling Process
To ensure optimal performance in evaporative cooling systems, it’s crucial to comprehend the role of each key element that contributes to the airflow and moisture regulation process.
- Water Distribution System: Ensures an even flow of water over the cooling pads, allowing for maximum evaporation. A malfunctioning distribution system can lead to uneven cooling and wasted water.
- Cooling Pads: These are the primary surface where evaporation occurs. They should be kept clean and properly saturated to maintain effective cooling. Damaged or dried-out pads reduce efficiency significantly.
- Fan: The fan draws warm air into the system, passing it through the saturated pads. Its size and speed determine the volume of air that can be cooled, directly affecting the overall cooling efficiency.
- Motor: Powers the fan. If the motor malfunctions, the fan will not operate at the required speed, drastically reducing cooling efficiency. Regular maintenance ensures consistent performance.
- Water Reservoir: Stores the water necessary for evaporation. A well-maintained reservoir ensures a steady supply of water, while clogged or dirty reservoirs can hinder the cooling process.
- Control System: Regulates water flow, fan speed, and sometimes temperature settings. Ensuring that sensors and thermostats are functioning correctly can help maintain energy efficiency and comfort levels.
Understanding these components’ interactions and maintaining each element in good working order is essential for achieving reliable and efficient cooling.