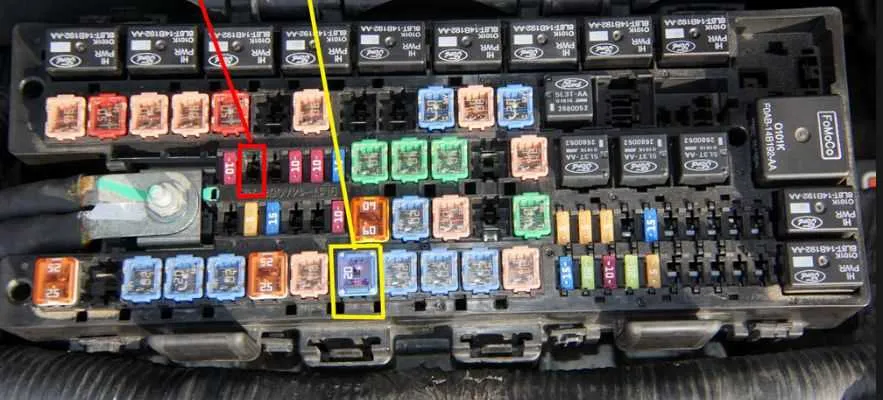

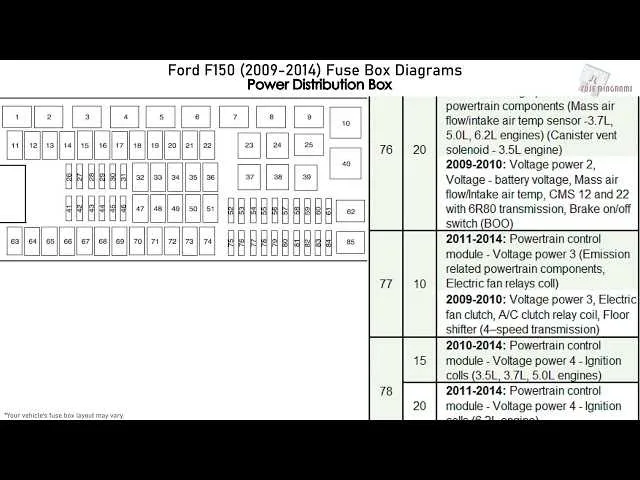
When troubleshooting the electrical components of your vehicle, it’s crucial to understand the location and function of the various relays and fuses involved. These components play a key role in the operation of critical systems like lighting, ignition, and more. If you’re facing issues with any of these, locating the correct section and identifying the right component can save you significant time and effort.
For efficient diagnostics, start by checking the primary panel under the dashboard and the secondary one in the engine compartment. Both areas house vital electrical connectors that link to multiple systems. Each relay or fuse corresponds to a specific part of the vehicle, and understanding how they are mapped can simplify the troubleshooting process.
To identify the components quickly, refer to the manual for an exact reference of each circuit and its role. By replacing any faulty relays or fuses, you can restore functionality to a variety of systems that may not be working due to electrical disruptions. This approach ensures a systematic, precise solution to electrical malfunctions.
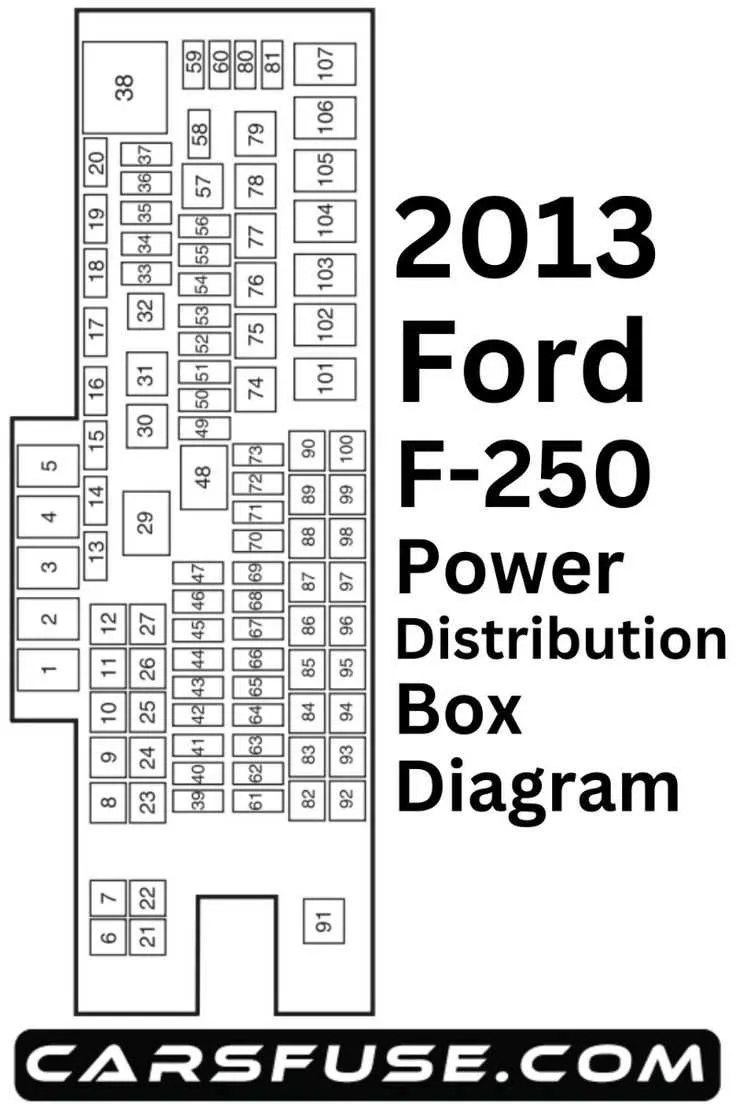
Electrical System Layout for 2013 Pickup Truck
For efficient troubleshooting of your vehicle’s electrical components, refer to the electrical system map located under the dashboard and near the engine compartment. This schematic provides a detailed overview of the specific relays and connections responsible for powering various systems like lights, ignition, and engine management.
Each cluster of connectors in the cabin or engine area houses multiple fuses that control individual circuits. In particular, focus on the section near the driver’s side footwell, which holds a major assembly for interior electrical components. The under-hood layout features a secondary panel for high-power systems such as air conditioning, power steering, and alternator regulation.
To address potential issues, check the labeling on the covers to identify which component is connected to each fuse. Make sure to replace any blown fuses with replacements that match the required amperage to avoid further damage. Regularly inspect the wiring for any signs of corrosion or wear that could affect the flow of current to critical systems.
Understanding the Electrical Layout of the 2013 Pickup’s Power Distribution System
To effectively manage the electrical components in your vehicle, start by familiarizing yourself with the configuration of the power distribution units. These units are crucial for routing power to various systems, including lights, entertainment, and engine components.
For the main distribution unit under the dashboard, locate the panel on the driver’s side, typically near the footwell. This section will provide power to essential features like the air conditioning, ignition systems, and transmission sensors.
For additional circuits controlling things like external lights and accessories, check the rear unit found near the engine compartment. Here, you’ll find dedicated terminals for components such as the headlights, windshield wipers, and cooling fans. Make sure to check the amperage rating on each fuse to prevent overloading any particular circuit.
In case of a malfunction, always consult the layout guide for the proper replacement component, ensuring the correct size and rating are used for each specific fuse. Replacing a damaged component with the wrong specification could lead to further issues, so it’s crucial to match amperage correctly.
How to Identify and Replace Fuses in the Vehicle’s Electrical Panel
To properly identify and replace electrical components in the vehicle’s system, follow these steps:
- Locate the electrical panel under the dashboard or in the engine compartment.
- Use the diagram inside the panel cover or refer to the manual to identify the correct components.
- Turn off the engine and disconnect the battery to avoid any electrical hazards.
- Examine the component in question to determine if it is damaged. A blown component will often show discoloration or a broken filament.
Replacement Process:
- Choose a replacement with the same amperage rating to avoid damage to the circuit.
- Use a fuse puller or needle nose pliers to remove the faulty part.
- Insert the new component securely, ensuring a firm connection.
- Test the circuit to verify the issue is resolved.
Regular checks of the electrical panel ensure the system remains operational and reduces the likelihood of failures.
Troubleshooting Common Electrical Panel Issues
If certain components fail to function or work intermittently, the first step is to inspect the electrical panel for blown links or corroded terminals. Start by checking the main power connections for any signs of damage or wear.
Loose Connections: Over time, terminals can become loose, leading to poor electrical contact. Tighten any screws or bolts that are securing wires to prevent power loss.
Corrosion: Corrosion on the connections can obstruct proper current flow. Clean any corrosion with a mixture of baking soda and water, or use a specialized cleaner designed for electrical components.
Blown Links: A link that appears blackened or broken indicates that it has blown. Replace the faulty link with one that matches the amperage rating exactly. Using a link with a different rating can result in electrical system malfunctions or even fires.
Fuse Rating Mismatches: Double-check that each fuse corresponds to the right amperage for its designated circuit. Using an over-rated fuse can damage sensitive components, while an under-rated fuse can blow more frequently.
Contact Cleaning: Clean all contact points with a wire brush or contact cleaner to remove any dirt or debris that might be impeding current flow.
Check for Overloads: If multiple components are not working, an overload might have tripped the system. Reduce the load on circuits by disconnecting unnecessary accessories or equipment.
For persistent problems, consider consulting the vehicle’s manual for more detailed troubleshooting or seek assistance from a professional technician.