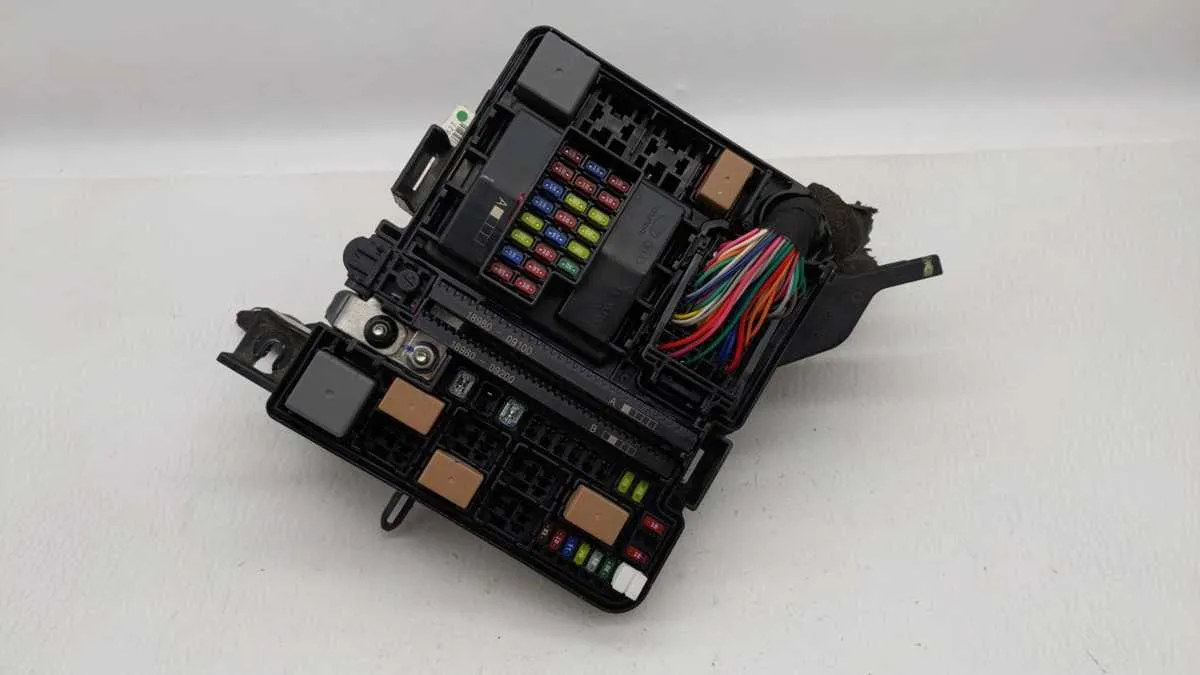

To properly identify the electrical components in your vehicle and troubleshoot any issues, refer to the wiring layout specific to the model year. The connections are crucial for ensuring power distribution across various systems like lighting, air conditioning, and entertainment. Proper understanding of the layout helps in safely diagnosing faults and replacing malfunctioning parts.
Before proceeding with any electrical work, always disconnect the power to avoid short circuits. Inspect the location of the control units, which are responsible for managing key electrical functions in your car. These units are usually found in easy-to-access compartments under the dashboard or within the engine compartment, depending on the circuit configuration.
In case of issues with certain functions, identify the exact unit and check its internal wiring for any damage. You can also use a multimeter to test the integrity of the connections. Regular maintenance and careful checking of the power system help prevent sudden malfunctions during critical moments.
For further assistance, refer to the user manual, which typically includes detailed schematics and part locations. Keep in mind that vehicle specifications may vary slightly, so ensure you’re consulting the correct version for your model year to avoid confusion and potential damage to other components.
Electrical Component Locations and Their Functions
To access the electrical system of the vehicle, follow these steps:
- Locate the main power relay unit inside the cabin near the driver’s side dashboard.
- For under-hood components, open the engine compartment and find the secondary power control panel near the battery.
- Inspect the control panel to identify critical connections like ignition, lighting, and air conditioning circuits.
Here’s a breakdown of important connections:
- Cabin Unit: Powers the interior lights, airbags, and central locking system.
- Underhood Unit: Controls engine-related circuits, such as the fuel pump relay, starter, and ECU connections.
- Rear Section: Manages rear lights, power outlets, and sensors.
If any circuit malfunctions, verify that the corresponding relay or fuse is intact and correctly seated. Always replace components with the same amperage rating as the original to avoid damage to the electrical system.
Use the vehicle manual for a more detailed explanation of each terminal’s function and color coding.
Understanding the Main Electrical Component Housing Location in 2015 Vehicle
The primary control unit for electrical circuits in the vehicle is located beneath the dashboard, on the driver’s side. To access it, you need to remove the cover panel situated near the left lower corner, just below the steering wheel.
Once the panel is removed, you will have direct access to the central housing, which contains the critical relays and power management components. The components are arranged in an easily identifiable layout with labeled positions, making it simple to pinpoint any blown elements for replacement or inspection.
It is essential to ensure that the vehicle is turned off before accessing the panel to avoid any risk of electrical shock or accidental damage to sensitive parts.
Note: If there is difficulty in locating the exact area, referring to the vehicle manual can provide additional clarification. In rare cases, the vehicle may have an alternative location under the hood, typically near the battery, which houses additional relays or fuses for certain systems.
How to Identify and Replace a Faulty Fuse in Your Vehicle
To address an electrical issue in your car, the first step is to locate the malfunctioning component. Start by examining the main power relay panel, typically under the dashboard or near the engine bay. Check for any blown components that may be causing the failure. A visual inspection should reveal if any part is damaged, discolored, or showing signs of wear.
If you’re unable to identify a problem visually, use a multimeter to test the connections. Set it to the resistance mode and measure across the contacts of the suspected element. A reading close to zero indicates the part is functional, while a high resistance value signals the need for replacement.
When replacing a faulty part, ensure you select one with the same specifications. The amperage rating is critical to avoid potential damage to the vehicle’s wiring system. A part with a higher rating could fail to protect the circuits, while one with a lower rating might blow too soon, causing further damage.
To replace the damaged item, pull out the old component using a small pair of pliers or a removal tool. Insert the new part by aligning it properly in the slot, ensuring a snug fit. Finally, test the system to verify the issue has been resolved.
Common Electrical Problems and Fixing Tips for Your Vehicle
If you experience a sudden loss of power in specific features, first check for a faulty connection or blown circuits. Start by inspecting the central wiring harness and relays. Often, issues arise from corrosion or wear on connectors, causing intermittent failures.
Another common issue is the malfunction of electrical components after a recent repair or service. This typically points to improper reassembly or overlooked connections. Check the grounding points for any loose or rusted connections that may impede proper current flow.
When components like the air conditioning or headlights fail to turn on, it may indicate a blown circuit. Verify if the corresponding relay is intact and operating as intended. If the system still doesn’t work, replace the blown unit and test for a proper reset of all affected components.
For a more thorough troubleshooting process, use a multimeter to check for voltage at different points. If a specific area is not receiving power, trace the wiring back to the main panel and ensure that the fuses supplying power are intact.
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Headlights not working | Blown circuit, faulty relay | Inspect and replace faulty relay or circuit |
| Air conditioning failure | Broken wire or relay | Check connections, replace the relay |
| Inconsistent power supply | Corroded connectors | Clean or replace connectors, inspect grounding |
| Malfunctioning interior electronics | Loose or broken connections | Secure connections, ensure relays are operational |