
If you’re experiencing issues with your car’s electrical components, it’s crucial to identify the source of the problem. The first step is to understand the location and layout of the primary circuit connections. In many vehicles, these connections are grouped in specific compartments that house fuses and relays, which protect critical components from electrical damage. Knowing where these areas are located will save you time when troubleshooting or replacing any malfunctioning parts.
Start by locating the compartment where the electrical components are housed. Usually, it can be found near the driver’s side dashboard or under the hood of the car. For many models, this compartment will have clear markings indicating which component controls each function, whether it’s the lighting system, power accessories, or engine management.
When looking for a wiring diagram, focus on identifying each specific section based on the electrical tasks it manages. Most vehicles have multiple sections controlling different aspects, such as the power windows, air conditioning, or the safety features. A quick reference to the detailed map can help you pinpoint which part needs attention. Make sure to always turn off the engine and remove the key before inspecting the components to avoid any electrical shock or damage.
Additionally, having a clear understanding of amperage ratings is essential. Different circuits require different amounts of power, and it’s important to match the right amperage for each fuse or relay to ensure the safety of the vehicle’s systems. A quick lookup of the specific vehicle’s manual or trusted online resources will provide accurate amperage values.
Electrical Component Layout for 2016 Model
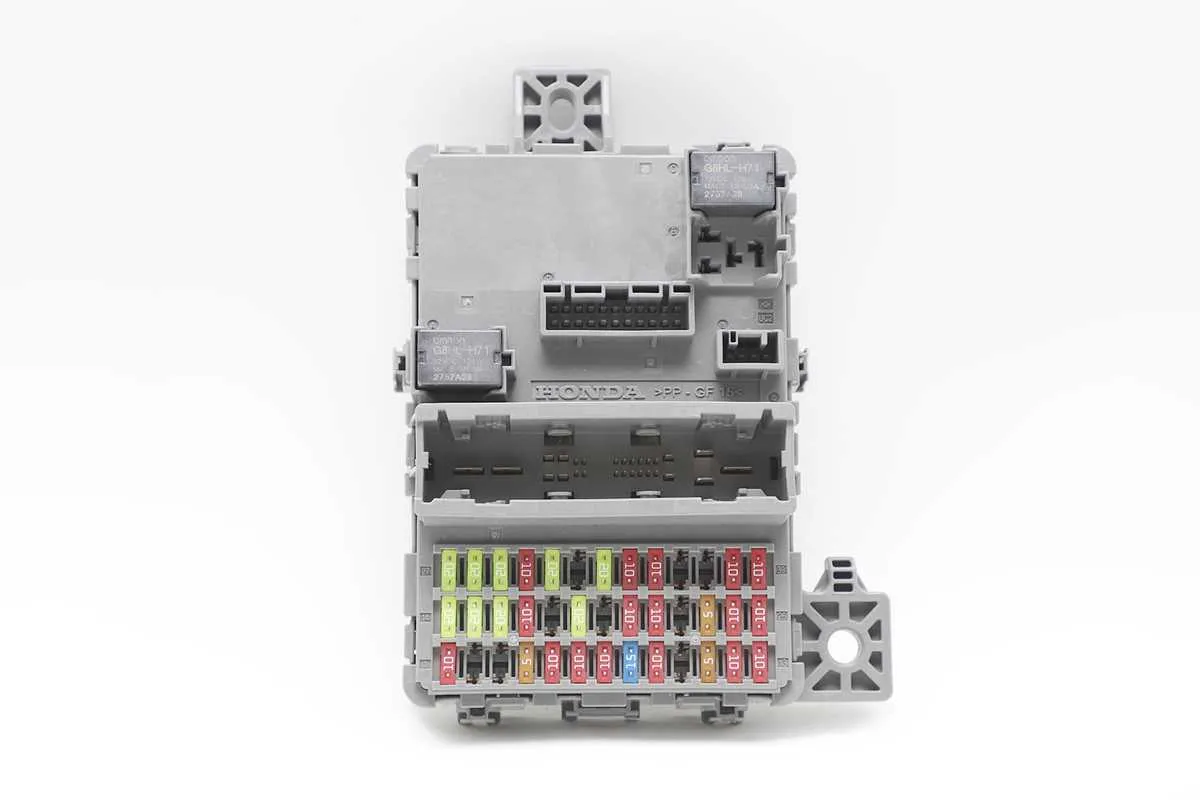

For proper maintenance, always refer to the schematic of the electrical control units. Each relay and fuse plays a crucial role in ensuring the vehicle runs smoothly. Below is a quick guide to understanding the key elements:
- Primary Distribution Unit – Found inside the cabin, located near the driver’s side dashboard.
- Secondary Distribution Unit – Positioned under the hood, near the engine compartment.
Key points to note for each section:
- The inside unit is responsible for circuits like lighting, infotainment, and interior electronics.
- The external unit typically handles components such as engine control, air conditioning, and the cooling system.
For troubleshooting, always check for blown units or corrosion in the wiring connections. A multimeter can be used to identify faults accurately. Be mindful that each component in the layout is labeled for easy identification.
- For the cabin unit: 15A fuse for interior lights, 30A for power windows, and 10A for the radio system.
- For the engine compartment unit: 40A fuse for the alternator, 20A for the cooling fan, and 15A for the air conditioner.
Never replace a blown unit with a higher amperage fuse. Always adhere to the specified values to avoid damage to the electrical system.
Identifying Electrical Component Locations in the 2016 Model
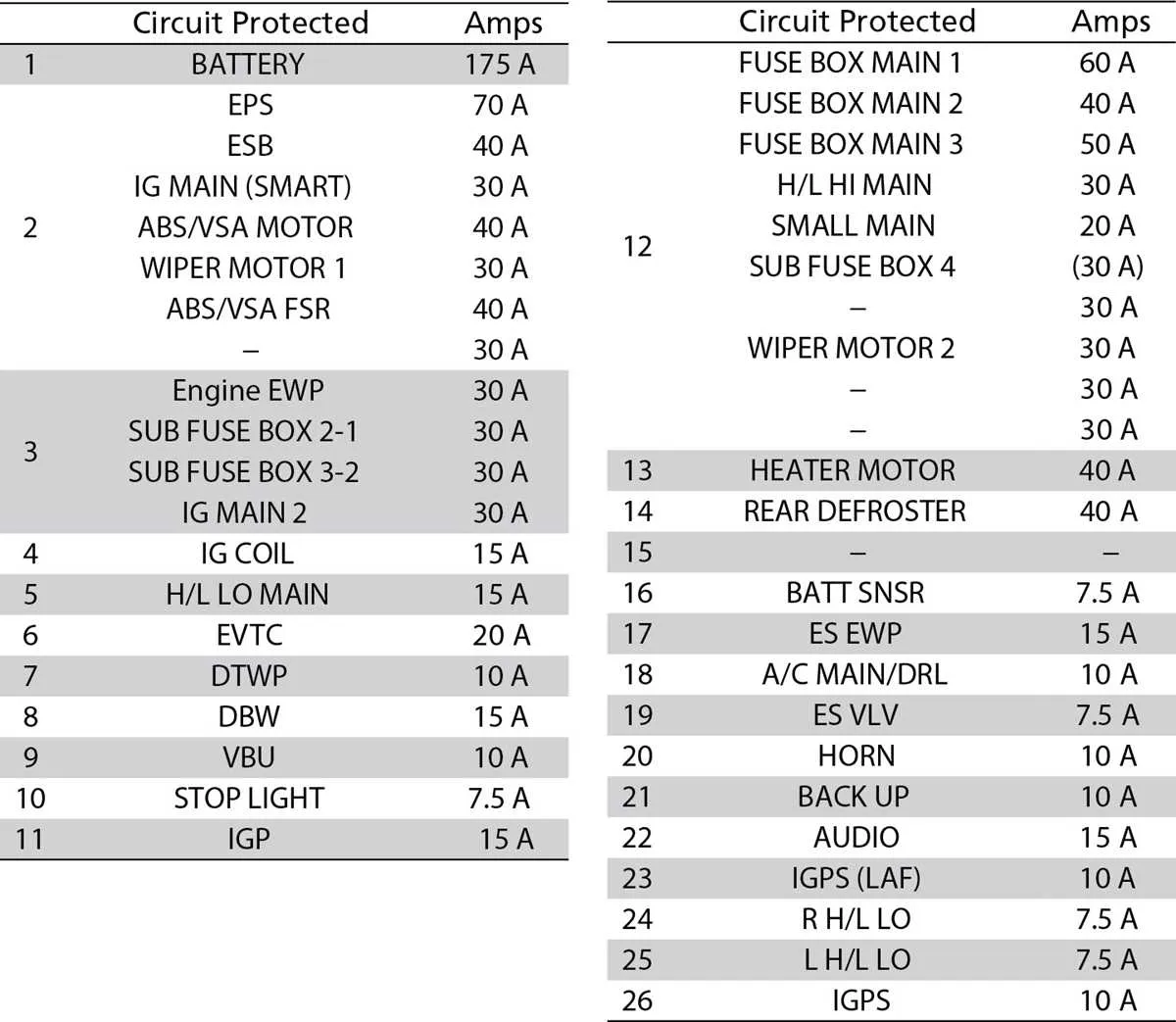
To locate specific electrical components in your vehicle, focus on two primary areas: the cabin compartment and the engine bay. The first location is behind the dashboard on the driver’s side, where a panel can be removed for access. The second area is near the engine, usually close to the battery or alongside the fender wall. Both locations are critical for resolving electrical issues effectively.
1. Cabin Access Panel: Open the driver-side door, and look for a small access panel near the footwell. This compartment contains the main electrical connections for interior systems like lighting and climate control. Use a flathead screwdriver to pop the panel open. Refer to the vehicle’s manual to identify the exact component you’re troubleshooting.
2. Under-Hood Access: The second location is found under the hood, typically near the windshield or near the battery compartment. There will be a large protective cover that you can lift. Here, you’ll find relays and other high-power components used for engine systems and auxiliary functions. Ensure the vehicle is turned off and the key is removed before accessing this area.
Tip: If you’re unsure about which component to replace, refer to the labels on the interior panels or consult your manual for specific circuit information. A multimeter can help verify the functionality of each connection to ensure proper repairs.
How to Troubleshoot Common Electrical Issues
Start by locating the main power distribution panel, which is usually under the dashboard or in the engine compartment. Open the cover and check the condition of the individual connectors. If you notice any burnt or damaged areas, it’s a sign that a particular circuit has been compromised. Replace any faulty elements with the correct rating to avoid future problems.
If no visible damage is found, use a multimeter to check the continuity of each circuit. Set the meter to measure resistance or continuity and probe the contacts. If the meter shows no continuity, the circuit is likely broken or the protective component has failed.
For electrical malfunctions, start with a basic check of the components powered by the faulty system. For example, if the headlights or radio are not functioning, check their dedicated lines in the distribution panel. Use the multimeter to test the power flow to these components. If there’s power reaching the part but it’s not working, the issue may lie within the component itself.
If multiple systems are affected, there could be a problem with the central relay. The relay controls multiple electrical systems, and if it fails, it could cause widespread issues. Swap it out with a known working relay and test to see if the problems persist.
Finally, for persistent issues, inspect the ground connections. Corrosion or loose grounds can prevent proper operation of the electrical system. Clean and tighten any ground terminals you find, as poor connections can lead to unpredictable behavior in the car’s electrical network.
Replacing Fuses: Step-by-Step Guide
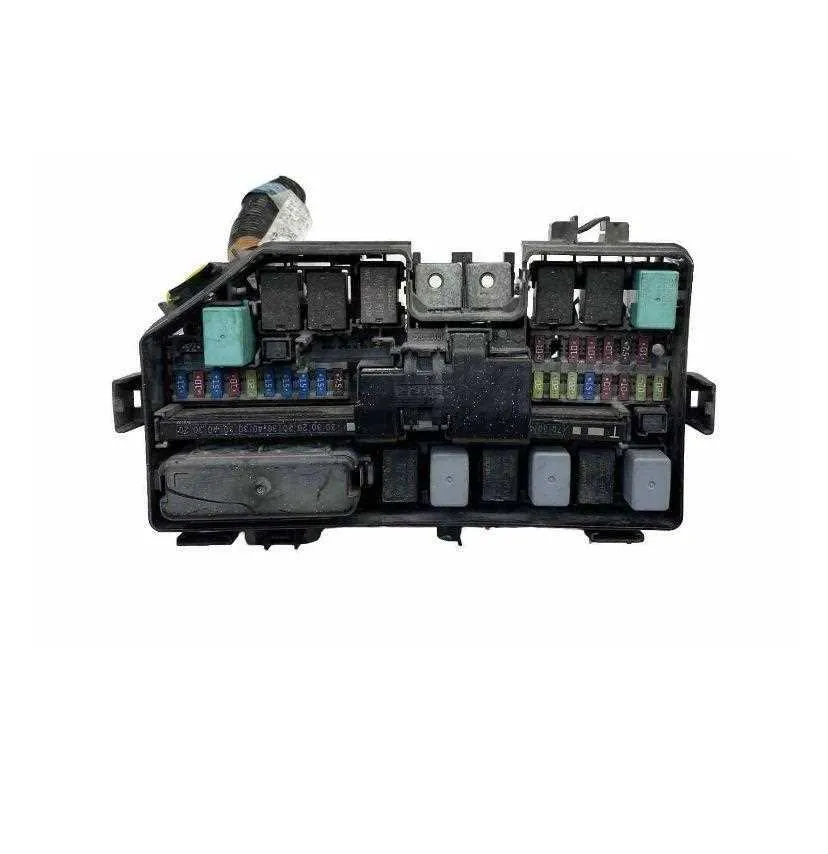

To replace a blown fuse, first identify its location. The main power distribution unit is usually under the dashboard or near the engine compartment. Consult the vehicle’s manual to find the exact spot for the component you’re working on.
1. Turn off the ignition: Ensure the vehicle is turned off before proceeding. This prevents any electrical mishaps during the replacement process.
2. Locate the fuse: Once the panel is open, locate the damaged element. Each component in the electrical system has its dedicated spot, clearly labeled for easy identification.
3. Remove the faulty component: Use a fuse puller or needle-nose pliers to gently pull out the faulty item. Avoid using excessive force to prevent damaging the holder.
4. Check amperage: Before inserting a new one, ensure the amperage rating matches the specifications. Refer to the owner’s manual for precise details on the correct amperage for each component.
5. Insert the new item: Place the replacement in the correct slot and press it firmly into place. Ensure it’s fully seated to avoid future issues.
6. Test the system: After the new piece is installed, turn on the ignition and check if the component functions properly. If the issue persists, double-check the amperage or inspect the system for other underlying problems.